-
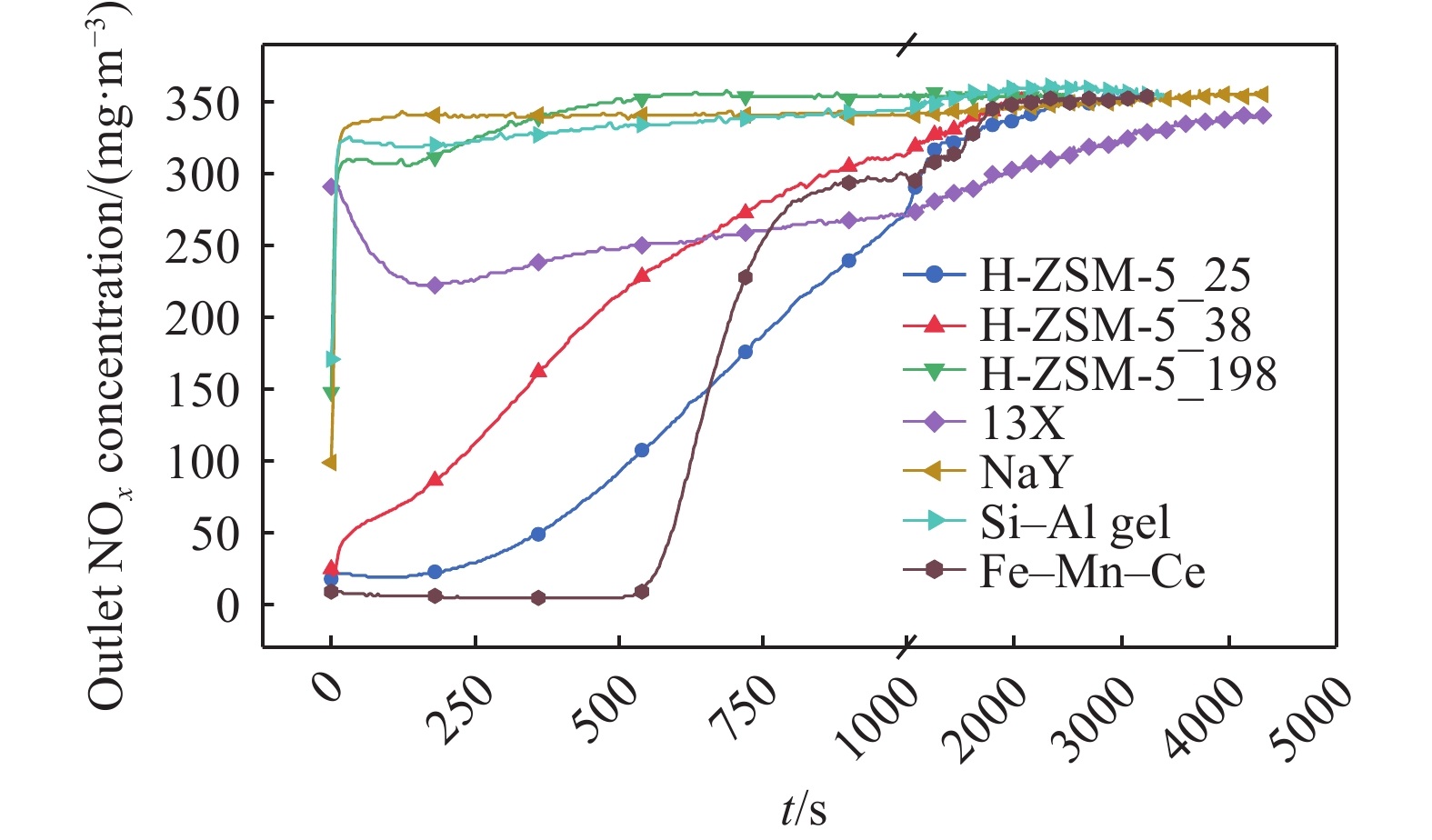
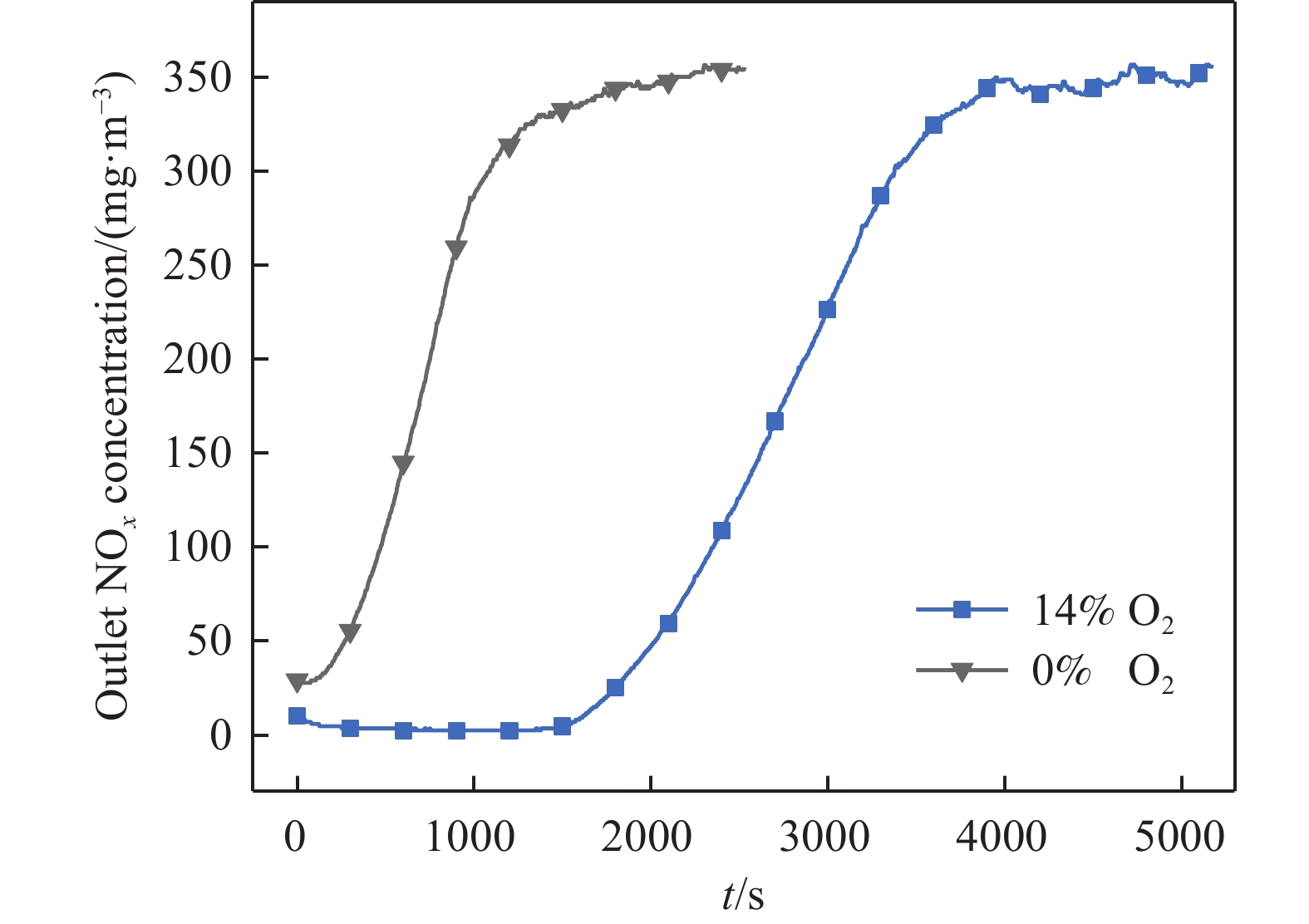
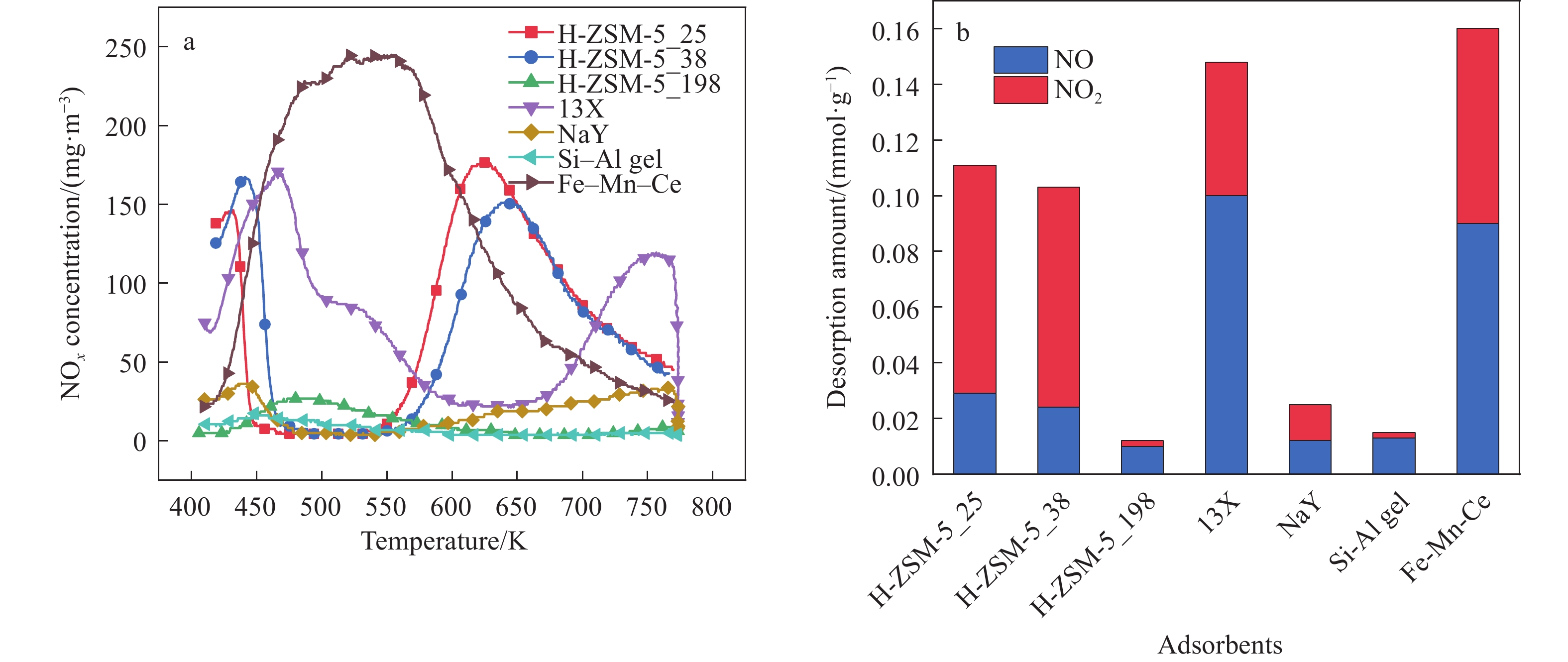
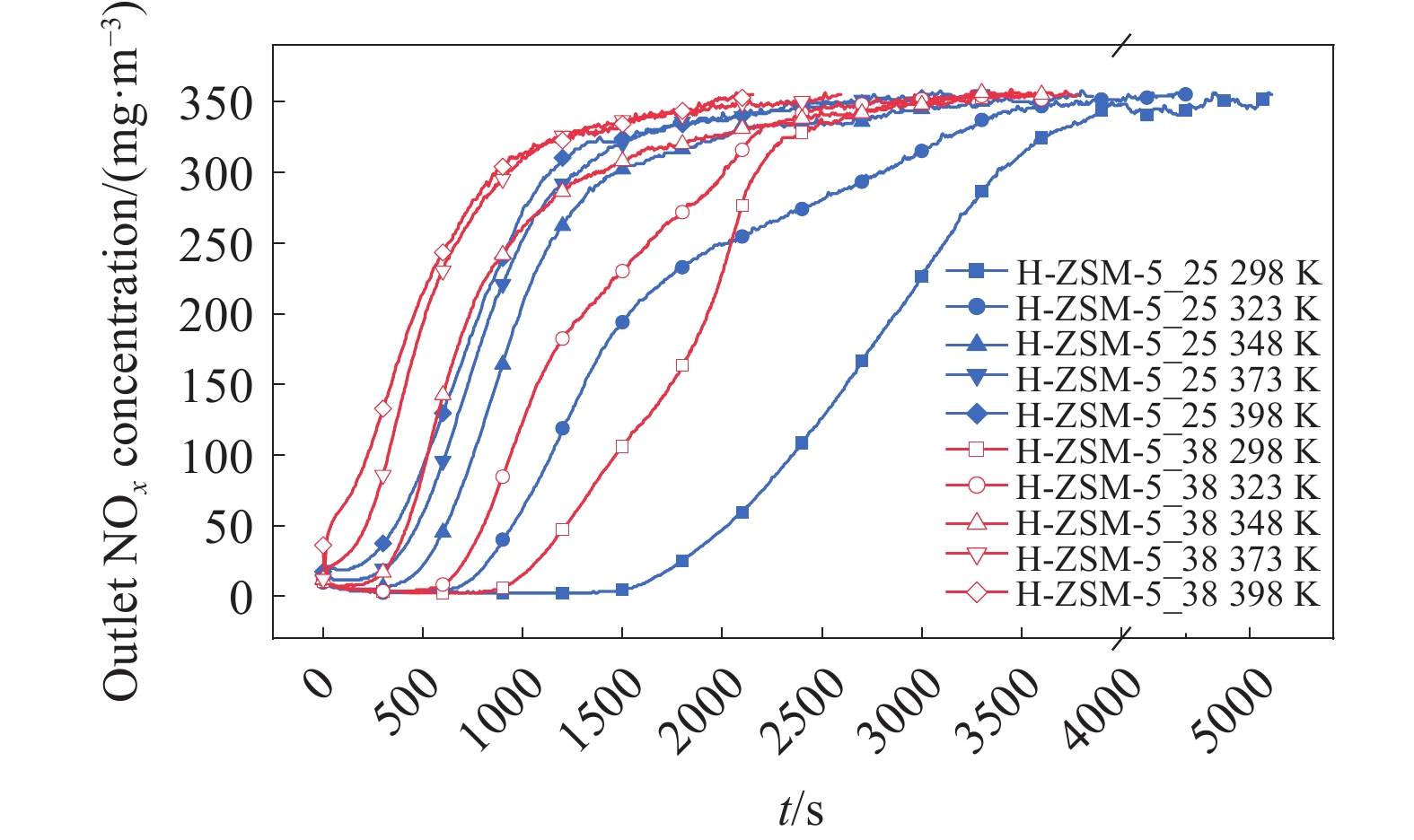
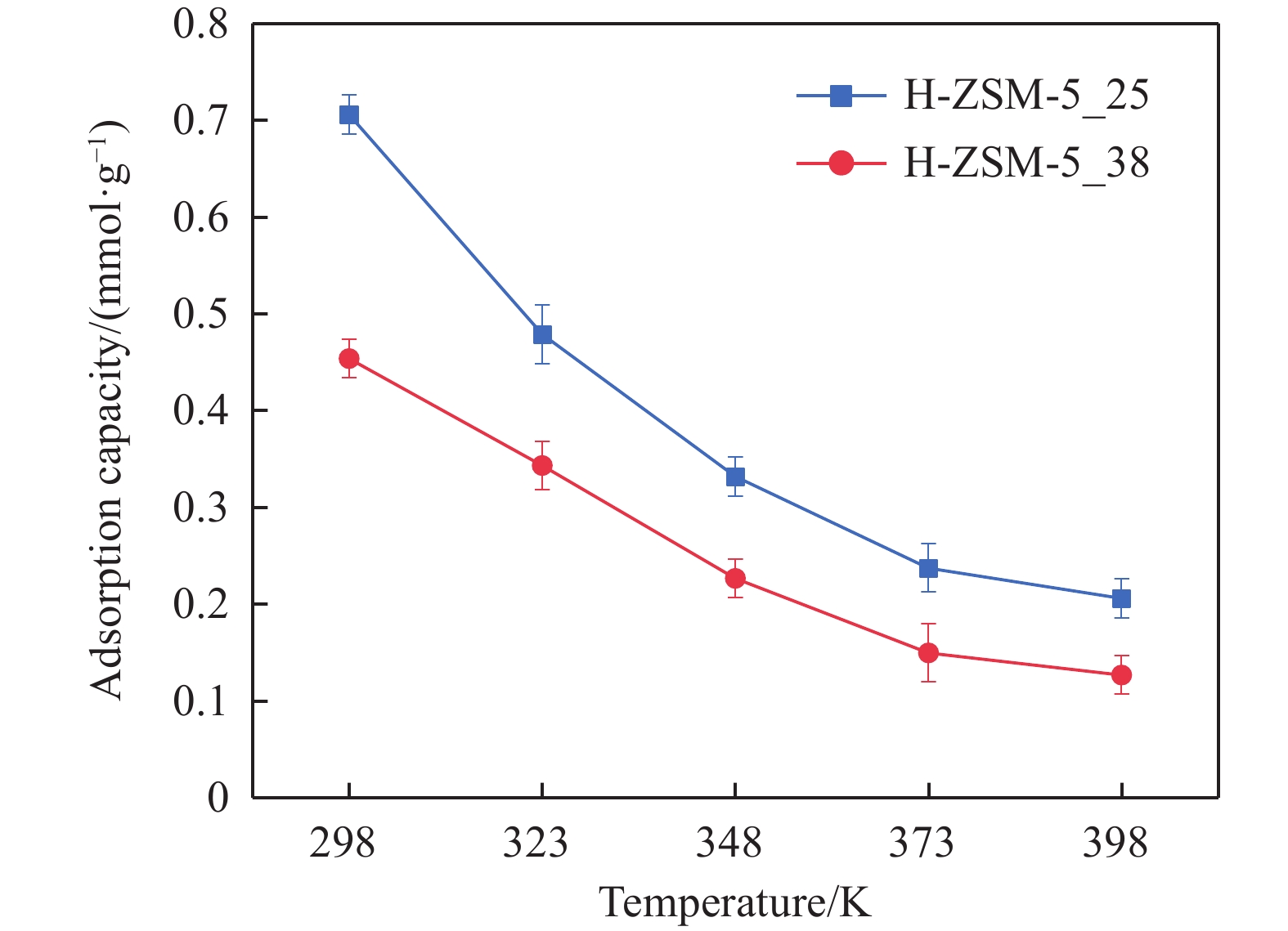
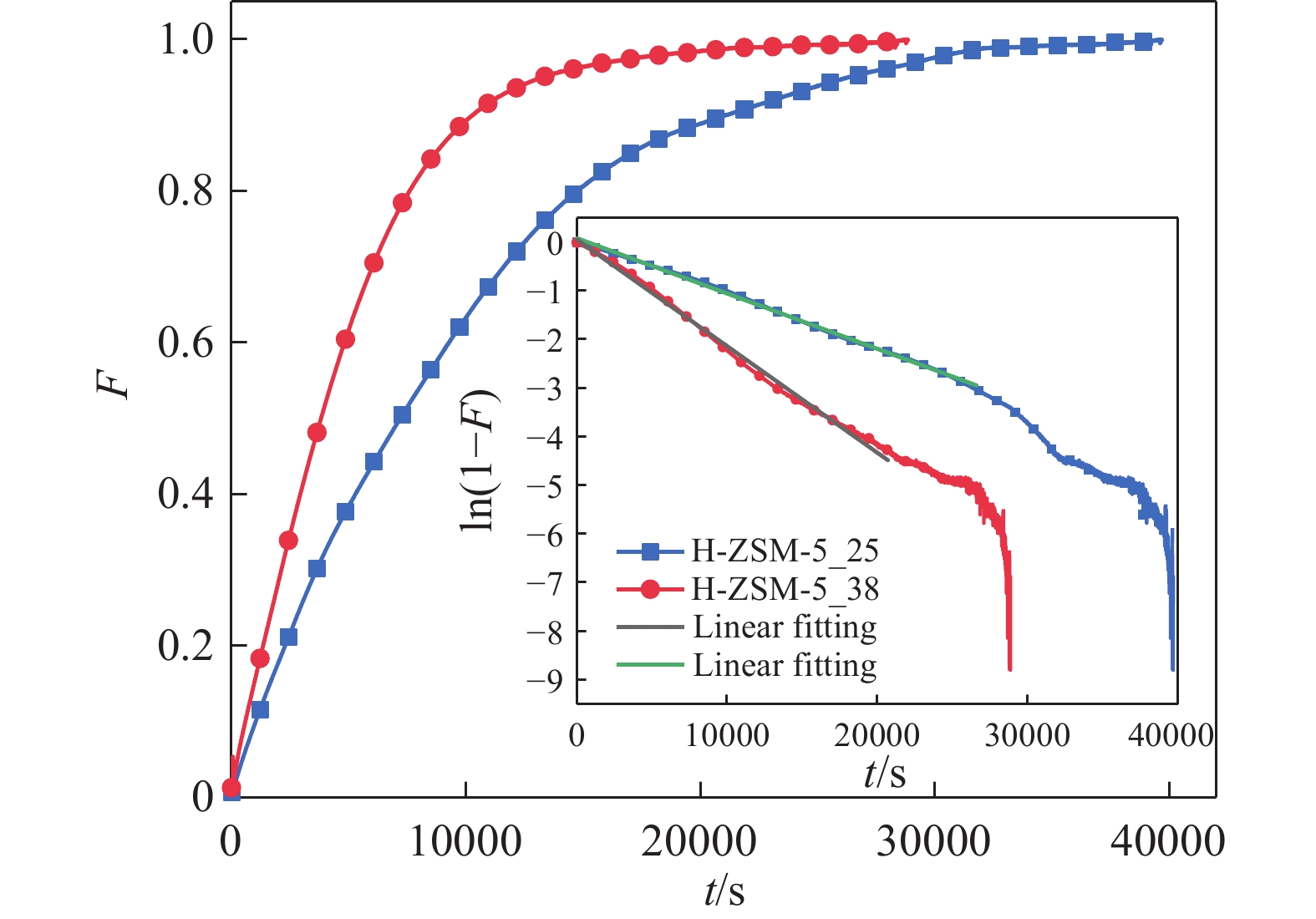
摘要: 吸附法是有望同時實現煙氣NOx超低排放深度凈化與資源化的關鍵技術,高效NOx吸附劑是其核心關鍵,然而目前針對滿足應用需求的NOx吸附劑仍缺乏系統認識。本文基于煙氣NOx凈化效率及材料熱穩定性實際需求,分析挑選了沸石、金屬氧化物、硅鋁膠等代表性吸附劑,研究了NOx在各吸附劑上的吸附穿透、吸附量、程序升溫脫附等關鍵特性,結合吸附劑孔道特性對比發現,中低硅H-ZSM-5沸石兼具較高NOx凈化深度、NOx吸附量、較低脫附溫度且可獲得更易于資源化的NOx解吸氣,因而可作為優選NOx吸附劑。進一步地,隨著吸附溫度升高,硅鋁比(w(SiO2)/w(Al2O3) )為25、38的H-ZSM-5的NOx吸附量均降低,其中低硅H-ZSM-5的NOx吸附量較高,但吸附傳質系數較低。本文可為煙氣NOx吸附凈化的效益環保技術提供指導。Abstract: Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are major air pollutants produced by fuel combustion that cause adverse effects on the environment and human health. The deep purification of NOx from ?ue gases has become a worldwide issue. In China, a rigorous ultra-low emission standard (ULES) of NOx ≤ 50 mg·m–3 has been implemented in the power and steel industries in recent years. NO2 is a valuable chemical feedstock that is worthy of being recycled from flue gas. Adsorption is a promising technology that can achieve deep purification and resource recovery of NOx from industrial flue gas, in which a high-performance NOx adsorbent plays a key role. However, a systematic understanding of NOx adsorbents for practical applications is still lacking. This study compares and analyzes the NOx adsorption and desorption performances of typical practical adsorbents including zeolites, metal oxides, and silica-alumina gels based on the practical need for both NOx purification efficacy and material thermal stability. NOx adsorption capacities, breakthrough curves, uptake curves, and temperature-programmed desorption (TPD) curves were also measured. Results show that compared to Fe–Mn–Ce and 13X as competitive adsorbents, H-ZSM-5_25 showed NOx deep purification (purification efficiency close to 100% before adsorption breakthrough), great NOx adsorption capacity (0.206 mmol·g–1), and high NO2 concentration ratio in desorption, which are likely due to its high NO catalytic oxidation rate and comparable NO2 physical adsorption rate. Regarding the desorption characteristics, H-ZSM-5_25 showed a bimodal TPD desorption peak with a lower desorption temperature (400–470 K) in the low-temperature region. Meanwhile, NO2 is the primary NOx component in the desorbed gas (adsorption-desorption enrichment ratio of NO2 being up to 57), which can easily be recovered using the liquefaction method. Furthermore, by comparing the adsorption performances on the H-ZSM-5 with different silica-to-alumina ratios, the NOx adsorption was found to decrease (from 0.706 to 0.206 mmol·g–1 for H-ZSM-5_25 and from 0.454 to 0.127 mmol·g–1 for H-ZSM-5_38) with increasing temperature (298–398 K). The dependence of the NO2 adsorption on the temperature was more significant for H-ZSM-5_25 compared to H-ZSM-5_38. Compared to H-ZSM-5_38, H-ZSM-5_25 with a lower silica-to-alumina ratio (consequently, more cation sites) rendered greater NO oxidation performance, a potentially higher NO2 adsorption capacity, and a greater decreasing trend of the adsorption capacity with increasing temperature. Results of adsorption kinetic experiments showed that the NOx mass transfer parameters on H-ZSM-5_25 were lower than those on H-ZSM-5_38 with a smaller primary micro pore channel. Results of the current work can provide technical references for economic flue gas denitrification.
-
Key words:
- flue gas purification /
- nitrogen oxide /
- adsorbent /
- adsorption /
- recovery
-
表 1 吸附劑的物理參數及NOx吸附量
Table 1. Physical parameters and NOx adsorption capacity of adsorbents
Adsorbents Brunauer–Emmett–
Teller surface area/(m2·g–1)Pore volume/
(cm3·g–1)Primary micropore channel/nm NOx adsorption capacity/
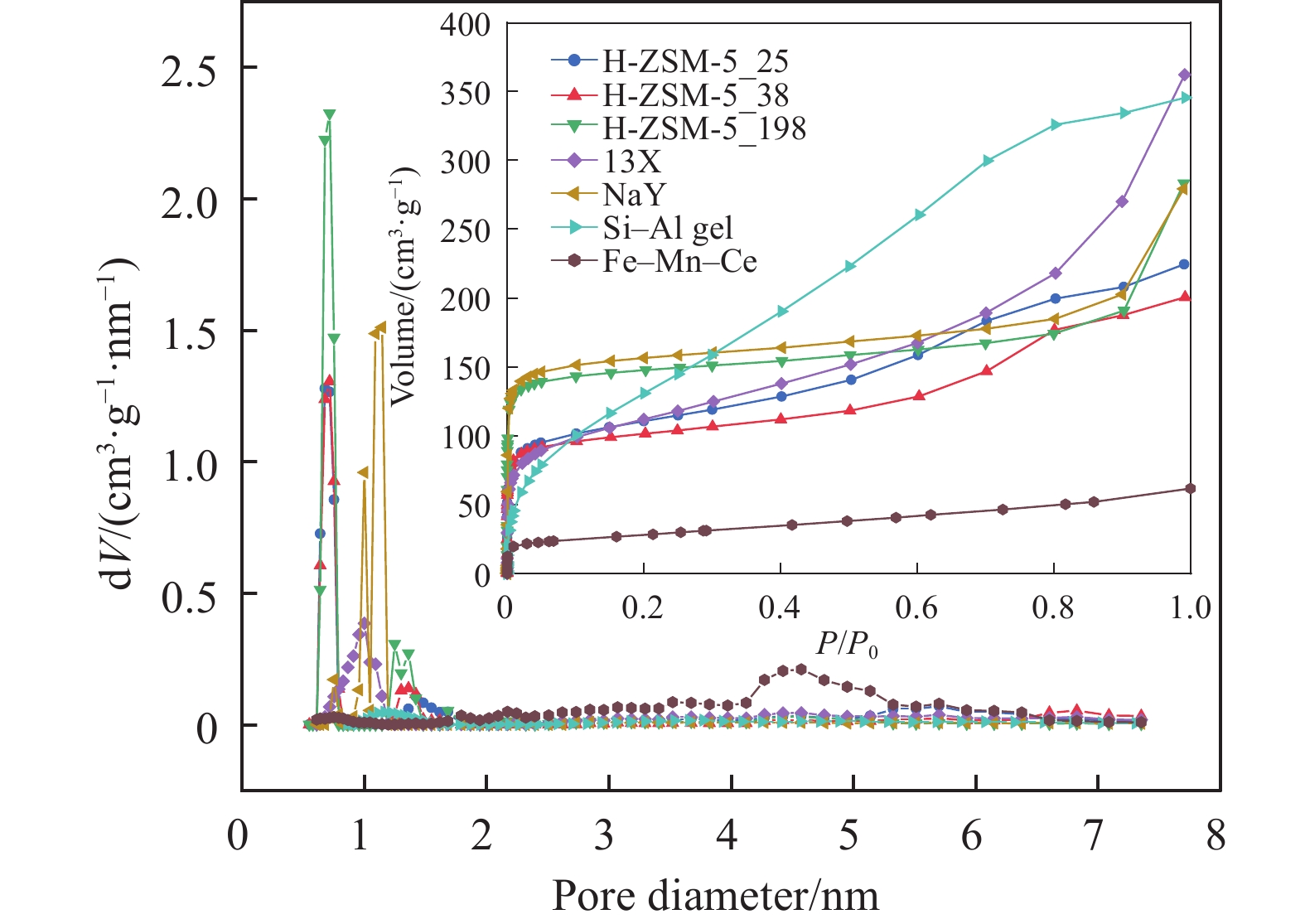
(mmol·g–1)H-ZSM-5_25 353 0.32 0.68 0.206 H-ZSM-5_38 337 0.30 0.72 0.127 H-ZSM-5_198 397 0.43 0.72 0.013 13X 393 0.48 1.00 0.181 NaY 537 0.38 1.15 0.027 Si–Al gel 463 0.43 1.17 0.016 Fe–Mn–Ce 99 0.09 4.58 0.200 久色视频表 2 LDF模型擬合參數
Table 2. Linear driving force model fitting parameters
Adsorbents R2 –ki C H-ZSM-5_25 0.998 –1.14 × 10–4± 3.79 × 10–8 0.08 ± 5.83 × 10–4 H-ZSM-5_38 0.995 –2.19 × 10–4 ± 1.32 × 10–7 0.05 ± 0.01 -
參考文獻
[1] Shelef M. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with N-free reductants. Chem Rev, 1995, 95(1): 209 doi: 10.1021/cr00033a008 [2] Parvulescu V I, Grange P, Delmon B. Catalytic removal of NO. Catal Today, 1998, 46(4): 233 doi: 10.1016/S0920-5861(98)00399-X [3] Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Opinions on promoting the implementation of ultra-low emissions in the steel industry [EB/OL]. Government Information Disclosure (2019-04-28) [2021-11-01].https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk03/201904/t20190429_701463.html中華人民共和國生態環境部. 關于推進實施鋼鐵行業超低排放的意見[EB/OL]. 政府信息公開 (2019-04-28) [2021-11-01].https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk03/201904/t20190429_701463.html [4] Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. HJ 2053—2018 Technical Specifications for Flue Gas Ultra-low Emission Engineering of Coal-fired Power Plant. Beijing: China Environmental Press, 2018中華人民共和國生態環境部. HJ 2053—2018燃煤電廠超低排放煙氣治理工程技術規范. 北京: 中國環境科學出版社, 2018 [5] Meng Z H, Wang C Y, Wang X R, et al. Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NOx from flue gas using (NH4)2S2O3/steel slag slurry combined with ozone oxidation. Fuel, 2019, 255: 115760 doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115760 [6] Paulauskas, J?gi, Striūgas, et al. Application of non-thermal plasma for NOx reduction in the flue gases. Energies, 2019, 12(20): 3955 doi: 10.3390/en12203955 [7] Zhang Q, He S L, Zhang Z, et al. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOz and anti-toxicity of MnOx–FeOy/TiO2–ZrO2–CeO2. Chin J Eng, 2020, 42(3): 321張晴, 賀拴玲, 張錚, 等. MnOx–FeOy/TiO2–ZrO2–CeO2低溫選擇性催化還原NOz和抗毒性研究. 工程科學學報, 2020, 42(3):321 [8] Ding L, Qian L X, Yang T, et al. Influence of Zn in the iron ore sintering flue gas on the removal of NOx and dioxins by V2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalyst. Chin J Eng, 2021, 43(8): 1125丁龍, 錢立新, 楊濤, 等. 燒結煙氣中Zn對V2O5–WO3/TiO2催化劑脫除NOx和二噁英性能的影響. 工程科學學報, 2021, 43(8):1125 [9] Xing Y, Zhang W B, Su W, et al. Research of ultra-low emission technologies of the iron and steel industry in China. Chin J Eng, 2021, 43(1): 1邢奕, 張文伯, 蘇偉, 等. 中國鋼鐵行業超低排放之路. 工程科學學報, 2021, 43(1):1 [10] Yang R T. Gas Separation by Adsorption Processes. London: World Scientific, 1997 [11] Ren F P, Tian X Z, Ren Y L, et al. Nitrogen dioxide-catalyzed aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohols under cocatalyst and acid-free conditions. Catal Commun, 2017, 101: 98 doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2017.08.003 [12] Kong Y, Cha C Y. NOx adsorption on char in presence of oxygen and moisture. Carbon, 1996, 34(8): 1027 doi: 10.1016/0008-6223(96)00050-4 [13] Hu M M, Zhang Z Q, Atkinson J D, et al. Porous materials for steady-state NO conversion: Comparisons of activated carbon fiber cloths, zeolites and metal-organic frameworks. Chem Eng J, 2019, 360: 89 doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.102 [14] Machida M, Yoshii A, Kijima T. Temperature swing adsorption of NOx over ZrO2-based oxides. Int J Inorg Mater, 2000, 2(5): 413 doi: 10.1016/S1466-6049(00)00062-3 [15] Xing N, Wang X P, Yu Q, et al. Adsorption performance of zeolites for NO and NO2. Chin J Catal, 2007, 28(3): 205 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9837.2007.03.006邢娜, 王新平, 于青, 等. 分子篩對NO和NO2的吸附性能. 催化學報, 2007, 28(3):205 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9837.2007.03.006 [16] An J L, Wang Y S, Li X, et al. Analysis of the relationship between NO, NO2 and O3 concentrations in Beijing. Environ Sci, 2007, 28(4): 4706安俊琳, 王躍思, 李昕, 等. 北京大氣中NO、NO2和O3濃度變化的相關性分析. 環境科學, 2007, 28(4):4706 [17] Brown C E, Hall P G. Physical adsorption of nitric oxide on graphite and silica and adsorption of gases on nitric oxide preadsorbed on carbon. J Colloid Interface Sci, 1973, 42(2): 334 doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(73)90297-X [18] Brown C E, Hall P G. Physical adsorption of nitric oxide on metal oxides. Surf Sci, 1973, 36(2): 569 doi: 10.1016/0039-6028(73)90403-2 [19] Deng H, Yi H H, Tang X L, et al. Adsorption equilibrium for sulfur dioxide, nitric oxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen on 13X and 5A zeolites. Chem Eng J, 2012, 188: 77 doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.02.026 [20] Penkova A, Hadjiivanov K, Mihaylov M, et al. FTIR spectroscopic study of low temperature NO adsorption and NO + O2 coadsorption on H-ZSM-5. Langmuir, 2004, 20(13): 5425 doi: 10.1021/la0496643 [21] Szanyi J, Hun Kwak J, Moline R A, et al. The adsorption of NO2 and the NO+O2 reaction on Na–Y, FAU: An in situ FTIR investigation. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2003, 5(18): 4045 doi: 10.1039/B306585E [22] Liu Y S, Sun N Q, Li Z Y, et al. Recovery of high-purity NO2 and SO2 products from iron-ore sintering flue gas by distillation: Process design, optimization and analysis. Sep Purif Technol, 2021, 264: 118308 doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118308 [23] Ghouma I, Jeguirim M, Dorge S, et al. Activated carbon prepared by physical activation of olive stones for the removal of NO2 at ambient temperature. Comptes Rendus Chimie, 2015, 18(1): 63 doi: 10.1016/j.crci.2014.05.006 [24] Liu H R. Variation of spontaneous combustion point of activated carbon with different oxidation degree. Fire Sci Technol, 2013, 32(4): 367 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2013.04.006劉函如. 不同氧化程度的活性炭自燃點變化規律研究. 消防科學與技術, 2013, 32(4):367 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2013.04.006 [25] Silas K, Wan Azlina Wan Ab Karim Ghani, Choong T S Y, et al. Carbonaceous materials modified catalysts for simultaneous SO2/NOx removal from flue gas: A review. Catal Rev, 2019, 61(1): 134 doi: 10.1080/01614940.2018.1482641 [26] Jiang H X, Wang Q Y, Wang H Q, et al. MOF-74 as an efficient catalyst for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2016, 8(40): 26817 doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b08851 [27] Bauer S, Serre C, Devic T, et al. High-throughput assisted rationalization of the formation of metal organic frameworks in the iron(III) aminoterephthalate solvothermal system. Inorg Chem, 2008, 47(17): 7568 doi: 10.1021/ic800538r [28] Zhang Z Q, Atkinson J D, Jiang B Q, et al. NO oxidation by microporous zeolites: Isolating the impact of pore structure to predict NO conversion. Appl Catal B Environ, 2015, 163: 573 doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.06.044 [29] Liu Y S, You Y, Li Z Y, et al. NOx removal with efficient recycling of NO2 from iron-ore sintering flue gas: A novel cyclic adsorption process. J Hazard Mater, 2021, 407: 124380 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124380 [30] You Y, Liu Y S, Yang X, et al. A new adsorption process for flue gas NOx purification and recovery. CIESC J, 2021, 72(4): 2132游洋, 劉應書, 楊雄, 等. 面向煙氣NOx凈化與回收的新型吸附工藝. 化工學報, 2021, 72(4):2132 [31] Huang H Y, Yang R T. Removal of NO by reversible adsorption on Fe?Mn based transition metal oxides. Langmuir, 2001, 17(16): 4997 doi: 10.1021/la0102657 [32] Yang X, Liu Y S, Li Z Y, et al. Vacuum exhaust process in pilot-scale vacuum pressure swing adsorption for coal mine ventilation air methane enrichment. Energies, 2018, 11(5): 1030 doi: 10.3390/en11051030 [33] Li Z Y, Liu Y S, Yang X, et al. Desorption kinetics of naphthalene and acenaphthene over two activated carbons via thermogravimetric analysis. Energy Fuels, 2015, 29(8): 5303 doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b01159 [34] Li G, Xiao P, Zhang J, et al. The role of water on postcombustion CO2 capture by vacuum swing adsorption: Bed layering and purge to feed ratio. Aiche J, 2014, 60(2): 673 doi: 10.1002/aic.14281 [35] Li Z Y, Liu Y S, Wang H H, et al. A numerical modelling study of SO2 adsorption on activated carbons with new rate equations. Chem Eng J, 2018, 353: 858 doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.119 [36] Zhu X Q, Liu Y S, Yang X, et al. Study of a novel rapid vacuum pressure swing adsorption process with intermediate gas pressurization for producing oxygen. Adsorption, 2017, 23(1): 175 doi: 10.1007/s10450-016-9843-4 [37] Mendes A M M, Costa C A V, Rodrigues A E. Linear driving force approximation for isothermal non-isobaric diffusion/convection with binary Langmuir adsorption. Gas Sep Purif, 1995, 9(4): 259 doi: 10.1016/0950-4214(95)00008-Y [38] Zhang B W, Tang X L, Yi H H, et al. Study on NO adsorptive removal on modified activated carbon. New Chem Mater, 2015, 43(7): 111張波文, 唐曉龍, 易紅宏, 等. 改性活性炭吸附去除NO實驗研究. 化工新型材料, 2015, 43(7):111 [39] Zhang J Q, Liu Y Y, Fan W B, et al. Adsorption and temperature programmed desorption of NO, NO+O2, NO2 and NO + NO2 over CoH-ZSM-5. Fuel, 2007, 86(10-11): 1577 doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2006.11.011 [40] Loiland J A, Lobo R F. Low temperature catalytic NO oxidation over microporous materials. J Catal, 2014, 311: 412 doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2013.12.013 [41] Li R, Wu B, Chen Y Q, et al. Influence of polyethylene glycol on the catalytic activity of MnFeOx for NO oxidation at low-temperature. Catal Lett, 2019, 149(7): 1864 doi: 10.1007/s10562-019-02793-9 [42] Wang Z, Guo M, Mu X Y, et al. Highly sensitive capacitive gas sensing at ionic liquid-electrode interfaces. Anal Chem, 2016, 88(3): 1959 doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04677 -




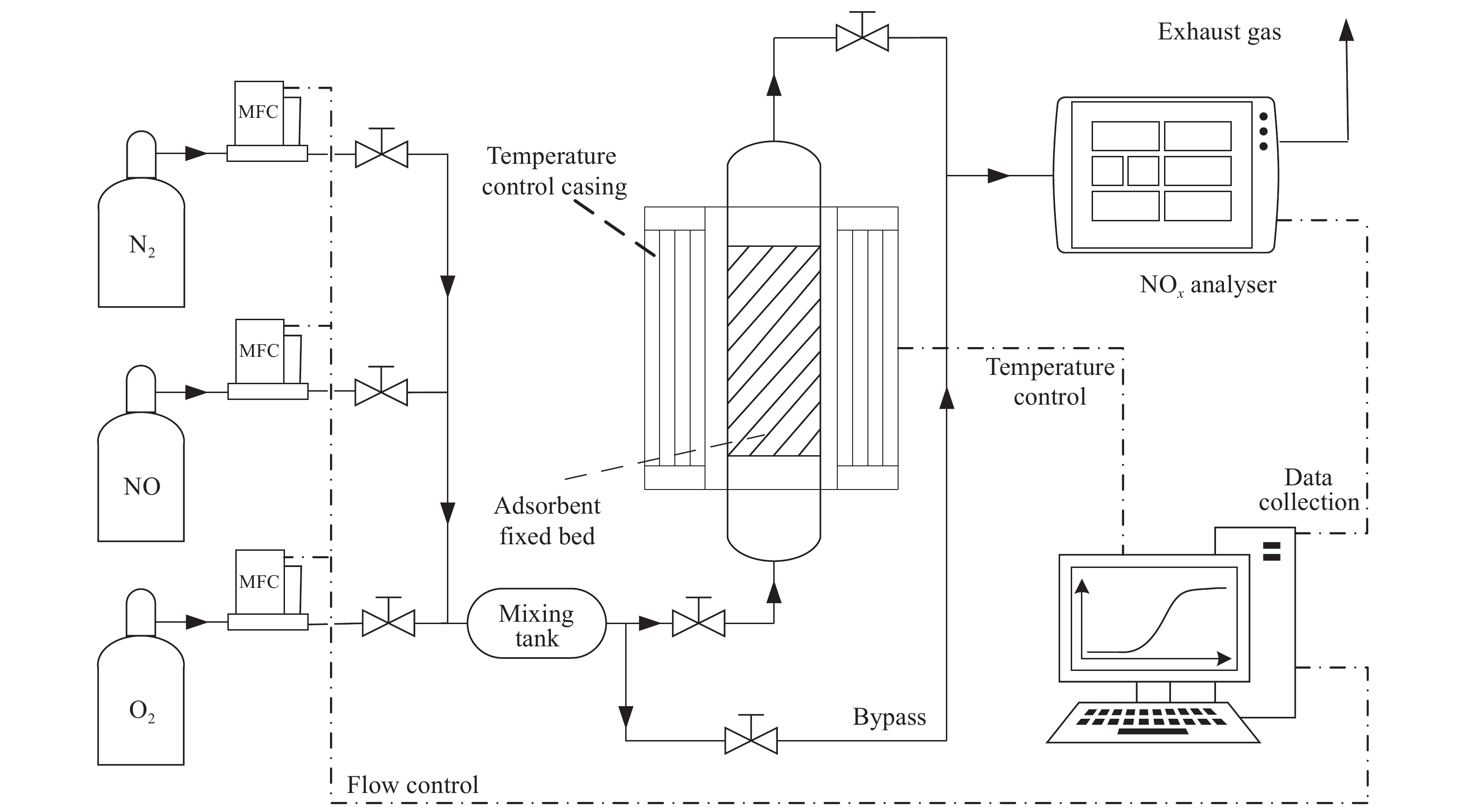
 下載:
下載: