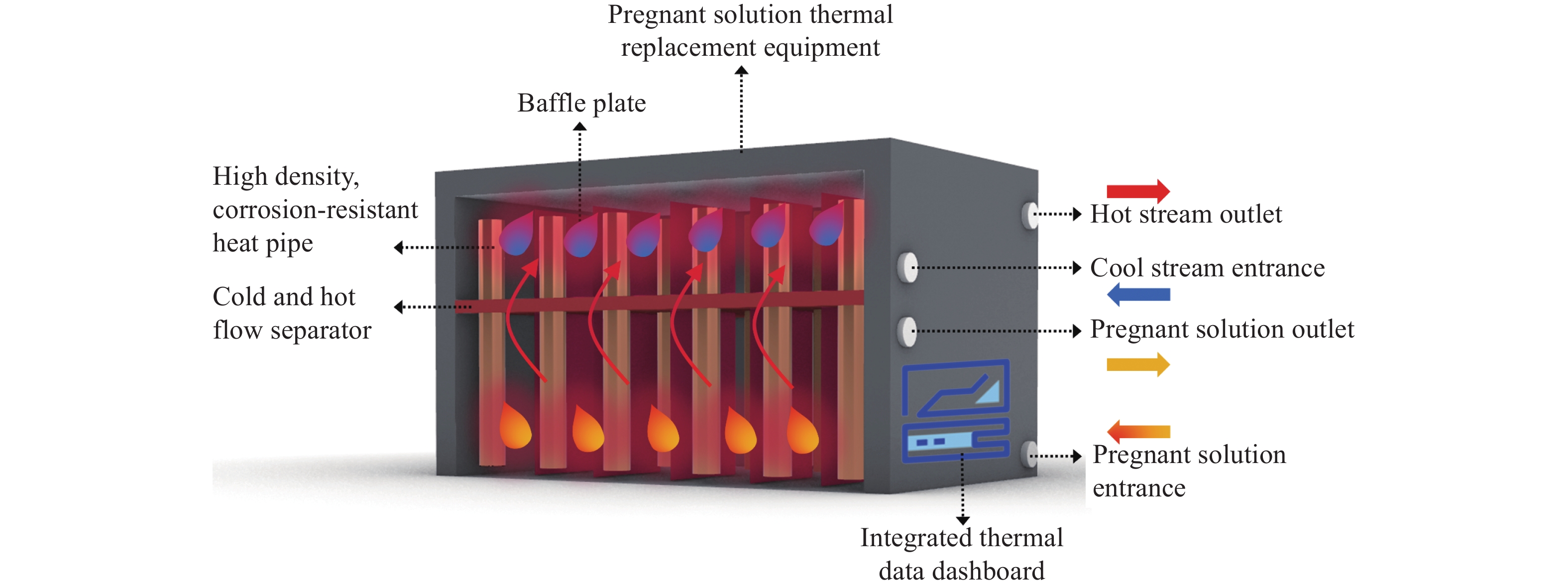
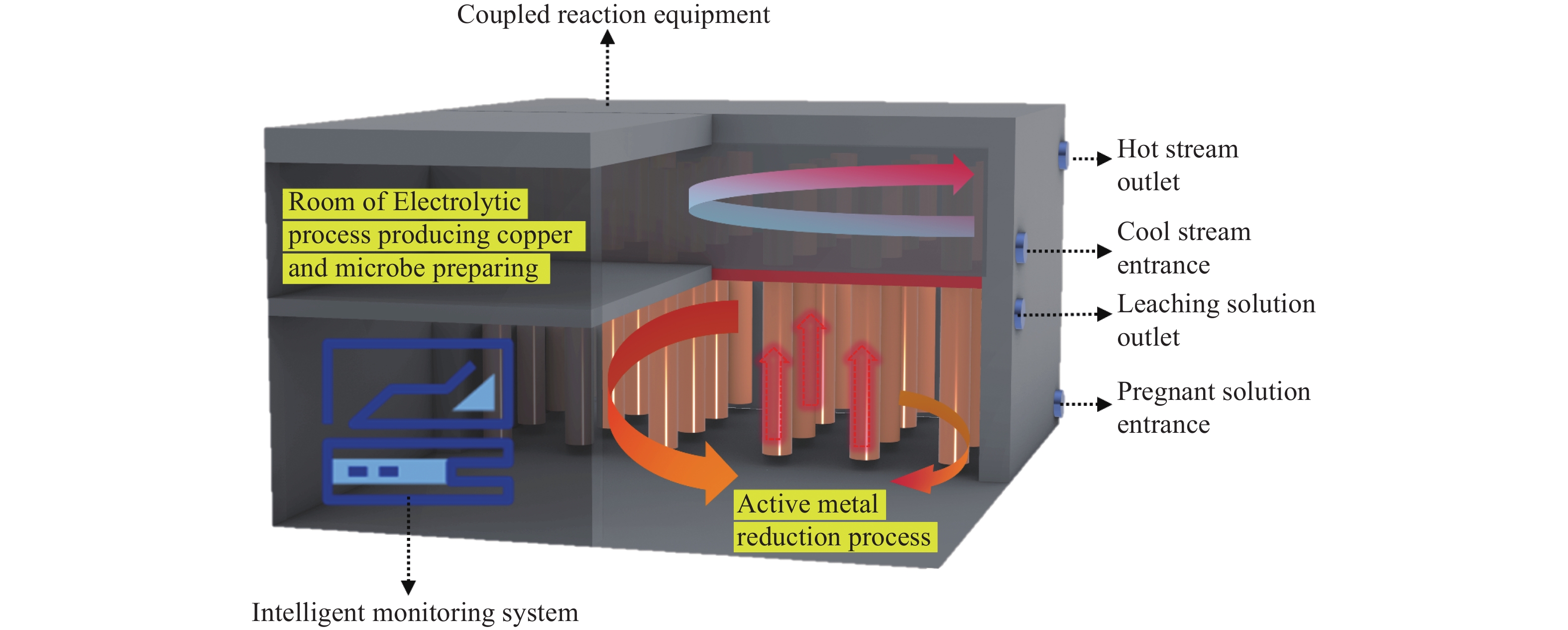
Exploration study of synergistic mining between the fluidized leaching process enhancement of deep metal mines and geothermal energy development
-
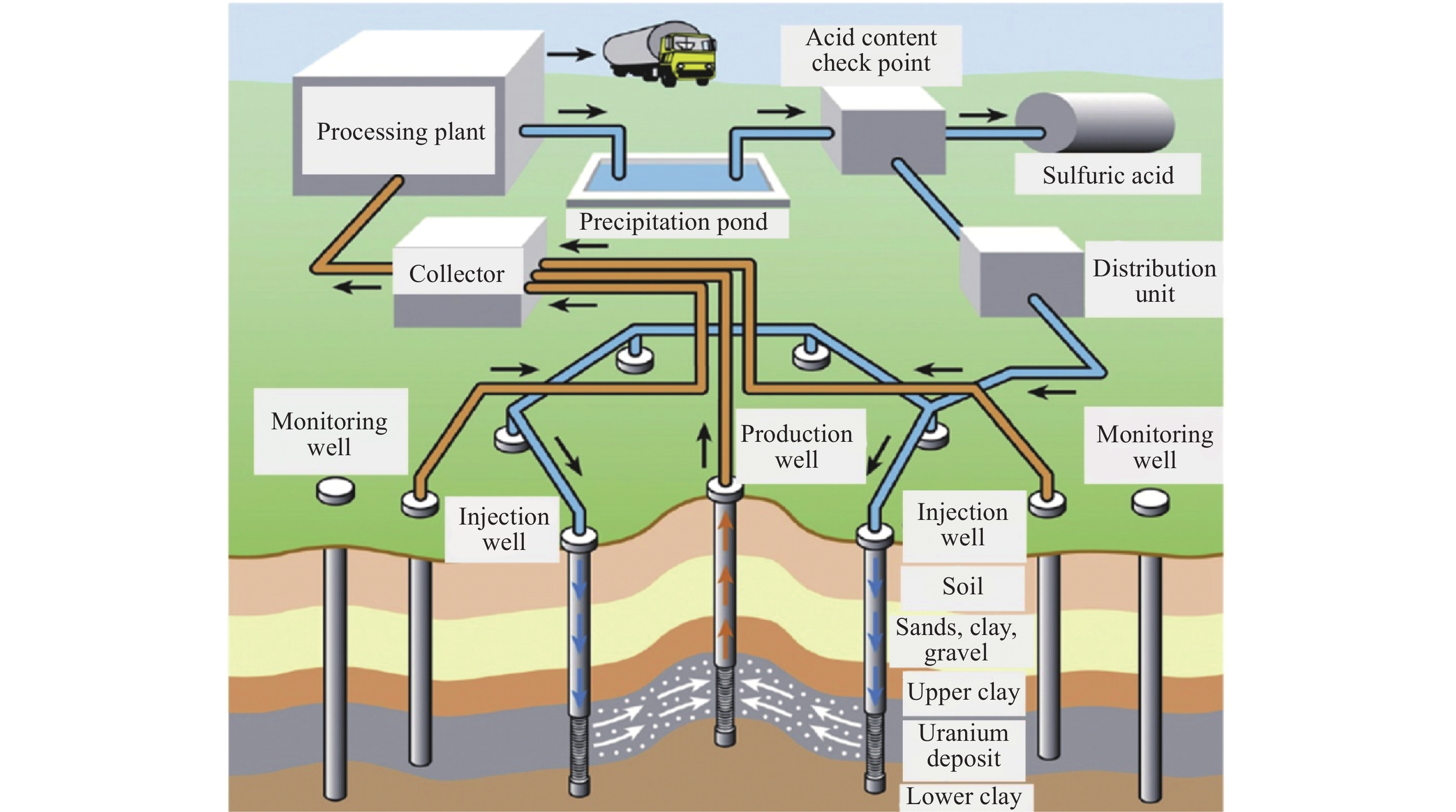
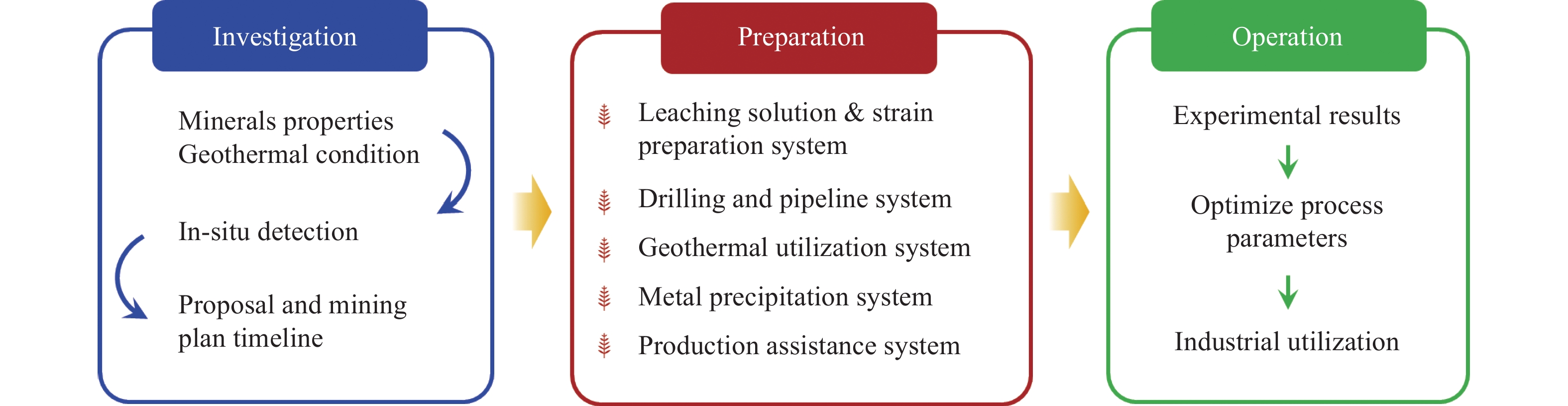
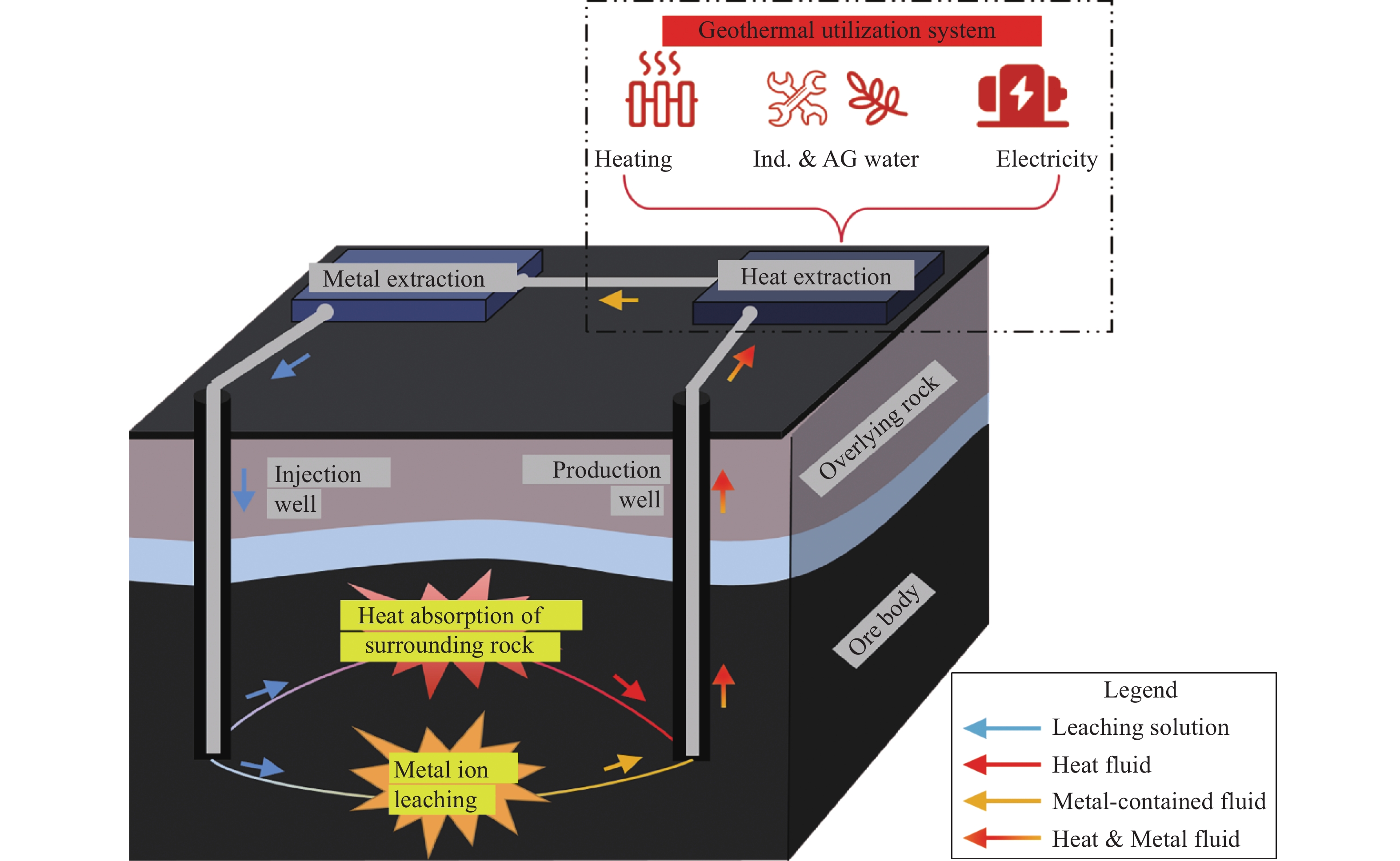
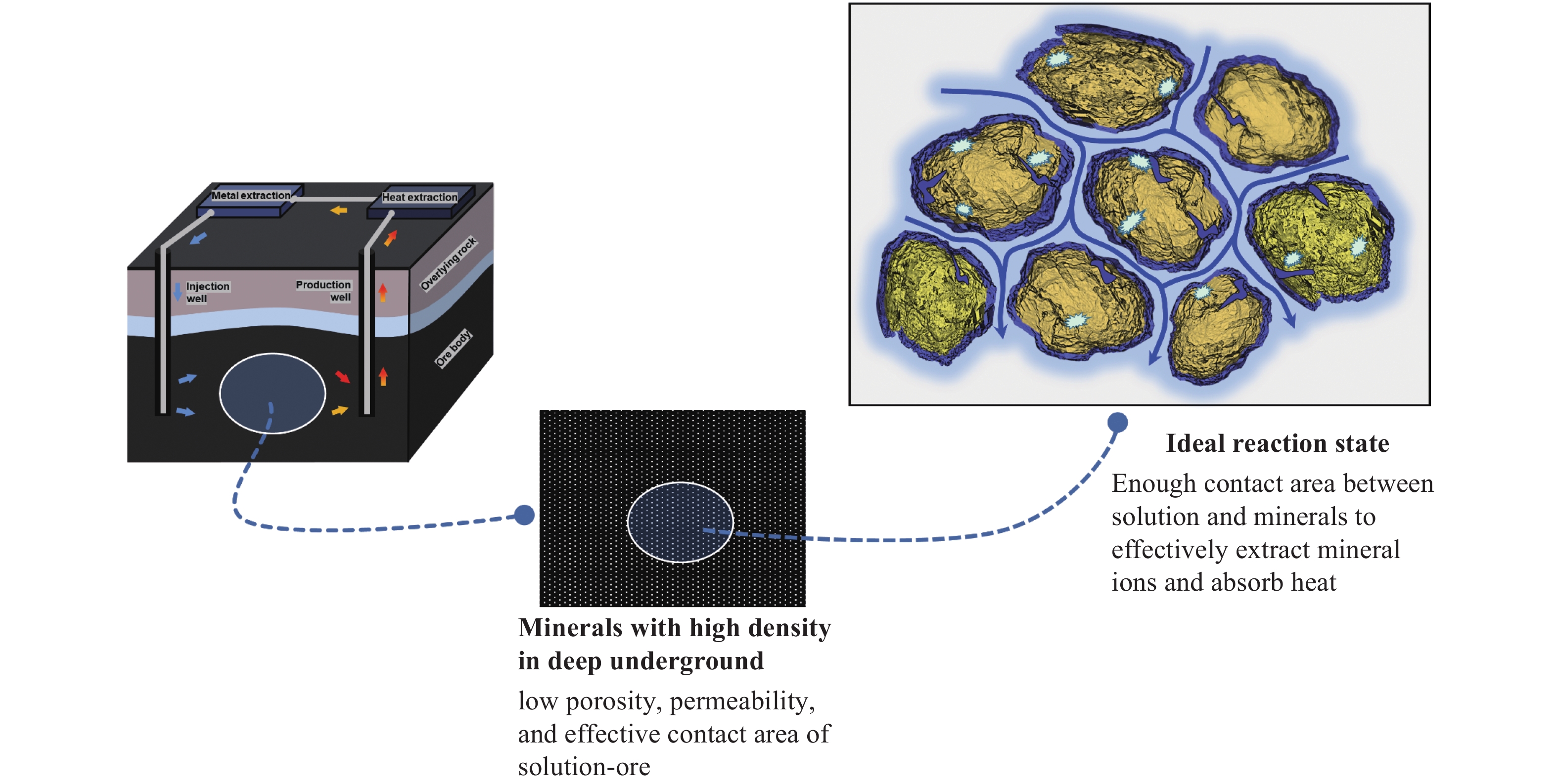
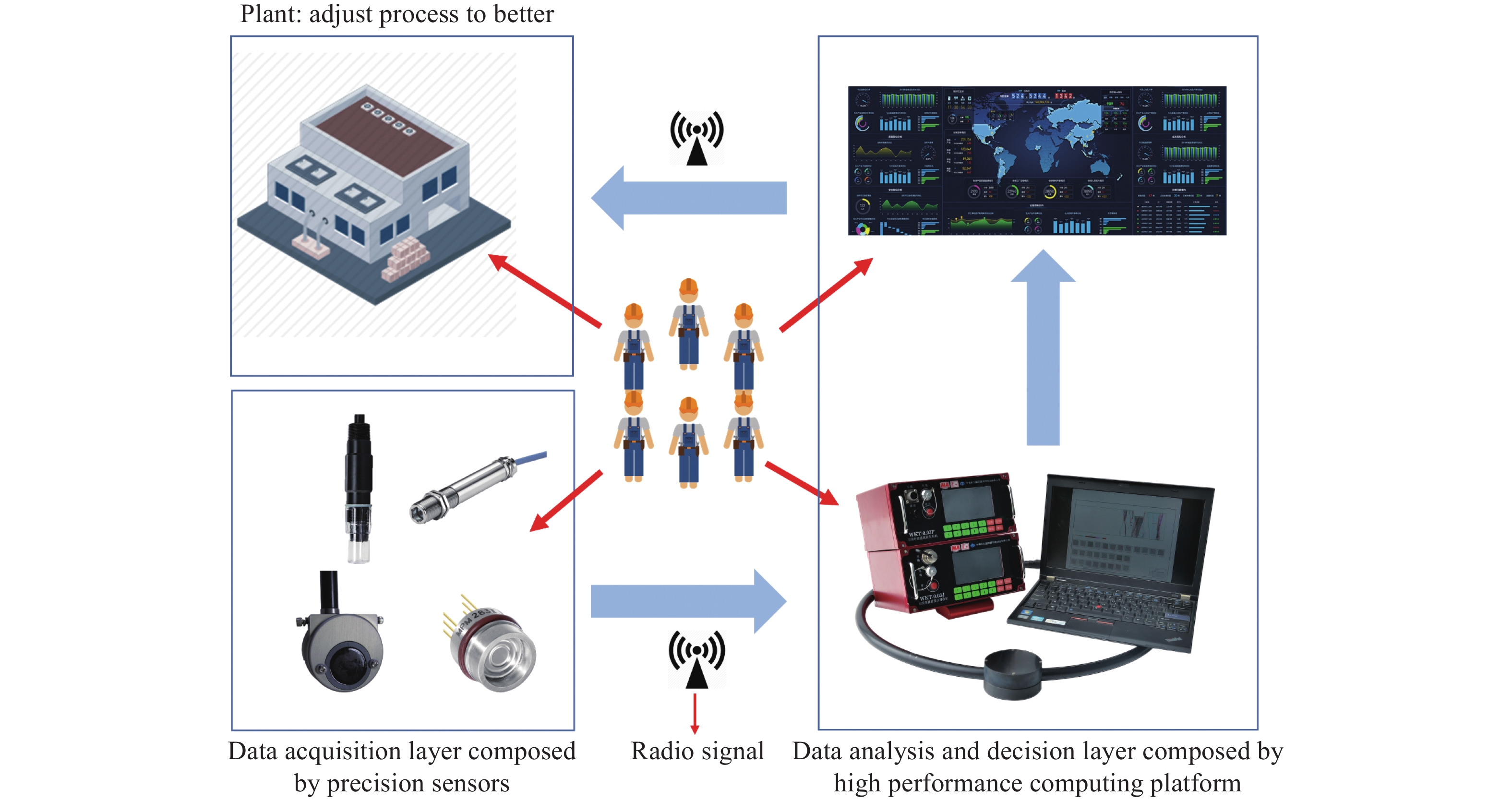
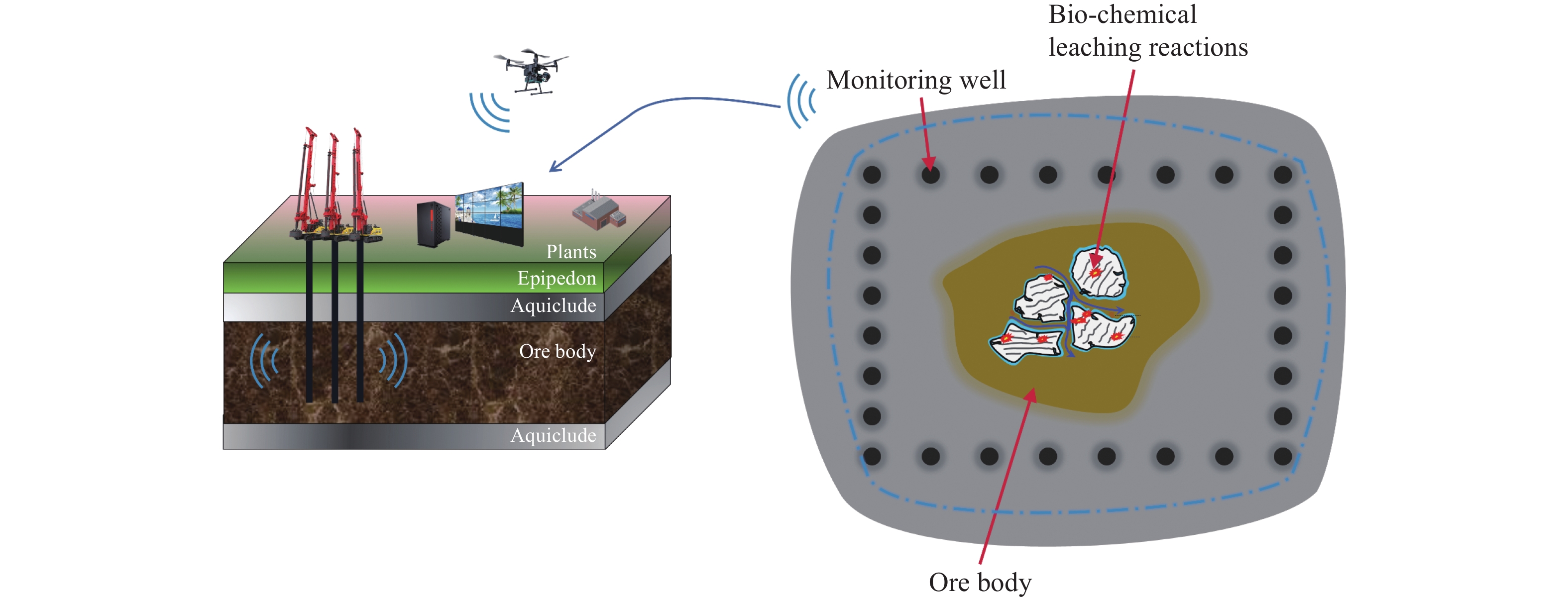
摘要: 立足深地金屬礦產資源開采,以當前鈾礦原位溶浸采礦工藝為基礎,結合“金屬礦流態化開采”和“深部地熱開發”的工藝技術特征,創新提出了深地金屬礦流態化浸出過程強化?地熱協同共采的工藝構想,探討了實現該工藝構想的思路架構、潛在方式并給出了初步設想,從礦物浸出、環境感知、過程控制、能量置換、協同關聯角度提出了關鍵系統,包括:致密固態礦產流態化系統、深地資源智慧感知系統、深地礦區溶浸液滲流控制系統、地熱?溶浸液能量置換系統、熱能置換?溶浸液循環耦聯系統共五個方面開展重點研討,系統分析了實現深地金屬礦流態化浸出?地熱協同共采過程中的基礎理論瓶頸、關鍵技術難題與未來發展趨向,相關研究旨在為深地金屬礦流態化浸出過程強化與地熱協同共采提供思路借鑒。Abstract: The abundant metal minerals and geothermal resources reserved in the deep earth can provide key support for global economic development and human survival. As a subversive and unconventional mining method, the fluidized mining of deep metal ore provides an essential idea for the efficient, low-carbon, and safe development of deep resources. In view of this, we focus on metal mineral resources in the deep earth based on the uranium in-situ leaching technology; by combining the technical characteristics of the “metal mineral fluidization mining” and “deep geothermal development,” we innovatively propose the process concept of strengthening the fluidized leaching process of deep metal ore-geothermal co-mining, The idea structure and potential techniques to realize the process concept were discussed, and preliminary assumptions were given. This study mainly includes three steps: 1) investigation (such as investigating mineral properties and geothermal conditions), 2) preparation of systems (including drilling and pipeline transportation system, leaching solution and strain preparation system, geothermal utilization system, metal precipitation system, and production assistance system), 3) operation (including experimental results, optimize process parameter, and industrial utilization). Key systems, such as a dense solid mineral fluidization system, were proposed from the perspectives of mineral leaching, environmental perception, process control, energy replacement, and synergistic correlation. Key discussions were performed in five aspects: 1) the intelligent perception system for deep earth resources to solve the problems of low permeability, low penetration, premature solution preferential flow, low leaching rate, and excessive blockage, thereby decreasing the percentage of unsaturated leaching areas and effectively recycling the lower-grade minerals; 2) the seepage control system for solution in deep mining areas, divided into data acquisition, data analysis, and decision-making parts, thereby realizing efficient coordination between ground immersion environment and production information, avoiding system slowdown, and reducing heat/electric energy consumption; 3) the energy replacement system for geothermal–leaching solution, including the geological exploration and production monitoring system and ecological reclamation monitoring system, resulting in targeted adjusting the fluid flow behavior, improving capillary penetration and mass transfer; 4) the coupling system for thermal energy replacement–leaching solution circulation, which has three requirements—one is high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance and heat insulation, the second is good thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance, and the third is to be equipped with an intelligent monitoring system; 5) the thermal energy replacement-solution circulation coupling system that is based on large-scale pregnant solution container and equipped with thermal energy replacement, metal precipitation, leaching solution and strain preparation devices. Besides, the basic theoretical bottlenecks, key technical problems, and future development trends in the process of fluidized leaching–geothermal cooperative co-mining of metal ores are carefully discussed in this study. This study will provide ideas and references for enhancing the fluidized leaching process of deep earth metal ores and geothermal co-mining.
-
Key words:
- deep mining /
- metal mines /
- fluidized process /
- geothermal energy /
- synergistic mining
-
久色视频
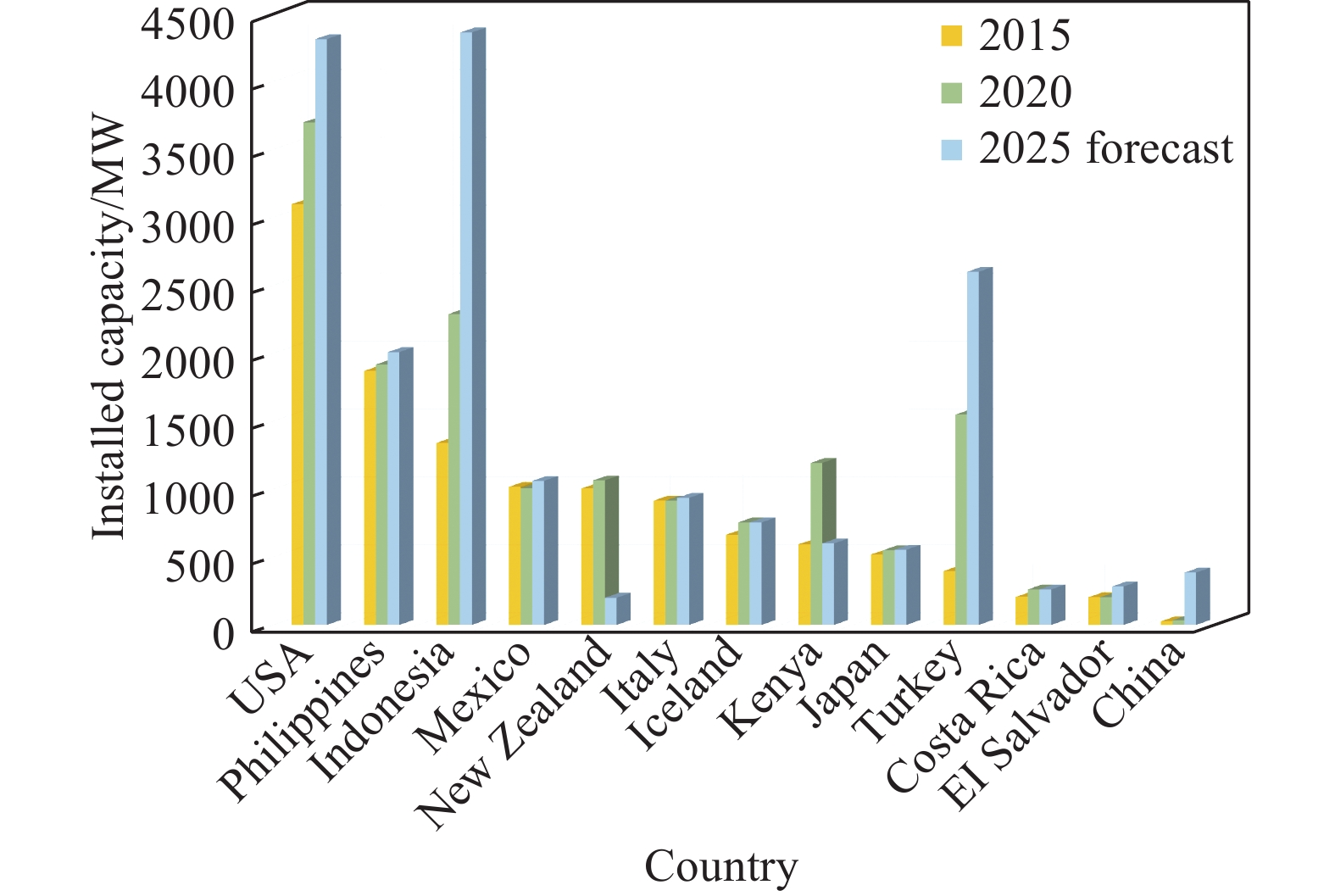
表 1 中國與其他十二個國家地熱發電裝機容量數據
Table 1. Data of installed capacity of geothermal power generation about China and 12 other countries
Year Installed capacity USA Philippines Indonesia Mexico New Zealand Italy Iceland Kenya Japan Turkey Costa Rica EI Salvador China 2015 3098 1870 1340 1017 1005 916 665 594 519 397 207 204 27 2020 3700 1918 2289 1005.8 1064 916 755 1193 550 1549 262 204 34.89 2025 forecast 4313 2009 4362 1061 200 936 755 600 554 2600 262 284 386 -
參考文獻
[1] Gu D S, Zhou K P. Development theme of the modern metal mining. Met Mine, 2012(7): 1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2012.07.001古德生, 周科平. 現代金屬礦業的發展主題. 金屬礦山, 2012(7):1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2012.07.001 [2] Xinhua News Agency. In 2021, the output of ten common non-ferrous metals in China was 64.543 million tons, and enterprises above designated size achieved a record high profit [EB/OL]. www. gov. cn (2022-02-17) [2022-04-10]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/202202/17/content_5674324.htm新華社. 2021年我國十種常用有色金屬產量6454.3萬噸規上企業實現利潤創新高 [EB/OL]. 中國政府網 (2022-02-17) [2022-04-10]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-02/17/content_5674324.htm [3] Wu A X, Wang H J, Yin S H, et al. Conception of in situ fluidization mining for deep metal mines. J Min Sci Technol, 2021, 6(3): 255 doi: 10.19606/j.cnki.jmst.2021.03.001吳愛祥, 王洪江, 尹升華, 等. 深層金屬礦原位流態化開采構想. 礦業科學學報, 2021, 6(3):255 doi: 10.19606/j.cnki.jmst.2021.03.001 [4] Xie H P, Gao F, Ju Y, et al. Theoretical and technological conception of the fluidization mining for deep coal resources. J China Coal Soc, 2017, 42(3): 547 doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.0299謝和平, 高峰, 鞠楊, 等. 深地煤炭資源流態化開采理論與技術構想. 煤炭學報, 2017, 42(3):547 doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.0299 [5] Xie H P, Ju Y, Gao M Z, et al. Theories and technologies for in situ fluidized mining of deep underground coal resources. J China Coal Soc, 2018, 43(5): 1210 doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2018.0519謝和平, 鞠楊, 高明忠, 等. 煤炭深部原位流態化開采的理論與技術體系. 煤炭學報, 2018, 43(5):1210 doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2018.0519 [6] Xie H P, Gao F, Ju Y. Research and development of rock mechanics in deep ground engineering. Chin J Rock Mech Eng, 2015, 34(11): 2161 doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.1369謝和平, 高峰, 鞠楊. 深部巖體力學研究與探索. 巖石力學與工程學報, 2015, 34(11):2161 doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.1369 [7] He M C, Xie H P, Peng S P, et al. Study on rock mechanics in deep mining engineering. Chin J Rock Mech Eng, 2005, 24(16): 2803 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.16.001何滿潮, 謝和平, 彭蘇萍, 等. 深部開采巖體力學研究. 巖石力學與工程學報, 2005, 24(16):2803 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.16.001 [8] Xie H P, Gao F, Ju Y, et al. Quantitative definition and investigation of deep mining. J China Coal Soc, 2015, 40(1): 1 doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.1690謝和平, 高峰, 鞠楊, 等. 深部開采的定量界定與分析. 煤炭學報, 2015, 40(1):1 doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.1690 [9] He M C. Conception system and evaluation indexes for deep engineering. Chin J Rock Mech Eng, 2005, 24(16): 2854 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.16.007何滿潮. 深部的概念體系及工程評價指標. 巖石力學與工程學報, 2005, 24(16):2854 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.16.007 [10] Xie H P, Zhou H W, Xue D J, et al. Research and consideration on deep coal mining and critical mining depth. J China Coal Soc, 2012, 37(4): 535 doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2012.04.011謝和平, 周宏偉, 薛東杰, 等. 煤炭深部開采與極限開采深度的研究與思考. 煤炭學報, 2012, 37(4):535 doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2012.04.011 [11] Cai M F, Xue D L, Ren F H. Current status and development strategy of metal mines. Chin J Eng, 2019, 41(4): 417蔡美峰, 薛鼎龍, 任奮華. 金屬礦深部開采現狀與發展戰略. 工程科學學報, 2019, 41(4):417 [12] Cai M F. Main issues metallic mines now are facing and solutions of the problems. Min Eng, 2003, 1(1): 40 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8550.2003.01.017蔡美峰. 金屬礦山當前面臨的主要問題及對策. 礦業工程, 2003, 1(1):40 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8550.2003.01.017 [13] Yin S H, Wang L M, Wu A X, et al. Progress of research in copper bioleaching technology in China. Chin J Eng, 2019, 41(2): 143尹升華, 王雷鳴, 吳愛祥, 等. 我國銅礦微生物浸出技術的研究進展. 工程科學學報, 2019, 41(2):143 [14] Wang J C, Yang S L, Liu S Q, et al. Technology status and fluidized mining conception for steeply inclined coal seams. Coal Sci Technol, 2022, 50(1): 48王家臣, 楊勝利, 劉淑琴, 等. 急傾斜煤層開采技術現狀與流態化開采構想. 煤炭科學技術, 2022, 50(1):48 [15] Cai M F, Dor J, Chen X S, et al. Development strategy for Co-mining of the deep mineral and geothermal resources. Strateg Study CAE, 2021, 23(6): 43蔡美峰, 多吉, 陳湘生, 等. 深部礦產和地熱資源共采戰略研究. 中國工程科學, 2021, 23(6):43 [16] Liao C L, Sun Z D. Wyoming trona mine uses geothermal energy to heat underground air. Min Technol, 1988(10): 9廖成林, 孫鎮德. 懷俄明州天然堿礦利用地熱加熱井下空氣. 國外采礦技術快報, 1988(10):9 [17] Li D W, Wang Y X. Major issues of research and development of hot dry rock geothermal energy. Earth Sci, 2015, 40(11): 1858李德威, 王焰新. 干熱巖地熱能研究與開發的若干重大問題. 地球科學, 2015, 40(11):1858 [18] Wang G L, Zhang W, Liang J Y, et al. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China. Acta Geosci Sin, 2017, 38(4): 449 doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.04.02王貴玲, 張薇, 梁繼運, 等. 中國地熱資源潛力評價. 地球學報, 2017, 38(4):449 doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.04.02 [19] Song J, Tang C N, Kang F C. Synergetic mining mode of deep mineral and geothermal resources. Met Mine, 2020(5): 124 doi: 10.19614/j.cnki.jsks.202005018宋健, 唐春安, 亢方超. 深部礦產與地熱資源協同開采模式. 金屬礦山, 2020(5):124 doi: 10.19614/j.cnki.jsks.202005018 [20] Chen Q F, Zhou K P, Gu D S. Synergetic mining and cavity synergetic utilization. China Min Mag, 2011, 20(12): 77 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2011.12.020陳慶發, 周科平, 古德生. 協同開采與采空區協同利用. 中國礦業, 2011, 20(12):77 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2011.12.020 [21] Lu X R. Geothermal power generation, not enough temperature—An interview with Dor ji, academician of Chinese academy of engineering. China Petrochem, 2019(18): 17陸曉如. 地熱發電, 溫度還不夠——專訪中國工程院院士多吉. 中國石油石化, 2019(18):17 [22] State Council of the People's Republic of China. Guiding opinions of the State Council on accelerating the establishment and improvement of a green, low-carbon and circular economic development system [EB/OL]. www. gov. cn (2021-02-22) [2022-03-16]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2021-02/22/content_5588274.htm中華人民共和國國務院. 國務院關于加快建立健全綠色低碳循環發展經濟體系的指導意見 [EB/OL]. 中國政府網 (2021-02-22) [2022-04-10]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2021-02/22/content_5588274.htm [23] Li X W. Shandong defines the key points of prospecting: oil and gas, coal and geothermal [N/OL]. China Natural Resources News Agency (2006-06-02) [2022-04-10].https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CCND&dbname=CCND2006&filename=GTZY200606020012&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=psXS2j86qLkuvab0o8XPMAxk-s_Mbc6GyrtxKciZNGsFxBcTPj5kVeF-69TQ2n9_RHXTRLGfbDM%3d李現文. 山東明確找礦重點: 油氣、煤炭、地熱 [N/OL]. 中國自然資源報 (2006-06-02)[2022-04-10].https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CCND&dbname=CCND2006&filename=GTZY200606020012&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=psXS2j86qLkuvab0o8XPMAxk-s_Mbc6GyrtxKciZNGsFxBcTPj5kVeF-69TQ2n9_RHXTRLGfbDM%3d [24] Liu Q X. Probe into geothermal resources hosting and development, utilization in Shoushan No. 1 coalmine. Coal Geol China, 2007, 19(6): 49劉慶獻. 首山一礦地熱資源賦存及開發利用探討. 中國煤田地質, 2007, 19(6):49 [25] LIU Xiao-chen. Xianyang: proved packaged hot ore water geothermal field [N/OL]. Economic daily (2007-09-08)[2022-04-10].https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CCND&dbname=CCND2007&filename=JJRB200709080151&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=Lcjf9c2AQCXesbL8OsstRPslqo-lbG1hwvYMPgA433dLGJEd1mY7SA8oKj9W_QdlOTaVwS_hDxg%3d劉曉辰. 咸陽: 探明整裝熱礦水型地熱田 [N/OL]. 經濟日報 (2007-09-08)[2022-04-10].https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CCND&dbname=CCND2007&filename=JJRB200709080151&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=Lcjf9c2AQCXesbL8OsstRPslqo-lbG1hwvYMPgA433dLGJEd1mY7SA8oKj9W_QdlOTaVwS_hDxg%3d [26] Wu J H, Xie J G, Chen S Y, et al. et al. Status and valuation studies of geothermal resources in Jilin Province. J Chang Inst Technol Nat Sci Ed, 2008, 9(2): 49吳景華, 謝俊革, 陳樹義, 等. 吉林省地熱資源狀況與評價研究. 長春工程學院學報(自然科學版), 2008, 9(2):49 [27] Chen G W. Study on development and utilization value of Tongluo geothermal mine water in Taishan City, Guangdong Province. Pop Sci Technol, 2009, 11(2): 87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1151.2009.02.041陳廣文. 廣東省臺山市銅鑼地熱礦水開發利用價值研究. 大眾科技, 2009, 11(2):87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1151.2009.02.041 [28] Chen S H. The exploration project of "prospecting for ore, water and geothermal energy" in our province has achieved fruitful results [N/OL]. Guizhou Daily (2011-01-04)[2022-04-10].https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CCND&dbname=CCNDLAST2011&filename=GERB201101040053&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=4Q75w7A1-H4jDwSFbYppobigyMv5YcCd9-HFh_S9EPoNDaBrvPcsuuuvXJg7QySV-nKzAYWVJ00%3d陳少華. 我省“找礦找水找地熱”勘查工程成果豐碩[N/OL]. 貴州日報 (2011-01-04)[2022-04-10].https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CCND&dbname=CCNDLAST2011&filename=GERB201101040053&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=4Q75w7A1-H4jDwSFbYppobigyMv5YcCd9-HFh_S9EPoNDaBrvPcsuuuvXJg7QySV-nKzAYWVJ00%3d [29] Liu D Y, Chen L Y, Liu M J, et al. A geothermal system analysis of Ningcheng thermomineral water field, Chifeng City. Coal Geol China, 2003, 15(6): 40劉大野, 陳立云, 劉民娟, 等. 赤峰市寧城熱礦水田地熱系統分析. 中國煤田地質, 2003, 15(6):40 [30] Li Z J. History of geothermal exploitation and utilization in Beijing. J Hebei Geo Univ, 1994, 17(3): 271李仲均. 北京市地熱開發利用史. 河北地質學院學報, 1994, 17(3):271 [31] Lu X R. The petroleum industry can also use geothermal energy and waste heat, but it needs innovative technology. China Petrochem, 2018(24): 15(陸曉如. 石油行業也可利用地熱、余熱, 但需要創新技術. 中國石油石化, 2018(24):15 [32] Huang J C, Li T S, Gu X X. Enlightenment of international geothermal utilization development situation to China. Petrochem Ind Technol, 2020, 27(9): 252 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2020.09.151黃嘉超, 李天舒, 谷雪曦. 國際地熱利用發展形勢對中國的啟發. 石化技術, 2020, 27(9):252 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2020.09.151 [33] LIPTÁK B. 3 technologies to to capture geothermal energy [EB/OL]. Control Global (2020-10-01) [2022-06-24].https://www.controlglobal.com/articles/2020/3-technologies-to-to-capture-geothermal-energy [34] Rybach L. Geothermal energy: Sustainability and the environment. Geothermics, 2003, 32(4-6): 463 doi: 10.1016/S0375-6505(03)00057-9 [35] Lin Y X, Wang W J, Jin J B. Key drilling fluid technology in the ultra deep section of well Ying-1 in the Shunbei oil and gas field. Petroleum Drill Tech, 2019, 47(3): 113 doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019068林永學, 王偉吉, 金軍斌. 順北油氣田鷹1井超深井段鉆井液關鍵技術. 石油鉆探技術, 2019, 47(3):113 doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019068 [36] Shi L, Wang H G, Ji G D. Current situation, challenges and developing trend of CNPC's oil & gas drilling. Nat Gas Ind, 2013, 33(10): 1 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2013.10.001石林, 汪海閣, 紀國棟. 中石油鉆井工程技術現狀、挑戰及發展趨勢. 天然氣工業, 2013, 33(10):1 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2013.10.001 [37] Zhao Y S, Liang W G, Feng Z J, et al. Science, technology and engineering of in situ modified mining by fluidization. J China Coal Soc, 2021, 46(1): 25 doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.yg20.1826趙陽升, 梁衛國, 馮子軍, 等. 原位改性流體化采礦科學、技術與工程. 煤炭學報, 2021, 46(1):25 doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.yg20.1826 [38] Seredkin M, Zabolotsky A, Jeffress G. In situ recovery, an alternative to conventional methods of mining: Exploration, resource estimation, environmental issues, project evaluation and economics. Ore Geol Rev, 2016, 79: 500 doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.06.016 [39] Yang S J, Li M. Discussion on recovery of residual ore from baifang copper mine in Hunan Province by in-situ crushing leaching method. Hunan Metall, 1998, 26(4): 31楊仕教, 李明. 用就地破碎浸出法回收湖南柏坊銅礦殘礦的探討. 湖南冶金, 1998, 26(4):31 [40] Wang C H. Actively popularize and apply the in situ crushing leaching method. Jiangxi Nonferrous Met, 1996(2): 9王昌漢. 積極推廣和應用就地破碎浸礦法. 江西有色金屬, 1996(2):9 [41] Yang S J, Gu D S, Ding D X, et al. Residual ore body recovery by in situ fragmentation-leaching in Beifang copper mine. Nonferrous Met, 2002(4): 102楊仕教, 古德生, 丁德馨, 等. 用原地破碎浸出采礦法回收柏坊銅礦殘礦. 有色金屬, 2002(4):102 [42] Yang S J, Li M. Selection and construction of polycrystalline substance for in-situ leaching of blasted uranium ore in a uranium mine. J Univ South China Sci Technol, 1998, 12(2): 78楊仕教, 李明. 某鈾礦就地破碎浸出采場底部結構的選擇與施工. 中南工學院學報, 1998, 12(2):78 [43] Wang C H. Several key techniques in the smash-leaching-mining on the spot. J Central South Inst Technol, 2001, 15(2): 13王昌漢. 就地破碎溶浸采礦法幾個關鍵技術的探討. 南華大學學報(理工版), 2001, 15(2):13 [44] Wang C H. Technical characteristics and optimum application conditions of In-situ leaching of uranium ore body. China Nucl Sci Technol Rep, 2000(1): 878王昌漢. 就地破碎浸鈾法的技術特性及最佳應用準則. 中國核科技報告, 2000(1):878 [45] Wang C H, Zhu H B, Li X. Confirming principles & characteristics of the ore-block's structure parameter in the smash-leaching-mining on the spot. J Central South Inst Technol, 2000, 14(4): 6王昌漢, 朱紅兵, 李旭. 就地破碎浸礦法的礦塊結構參數的確定原則及特點. 中南工學院學報, 2000, 14(4):6 [46] Wang C H. Preliminary study on field test of underground crushing and copper leaching method. Hydrometall China, 1997, 16(2): 12 doi: 10.13355/j.cnki.sfyj.1997.02.005王昌漢. 井下就地破碎浸銅法現場試驗前期研究. 濕法冶金, 1997, 16(2):12 doi: 10.13355/j.cnki.sfyj.1997.02.005 [47] Yang S J, Liao D X. An experimental study on In stiu explosive fragmentation and leaching in NO. 745 mine. Min Res Dev, 1998, 18(6): 7 doi: 10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.1998.06.003楊仕教, 廖大學. 七四五礦就地破碎浸出試驗研究. 礦業研究與開發, 1998, 18(6):7 doi: 10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.1998.06.003 [48] Ghorbani Y, Franzidis J P, Petersen J. Heap leaching technology—Current state, innovations, and future directions: A review. Miner Process Extr Metall Rev, 2016, 37(2): 73 [49] O'Gorman G, Michaelis H, Olson G J. Novel in situ metal and mineral extraction technology [R/OL]. OSTI. GOV (2004-09-22)[2022-04-10].https://www.osti.gov/biblio/835781 [50] Sinclair L, Thompson J. In situ leaching of copper: Challenges and future prospects. Hydrometallurgy, 2015, 157: 306 doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2015.08.022 [51] World Nuclear Association. Uranium mining overview [EB/OL]. World Nuclear Association (2022-06) [2022-04-10].https://world-nuclear.org/information-library/nuclear-fuel-cycle/mining-of-uranium/uranium-mining-overview.aspx [52] Wu A X, Wang H J, Yang B H, et al. Progress and prospect of leaching mining technology. Min Technol, 2006, 6(3): 39 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2900.2006.03.009吳愛祥, 王洪江, 楊保華, 等. 溶浸采礦技術的進展與展望. 采礦技術, 2006, 6(3):39 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2900.2006.03.009 [53] Kang F C, Tang C N. Overview of enhanced geothermal system (EGS) based on excavation in China. Earth Sci Front, 2020, 27(1): 185亢方超, 唐春安. 基于開挖的增強型地熱系統概述. 地學前緣, 2020, 27(1):185 [54] Whetten J T, Dennis B R, Dreesen D S, et al. The US hot dry rock project. Geothermics, 1987, 16(4): 331 doi: 10.1016/0375-6505(87)90014-9 [55] Equipment for Geotechnical Engineering. The White Paper of China Geothermal Energy Development Report (2018) was released. Equip Geotech Eng, 2019, 20(2): 3地址裝備. 《中國地熱能發展報告(2018)》白皮書發布. 地質裝備, 2019, 20(2):3 [56] Mao X, Guo D B, Luo L, et al. The global development process of hot dry rock (enhanced geothermal system) and its geological background. Geol Rev, 2019, 65(6): 1462 doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2019.06.013毛翔, 國殿斌, 羅璐, 等. 世界干熱巖地熱資源開發進展與地質背景分析. 地質論評, 2019, 65(6):1462 doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2019.06.013 [57] Wang Z Z, Ou C H, Wang H Y, et al. The characteristics and development of geothermal resources in China. Water Resour Hydropower Eng, 2019, 50(6): 187 doi: 10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2019.06.026王轉轉, 歐成華, 王紅印, 等. 國內地熱資源類型特征及其開發利用進展. 水利水電技術, 2019, 50(6):187 doi: 10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2019.06.026 [58] Liao Z J, Wan T F, Zhang Z G. The enhanced geothermal system(EGS): Huge capacity and difficult exploitation. Earth Sci Front, 2015, 22(1): 335廖志杰, 萬天豐, 張振國. 增強型地熱系統: 潛力大、開發難. 地學前緣, 2015, 22(1):335 [59] Li J, Wu J Y, Yang Z, et al. Review of geothermal power generation technologies and key influencing factors. Therm Power Gener, 2022, 51(3): 1李健, 武江元, 楊震, 等. 地熱發電技術及其關鍵影響因素綜述. 熱力發電, 2022, 51(3):1 [60] Chen Q F, Su J H. Synergetic mining and its technology system. J Central South Univ Sci Technol, 2013, 44(2): 732陳慶發, 蘇家紅. 協同開采及其技術體系. 中南大學學報(自然科學版), 2013, 44(2):732 [61] Zhang B, Xue P Y, Liu L, et al. Exploration on the method of ore deposit-geothermal energy synergetic mining in deep backfill mines. J China Coal Soc, 2021, 46(9): 2824張波, 薛攀源, 劉浪, 等. 深部充填礦井的礦床-地熱協同開采方法探索. 煤炭學報, 2021, 46(9):2824 [62] Li Y Y, Dor J, Zhang C J, et al. Genetic relationship between geothermal energy and hydrothermal uranium deposits: Research progress and method. Geol Rev, 2020, 66(5): 1361李燕燕, 多吉, 張成江, 等. 地熱與熱液型鈾礦成因聯系: 研究現狀及解決方法. 地質論評, 2020, 66(5):1361 [63] Yin S H, Wang L M, Wu A X, et al. Research progress in enhanced bioleaching of copper sulfides under the intervention of microbial communities. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2019, 26(11): 1337 doi: 10.1007/s12613-019-1826-5 [64] Chen L, He A, Zhao J L, et al. Pore-scale modeling of complex transport phenomena in porous media. Prog Energy Combust Sci, 2022, 88: 100968 doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2021.100968 [65] Cai M F, Tan W H, Wu X H, et al. Current situation and development strategy of deep intelligent mining in metal mines. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2021, 31(11): 3409 doi: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-42115蔡美峰, 譚文輝, 吳星輝, 等. 金屬礦山深部智能開采現狀及其發展策略. 中國有色金屬學報, 2021, 31(11):3409 doi: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-42115 [66] Wang G F, Zhang D S. Innovation practice and development prospect of intelligent fully mechanized technology for coal mining. J China Univ Min Technol, 2018, 47(3): 459 doi: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000851王國法, 張德生. 煤炭智能化綜采技術創新實踐與發展展望. 中國礦業大學學報, 2018, 47(3):459 doi: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000851 [67] Su H, Wan X H. A Corrosion-Resistant and High Temperature Resistant Cemented Carbide and Preparation Method Type: China Patent, CN106544566B. 2017-03-29蘇華, 萬小虎. 一種耐腐蝕耐高溫硬質合金及其制備方法: 中國專利, CN106544566B. 2017-03-29 -




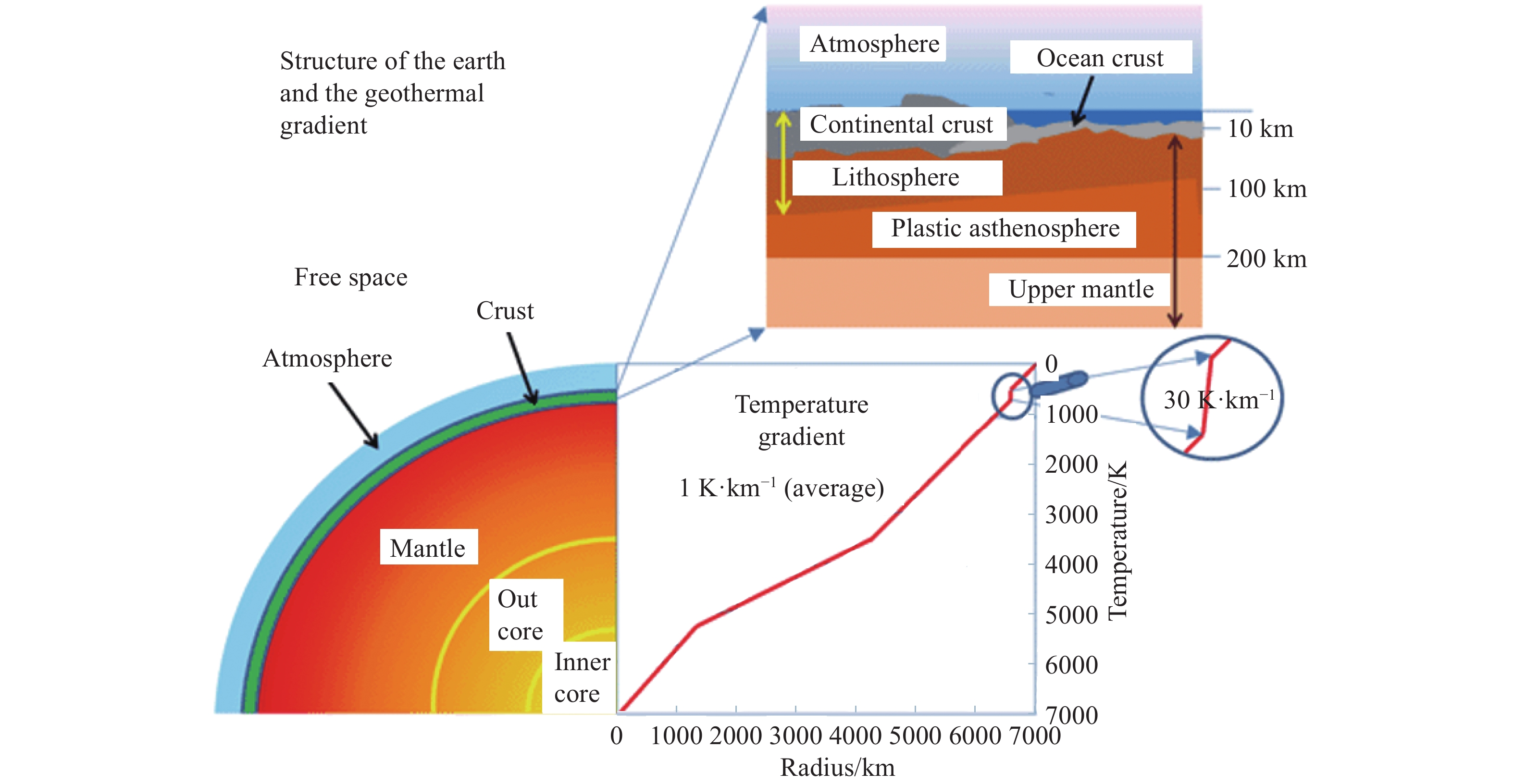
 下載:
下載: