-
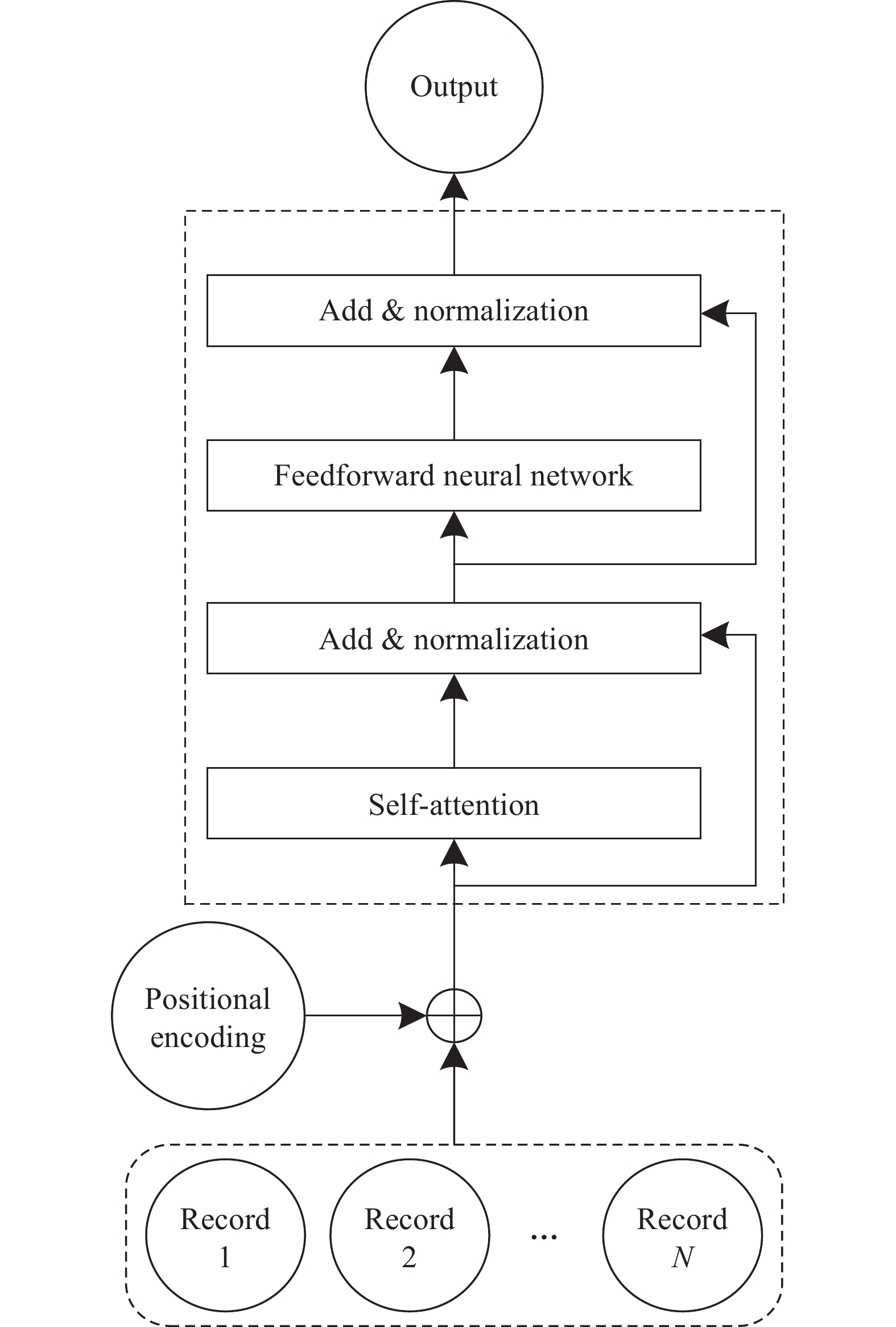
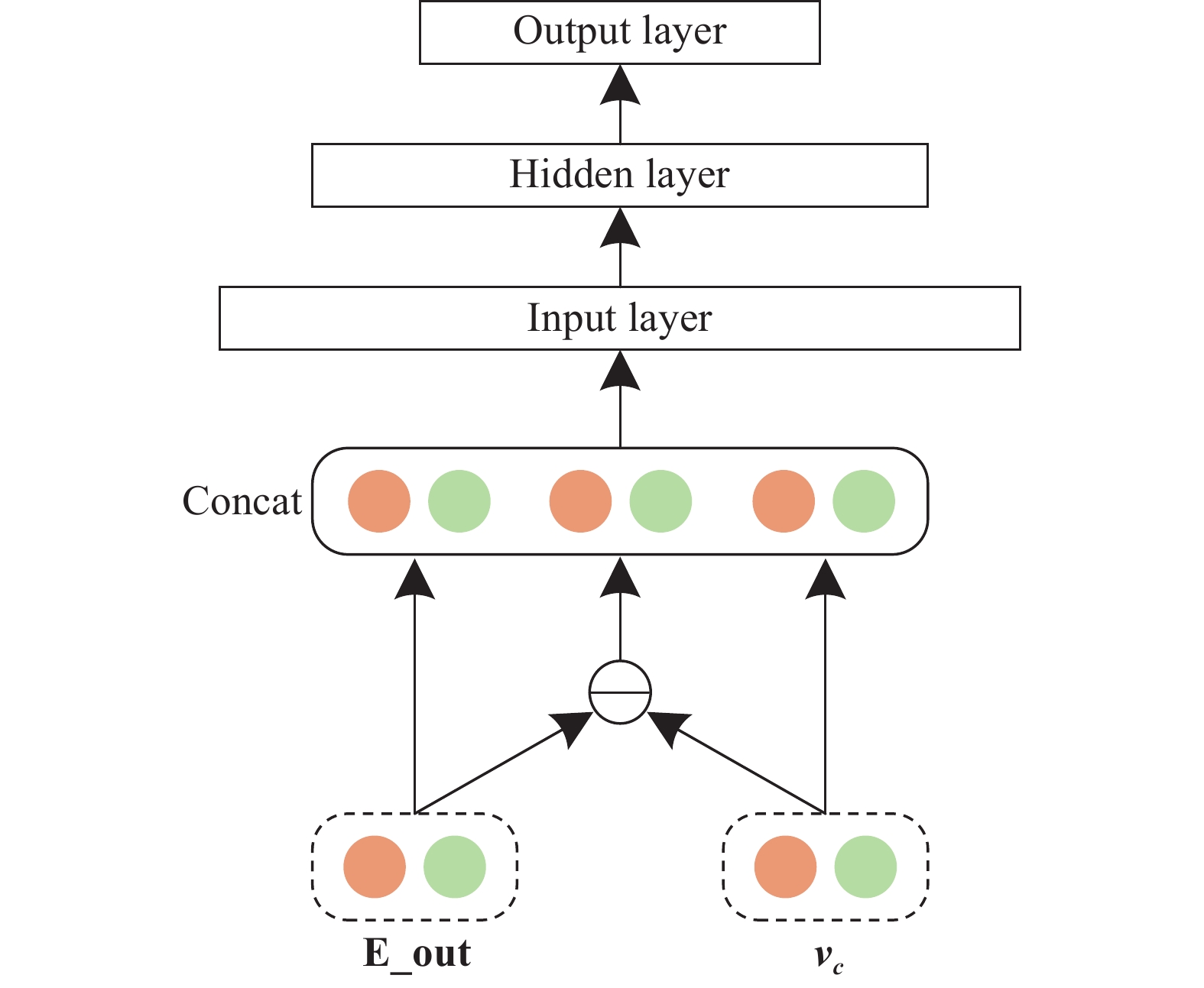
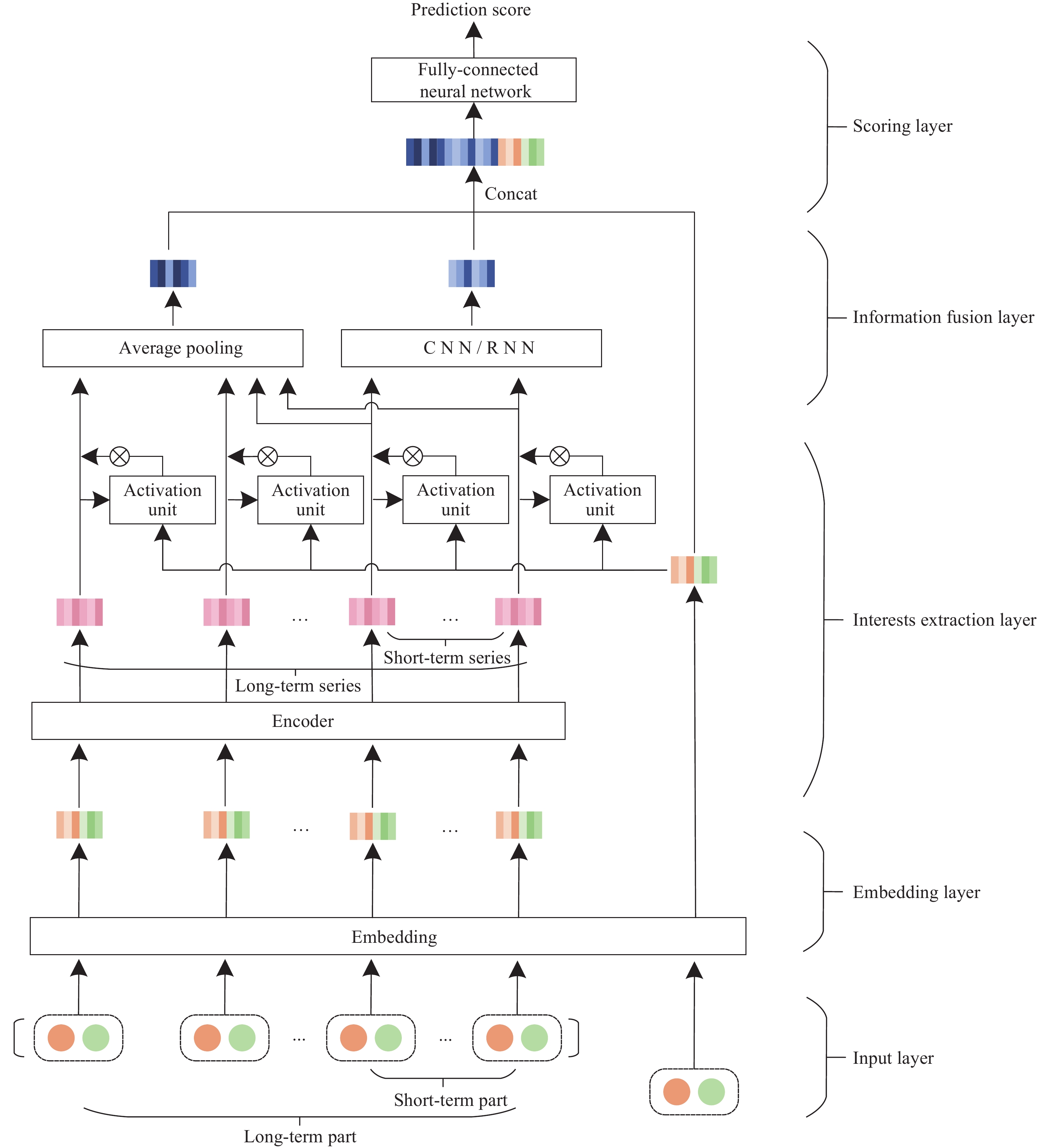
摘要: 針對現有深度神經網絡點擊率預測模型在對用戶偏好建模時,難以有效且高效地處理用戶行為序列的問題,提出長短期興趣網絡(Long and short term interests network, LSTIN)模型,充分利用用戶歷史記錄上下文信息和順序信息,提升點擊率預測精準性和訓練效率。使用基于注意力機制的Transformer和激活單元結構完成用戶長、短期興趣建模,對用戶短期興趣進一步使用循環神經網絡(Recurrent neural network, RNN)、卷積神經網絡(Convolutional neural networks, CNN)進行處理,最后使用全連接神經網絡進行預測。在亞馬遜公開數據集上開展實驗,將提出的模型與基于分解機的神經網絡(DeepFM)、深度興趣網絡(Deep interest network, DIN)等點擊率預測模型對比,結果表明提出的模型實現了考慮上下文信息和順序信息的用戶歷史記錄建模,接受者操作特征曲線下面積(Area under curve, AUC)指標為85.831%,相比于基礎模型(BaseModel)提升1.154%,相比于DIN提升0.476%。且因區分用戶長、短期興趣,模型能夠在提升預測精準性的同時保障訓練效率。Abstract: The click-through rate (CTR) prediction task is to estimate the probability that a user will click an item according to the features of user, item, and contexts. At present, CTR prediction has become a common and indispensable task in the field of e-commerce. Higher accuracy of CTR prediction results conduces to present more accurate and personalized results for recommendation systems and search engines to increase users’ actual CTR of items and bring more economic benefits. More researchers used a deep neural network (DNN) to solve the CTR prediction problem under the background of big data technology in recent years. However, there are a few models that can process time series data and fully consider the context information of users’ history effectively and efficiently. CTR prediction models based on a DNN learn users’ interests from their history; however, most of the existing models regard user interest, ignoring the differences between the long-term and short-term interests. This paper proposes a CTR prediction model named Long- and Short-Term Interest Network (LSTIN) to fully use the context information and order information of user history records. This use will help improve the accuracy and training efficiency of the CTR prediction model. Based on the attention mechanism, the transformer and activation unit structure are used to model long-term and short-term user interests. The latter is processed using the recurrent and convolutional neural networks further. Eventually, a fully-connected neural network is applied for prediction. Different from DeepFM and Deep Interest Network (DIN) in experiments on an Amazon public dataset, LSTIN achieves modeling with context and order information of user history. The AUC of LSTIN is 85.831%, which is 1.154% higher than that of BaseModel and 0.476% higher than that of DIN. Besides, LSTIN achieves distinguishing the long-term and short-term interests of users, which improves the performance and maintains the training efficiency of the CTR prediction model.
-
Key words:
- CTR prediction /
- long and short term interest network /
- deep neural network /
- attention mechanism /
- RNN /
- CNN
-
表 1 數據集統計信息
Table 1. Statistical information of a dataset
Data set Number of users Number of commodities Number of categories Number of samples Amazon
(Electronics)192403 63001 801 1689188 久色视频表 2 算法性能對比
Table 2. Algorithm performance
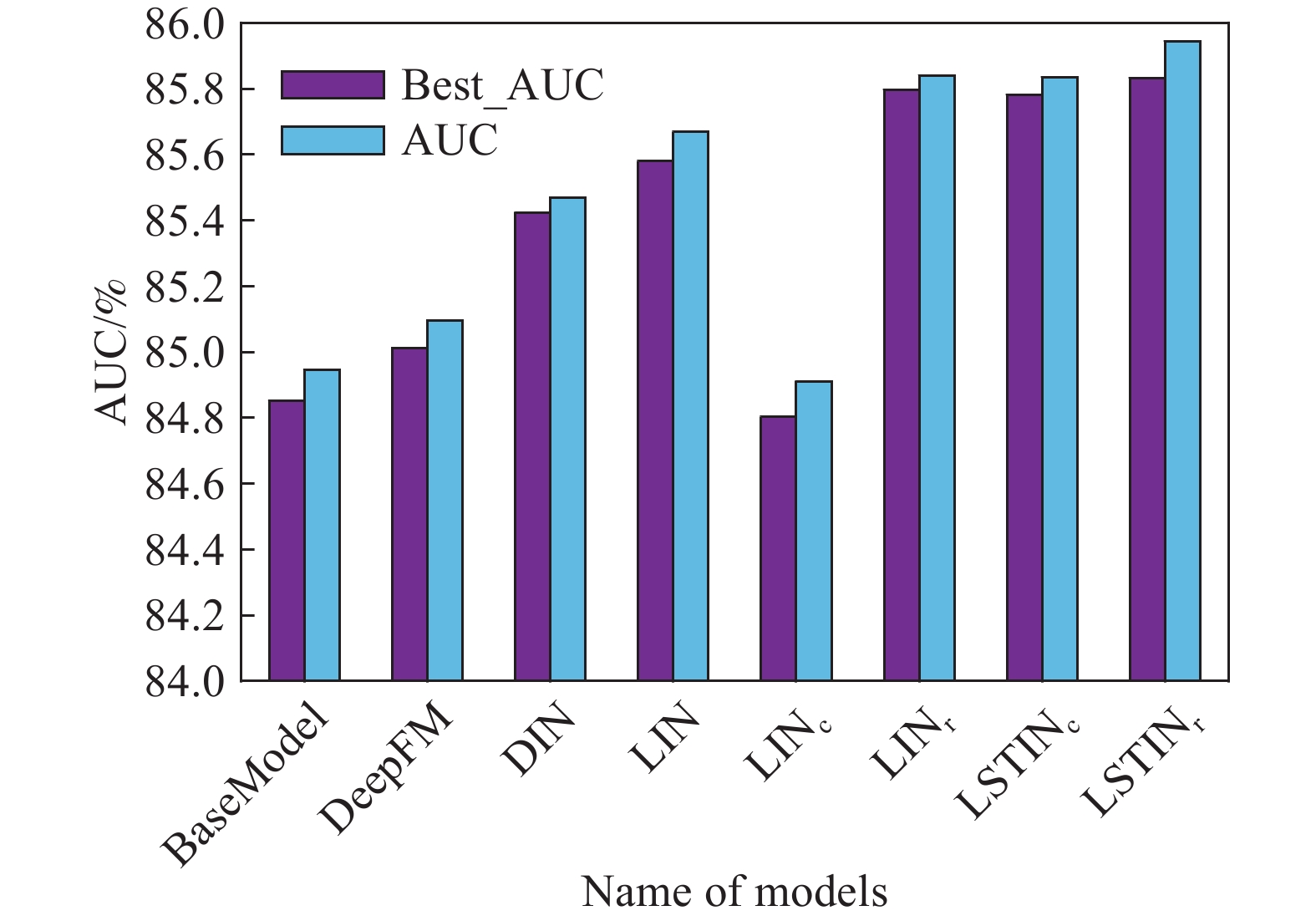
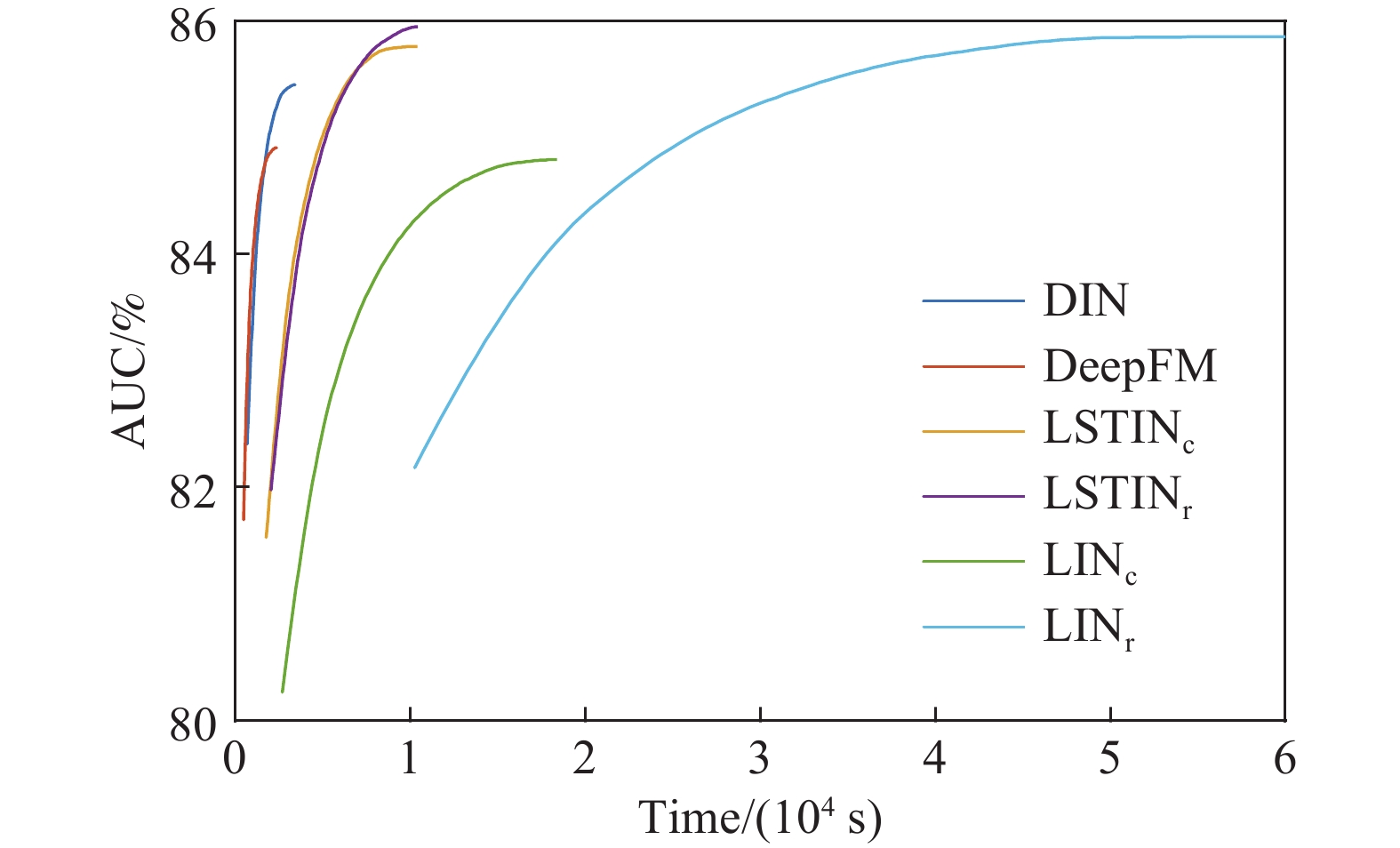
Category Name AUC/% Best AUC/% RP(BaseModel)/% RP (DIN)/% Existing models BaseModel 84.852 84.946 0 ?0.670 DeepFM 85.012 85.095 0.189 ?0.482 DIN 85.424 85.468 0.674 0 Modesl of this paper LIN 85.581 85.669 0.859 0.184 LINc 84.803 84.911 ?0.058 ?0.727 LINr 85.796 85.841 1.113 0.435 LSTINc 85.781 85.834 1.095 0.418 LSTINr 85.831 85.943 1.154 0.476 -
參考文獻
[1] Shen X L, Li Z J, He C H. Hybrid recommendation algorithm based on rating filling and trust information. J Comput Appl, 2020, 40(10): 2789沈學利, 李子健, 赫辰皓. 基于評分填充與信任信息的混合推薦算法. 計算機應用, 2020, 40(10):2789 [2] Song H Q, Du S Y, Zhou Y C, et al. Big data intelligent platform and application analysis for oil and gas resource development. Chin J Eng, 2021, 43(2): 179宋洪慶, 都書一, 周園春, 等. 油氣資源開發的大數據智能平臺及應用分析. 工程科學學報, 2021, 43(2):179 [3] Tao Z L, Wang X, He X N, et al. HoAFM: A high-order attentive factorization machine for CTR prediction. Inf Process Manag, 2019, 57(6): 102076 [4] Zhou A Y, Zhou M Q, Gong X Q. Computational advertising: A data-centric comprehensive web application. Chin J Comput, 2011, 34(10): 1805 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2011.01805周傲英, 周敏奇, 宮學慶. 計算廣告: 以數據為核心的Web綜合應用. 計算機學報, 2011, 34(10):1805 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2011.01805 [5] Liu M J, Zeng G C, Yue W, et al. Review on click-through rate prediction models for display advertising. Comput Sci, 2019, 46(7): 38 doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2019.07.006劉夢娟, 曾貴川, 岳威, 等. 面向展示廣告的點擊率預測模型綜述. 計算機科學, 2019, 46(7):38 doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2019.07.006 [6] Richardson M, Dominowska E, Ragno R. Predicting clicks: Estimating the click through rate for new ADs // Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on World Wide Web. Alberta, 2007: 521 [7] Chen J X, Sun B G, Li H, et al. Deep CTR prediction in display advertising // Proceedings of the 24th ACM international conference on Multimedia. Amsterdam, 2016: 811 [8] Rendle S. Factorization Machines // 2010 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. Berlin, 2010: 995 [9] Zhang W N, Du T M, Wang J. Deep learning over multi-field categorical data: A case study on user response prediction // Proceedings of European Conference on Information Retrieval. Padua, 2016: 45 [10] Qu Y R, Cai H, Ren K, et al. Product-based neural networks for user response prediction // 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Data Mining. Barcelona, 2016: 1149 [11] Cheng H T, Koc L, Harmsen J, et al. Wide & Deep learning for recommender systems // Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Deep Learning for Recommender Systems. Boston, 2016: 7 [12] Guo H F, Tang R M, Ye Y M, et al. DeepFM: A factorization-machine based neural network for CTR prediction // Twenty-Sixth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Melbourne, 2017: 1725 [13] Zhou G R, Song C R, Zhu X Q, et al. Deep interest network for click-through rate prediction // Proceedings of KDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. London, 2018: 1059 [14] Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory. Neural Computat, 1997, 9(8): 1735 doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [15] Cheng Y, Yao L B, Zhang G H, et al. Text sentiment orientation analysis of multi-channels CNN and BiGRU based on attention mechanism. J Comput Res Dev, 2020, 57(12): 2583 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20190854程艷, 堯磊波, 張光河, 等. 基于注意力機制的多通道CNN和BiGRU的文本情感傾向性分析. 計算機研究與發展, 2020, 57(12):2583 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20190854 [16] Cho K, Merri?nboer B, Gulcehre C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation // Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods on Natural Language Processing. Doha, 2014: 1724 [17] Dai J H, Deng Y B. Extracting emotion-cause pairs based on emotional dilation gated CNN. Data Anal Knowl Discov, 2020, 4(8): 98代建華, 鄧育彬. 基于情感膨脹門控CNN的情感-原因對提取. 數據分析與知識發現, 2020, 4(8):98 [18] Kalchbrenner N, Grefenstette E, Blunsom P. A convolutional neural network for modelling sentences // Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Baltimore, 2014: 655 [19] Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need // Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, 2017: 6000 [20] Jiang D, Xu R B, Xu X, et al. Multi-view feature transfer for click-through rate prediction. Inf Sci, 2021, 546: 961 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.09.005 [21] Yu C M, Feng B L, An L. Sentiment analysis in cross-domain environment with deep representative learning. Data Anal Knowl Discov, 2017, 1(7): 73余傳明, 馮博琳, 安璐. 基于深度表示學習的跨領域情感分析. 數據分析與知識發現, 2017, 1(7):73 [22] Zhang Y F, Lu Z Q. Remaining useful life prediction based on an integrated neural network. Chin J Eng, 2020, 42(10): 1372張永峰, 陸志強. 基于集成神經網絡的剩余壽命預測. 工程科學學報, 2020, 42(10):1372 [23] Kim Y. Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification // Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Doha, 2014: 1746 [24] Zhang Y, Wallace B. A sensitivity analysis of (and practitioners’ guide to) convolutional neural networks for sentence classification. Comput Sci, https://arxiv.org/pdf/1510.03820.pdf [25] Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization // International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego, 2015 [26] Li Y J, Guo H X, Li Y N, et al. A boosting based ensemble learning algorithm in imbalanced data classification. Syst Eng Theory Pract, 2016, 36(1): 189李詒靖, 郭海湘, 李亞楠, 等. 一種基于Boosting的集成學習算法在不均衡數據中的分類. 系統工程理論與實踐, 2016, 36(1):189 -




 下載:
下載: