Numerical analysis of the novel lime calcination process for carbon dioxide capture
-
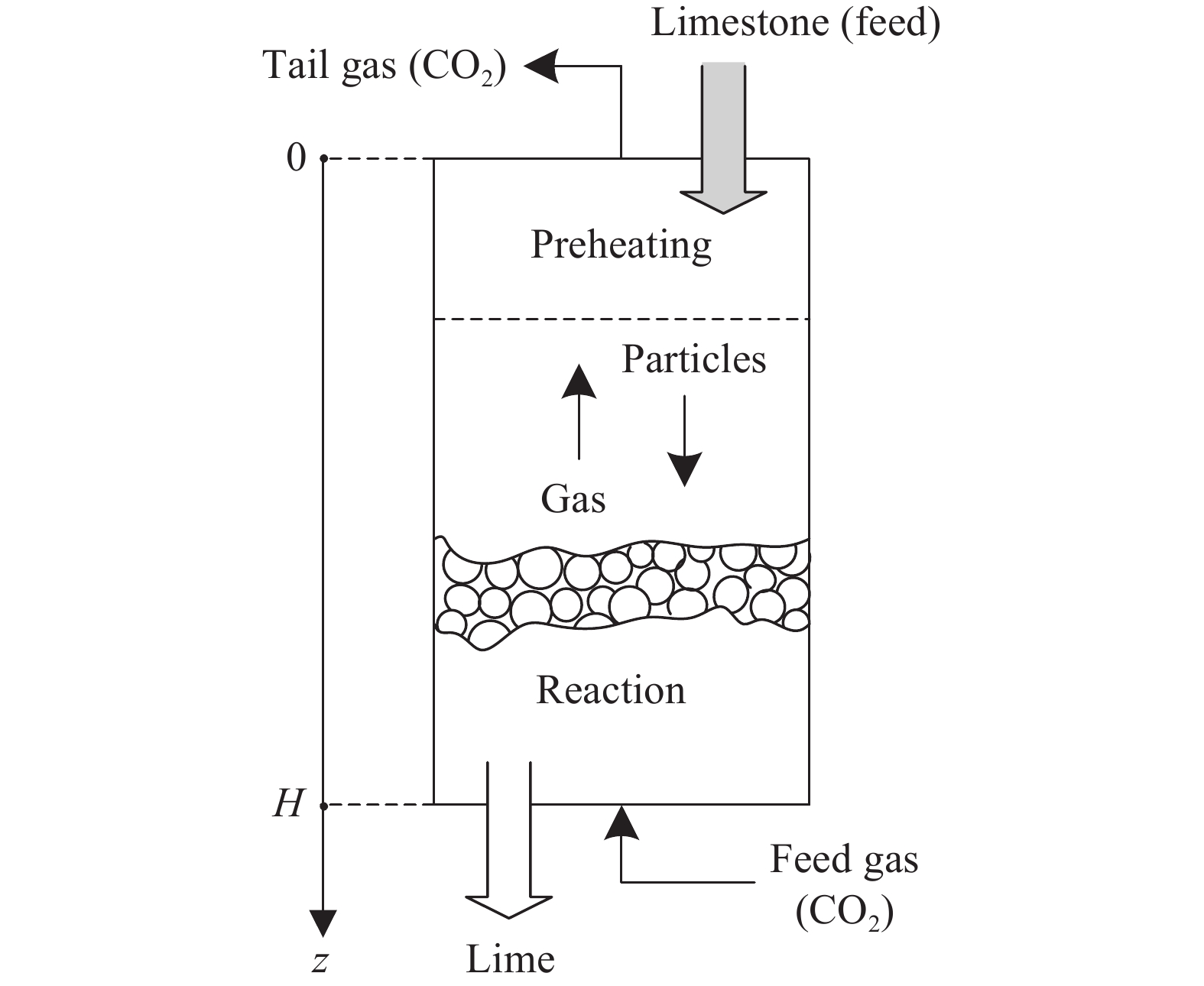
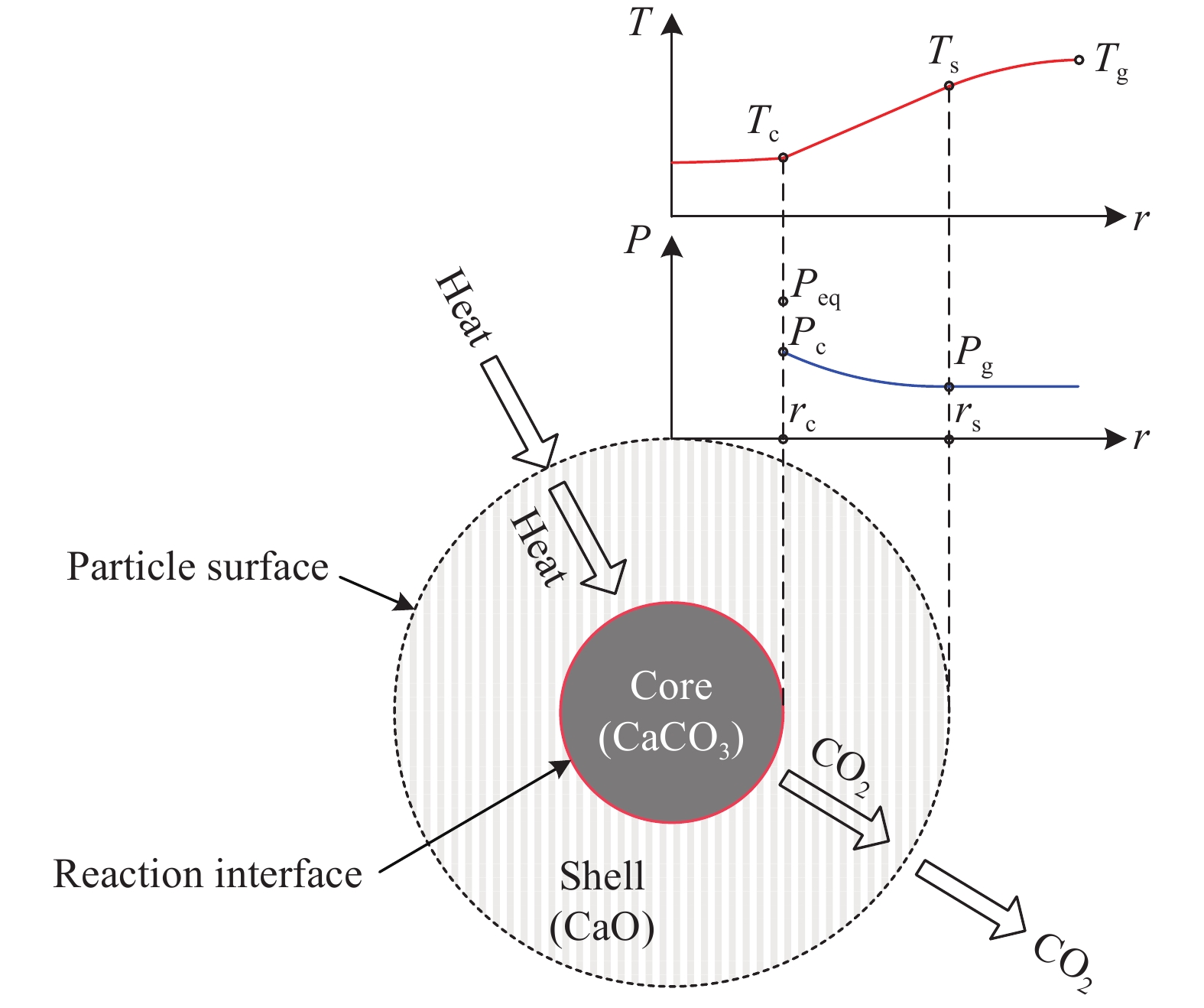
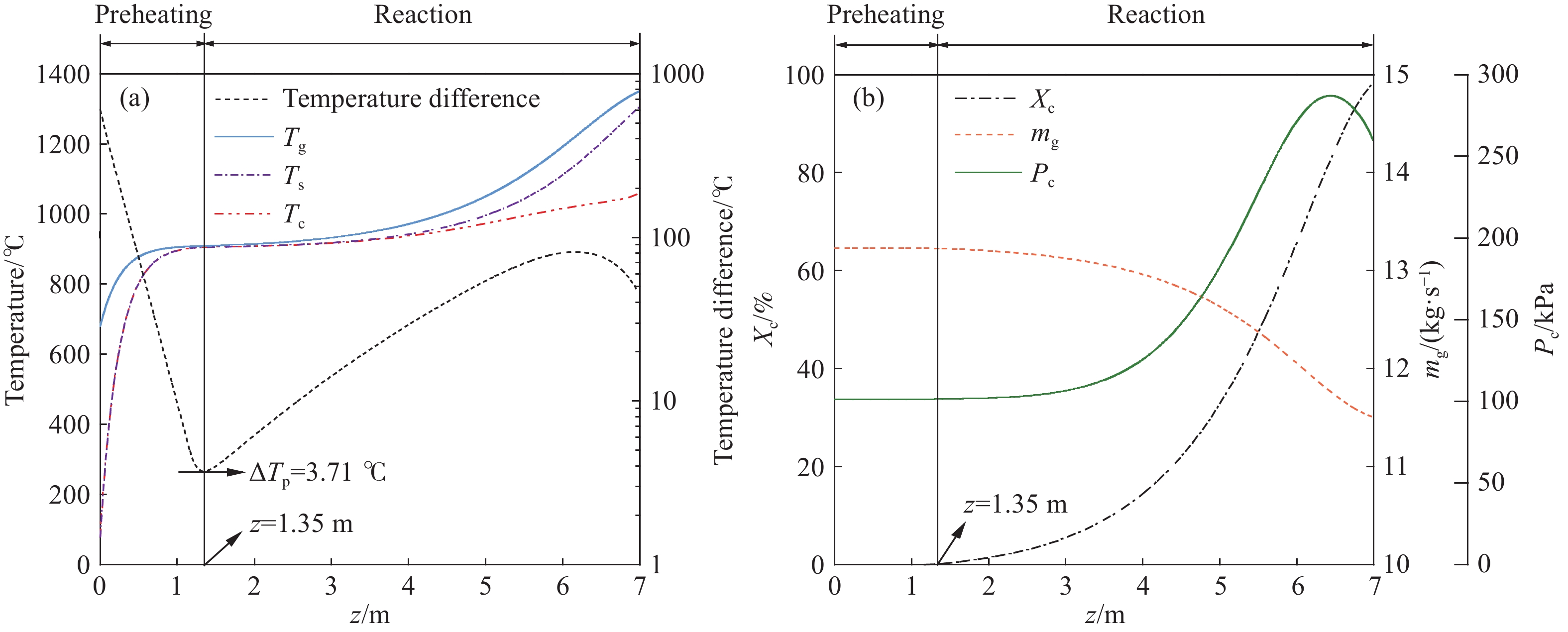
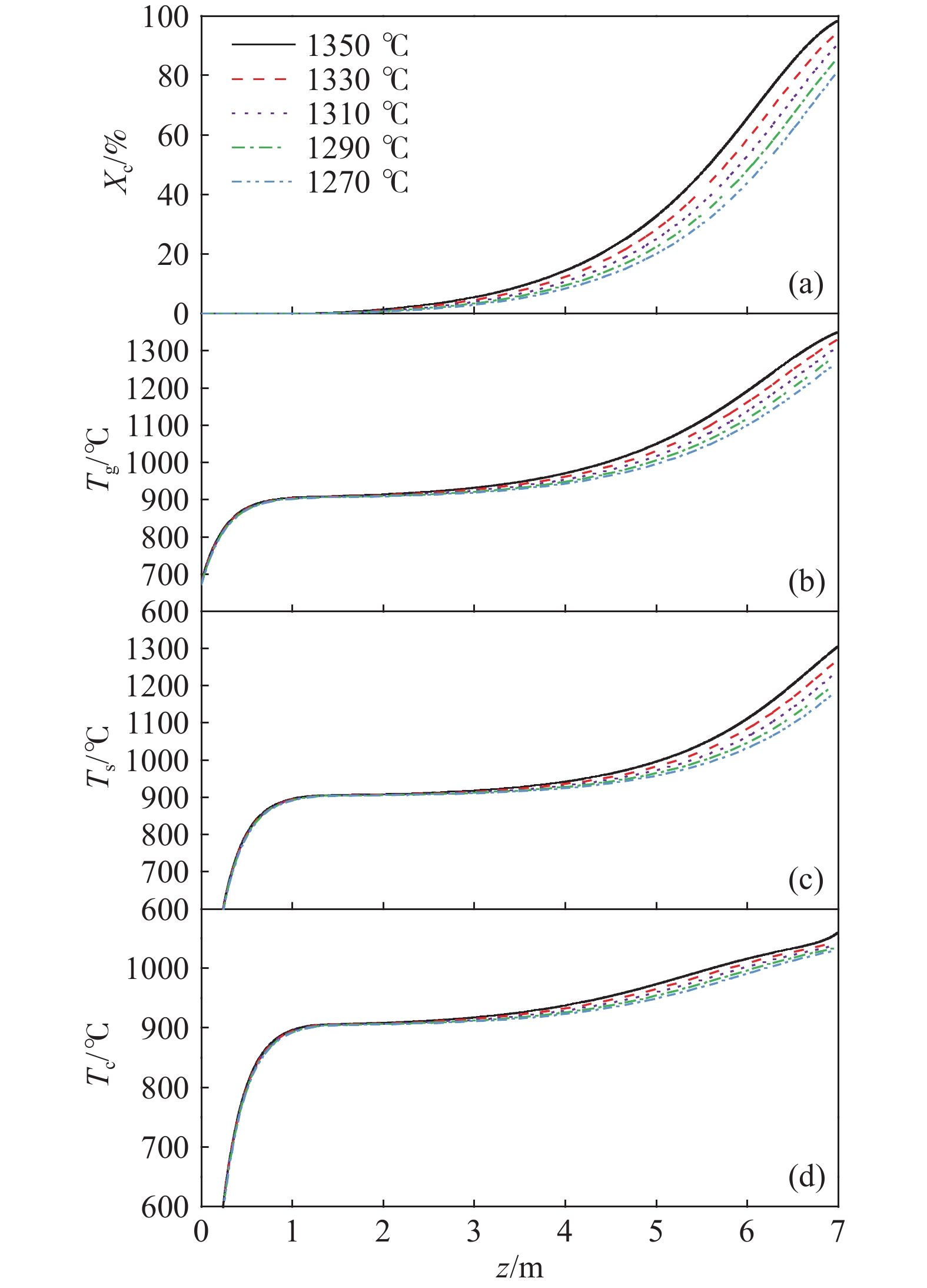
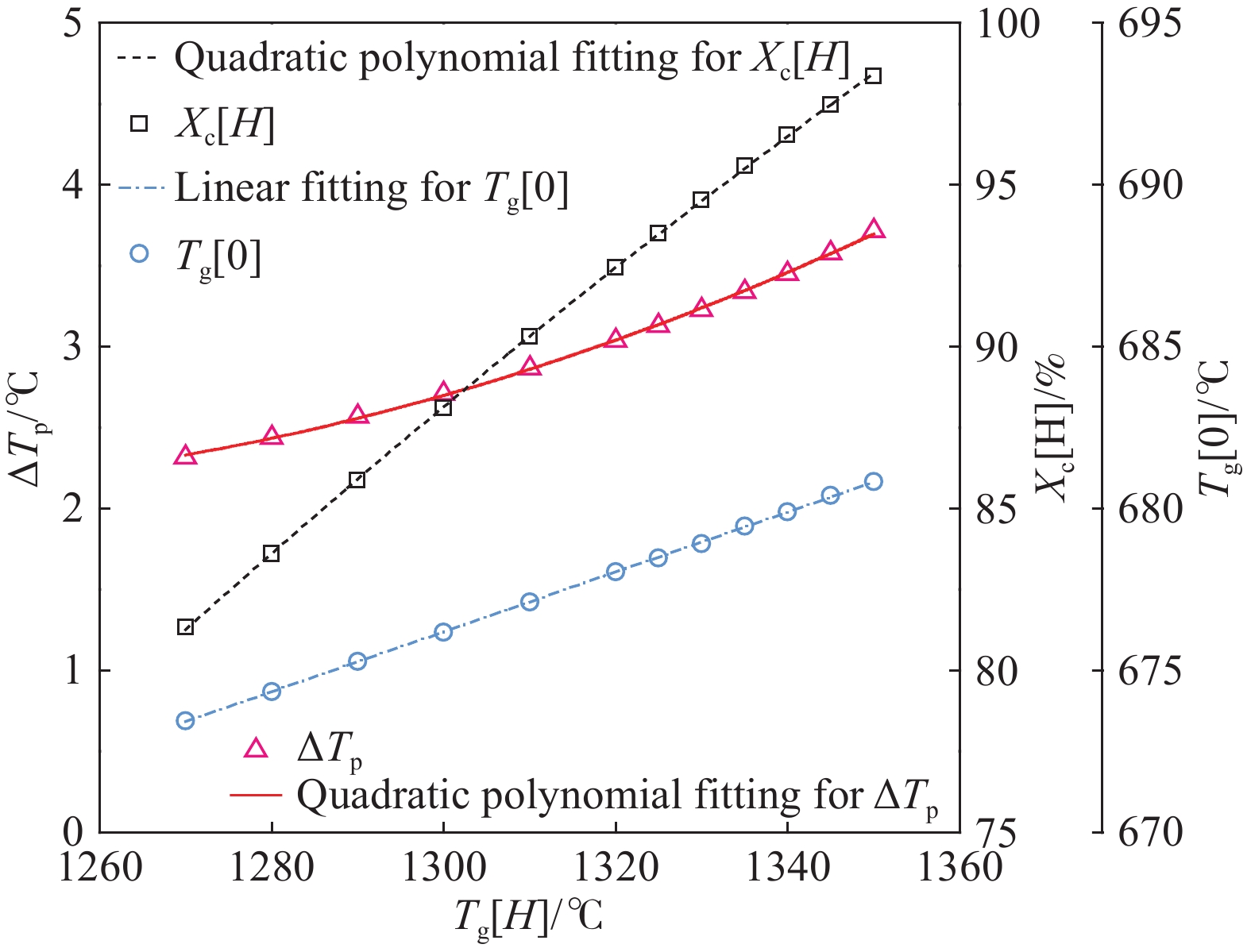
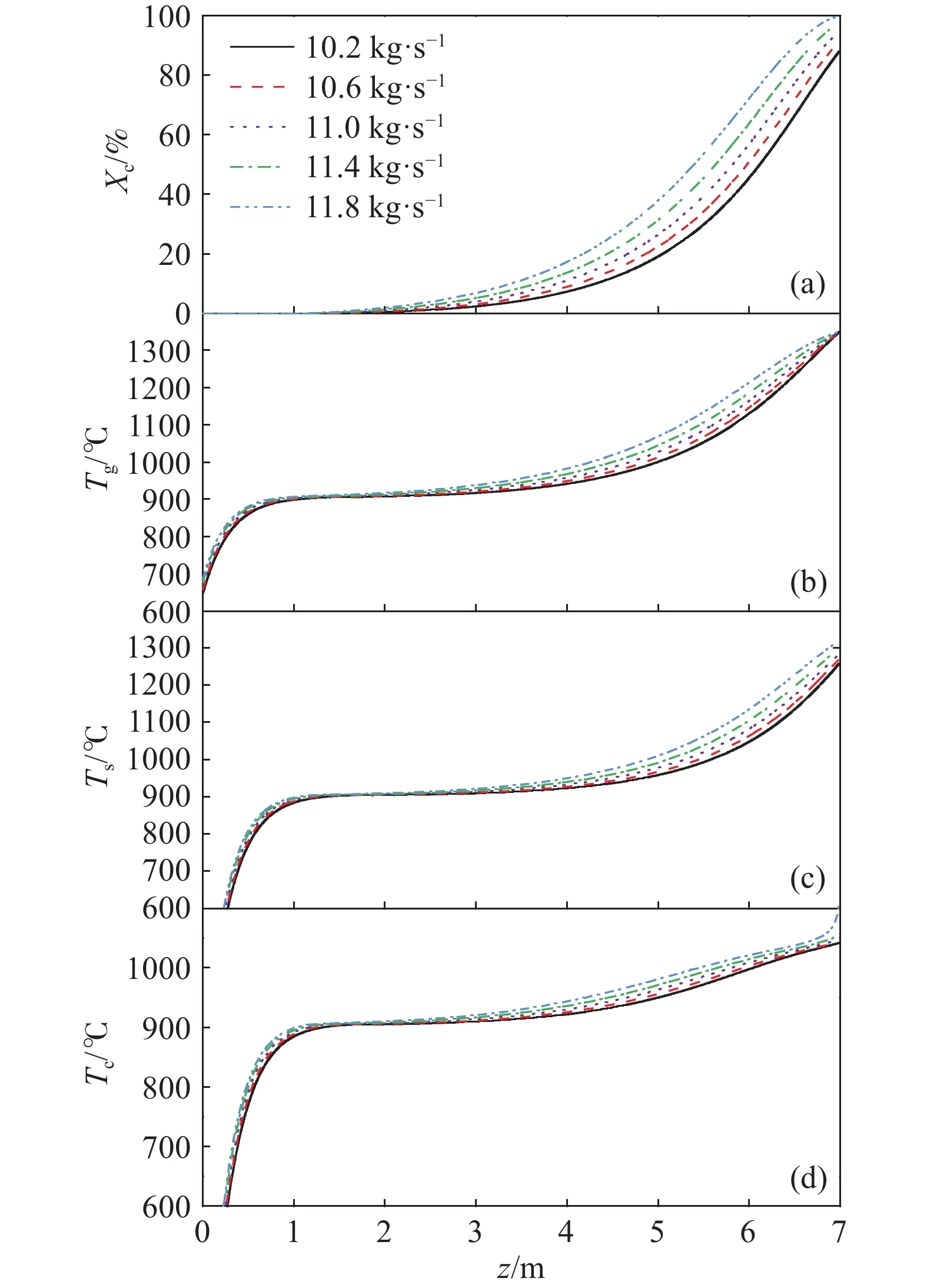
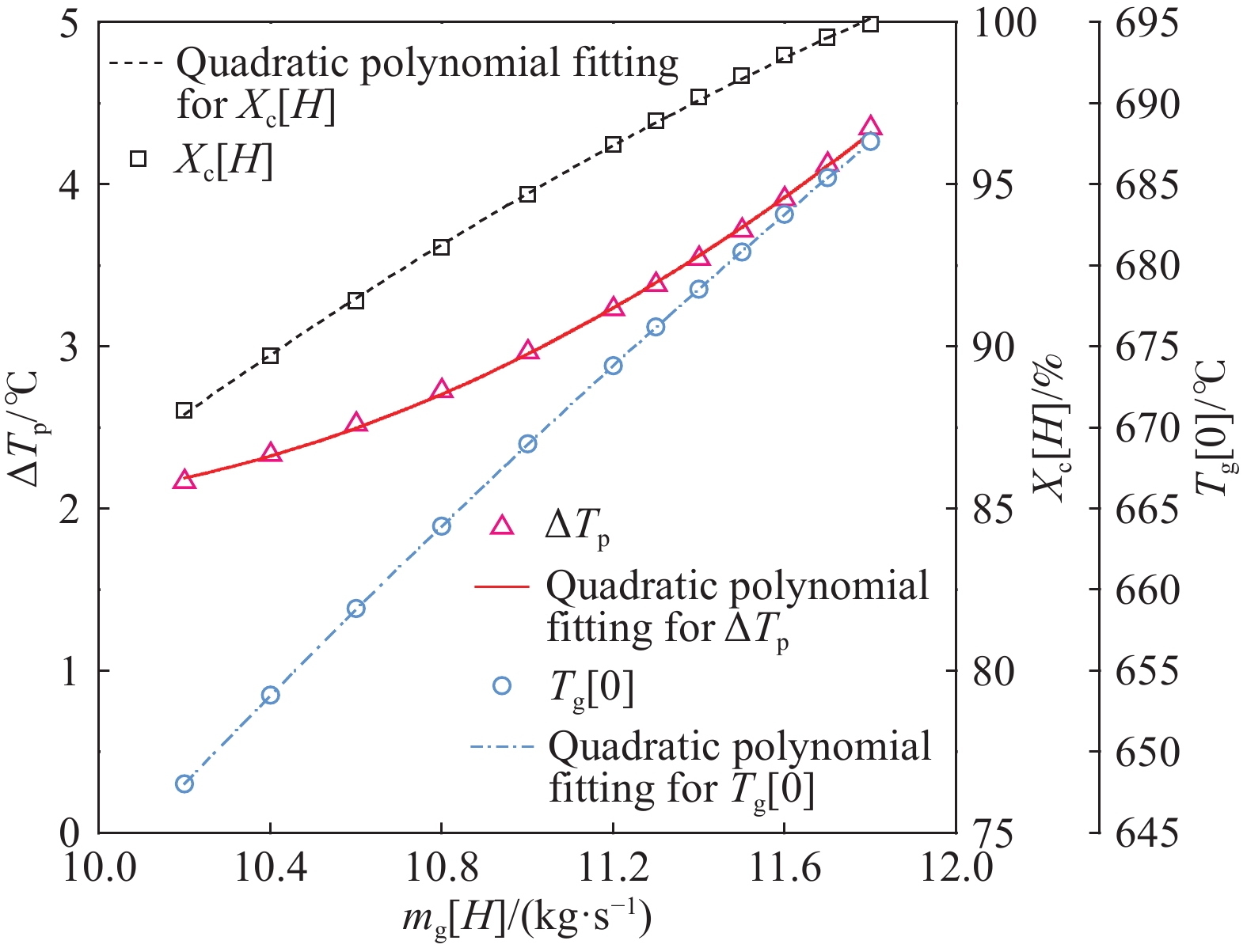
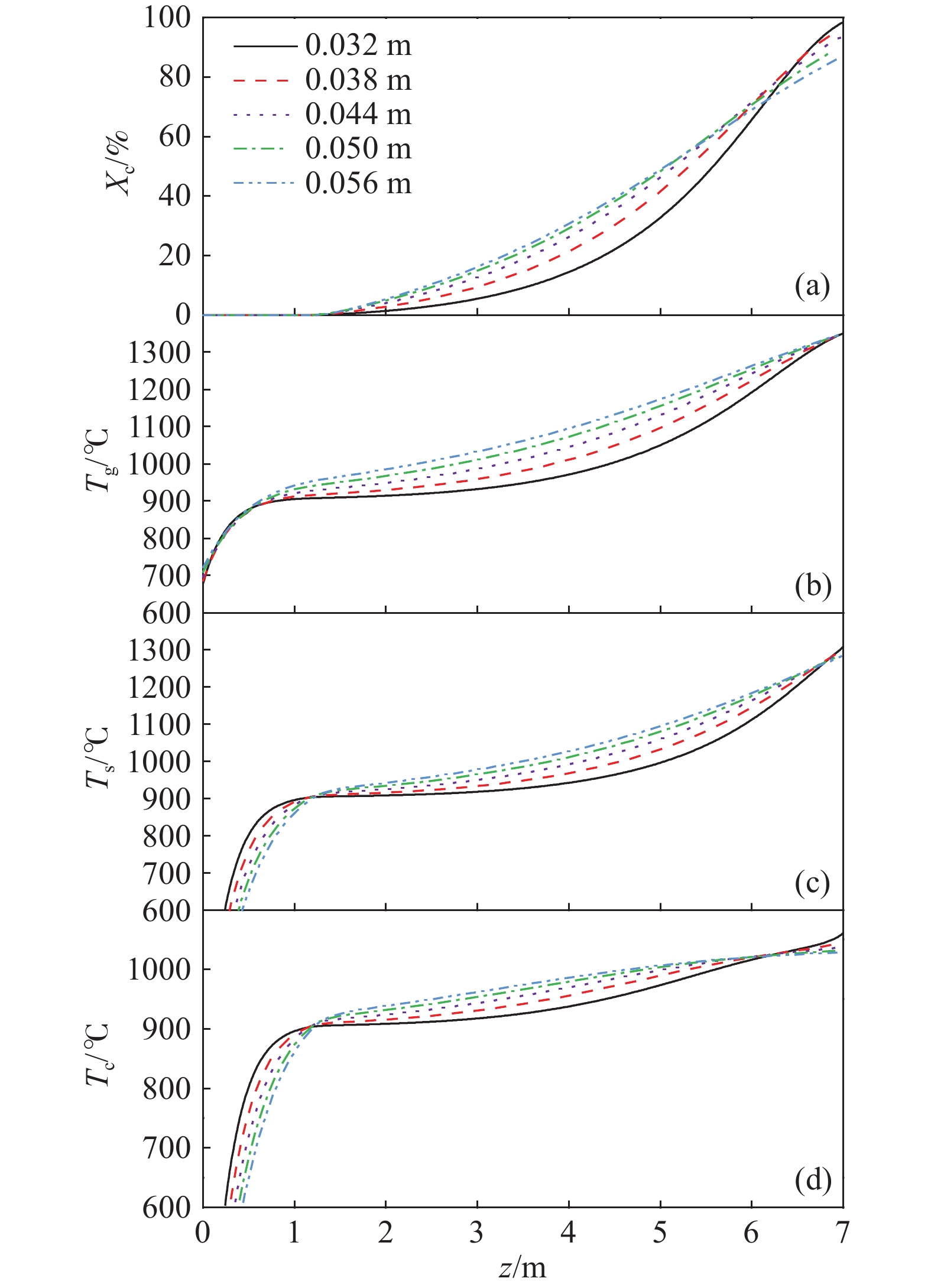
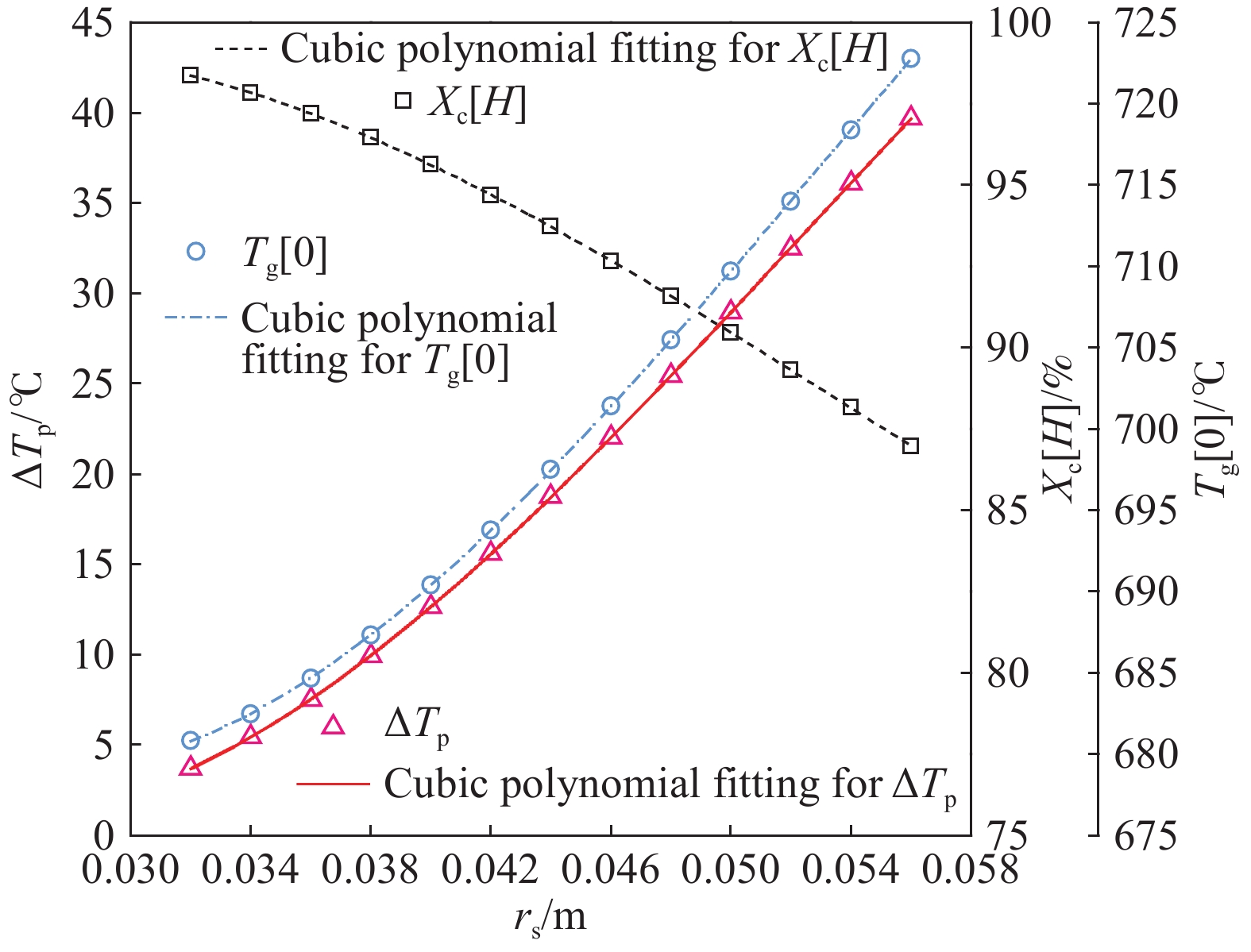
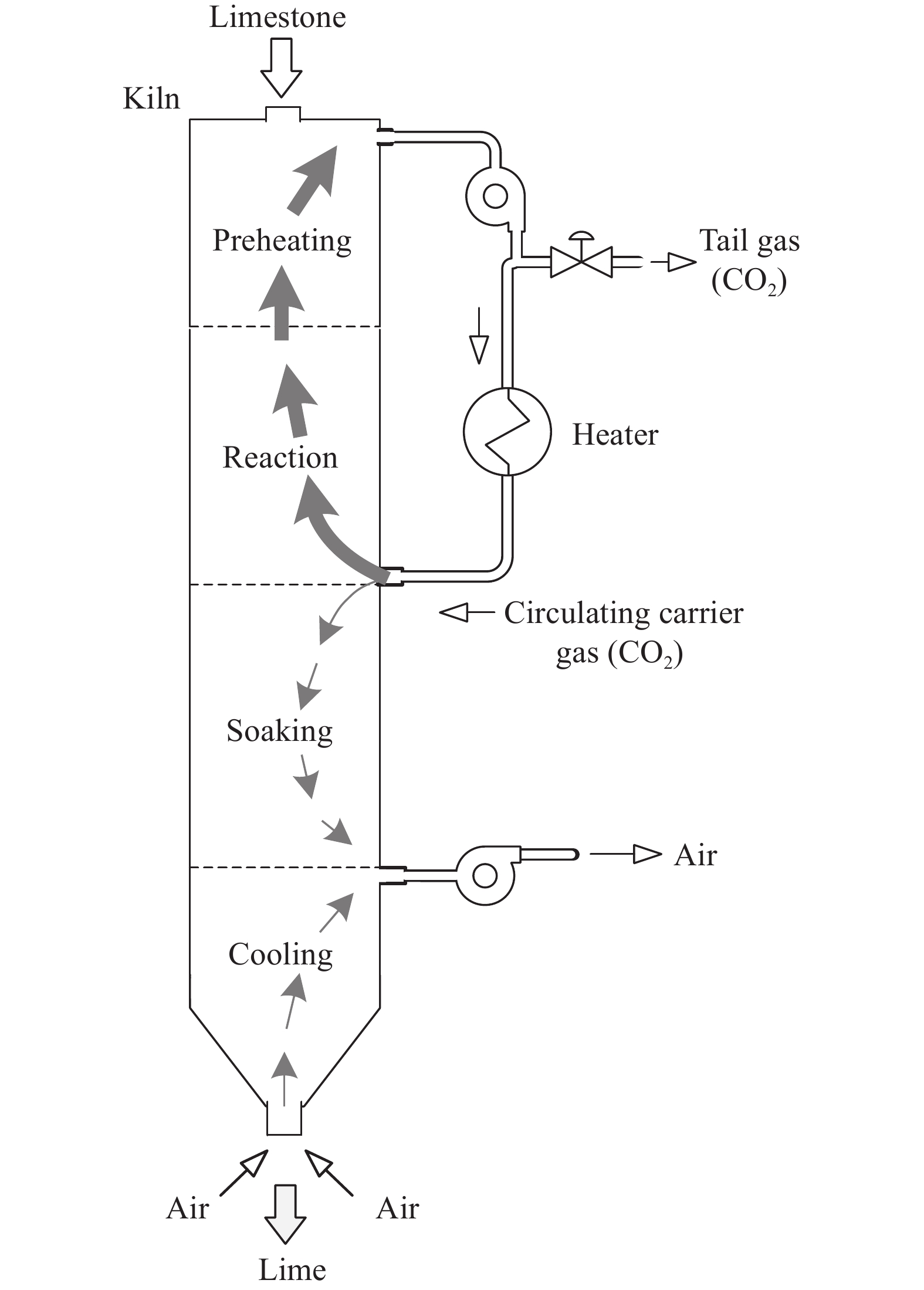
摘要: 常規石灰煅燒工藝中燃料在煅燒窯內燃燒,石灰石分解所釋放的二氧化碳(CO2)與煙氣混合,CO2捕集需進行氣體分離。而采用CO2作為循環載氣加熱石灰石料塊的新型煅燒過程,可避免上述混合問題,從而實現直接捕集石灰石分解產生的CO2。基于CO2加熱的新型煅燒過程與常規工藝煅燒過程有較大不同,為深入理解新型煅燒過程并對其進行準確設計和有效優化,建立了基于CO2加熱的石灰煅燒過程的數學模型。基于模型對一臺產量為200 t·d?1的煅燒窯進行了模擬計算,獲得了氣固溫差、氣相流量、氣相溫度、料塊表面溫度、反應界面溫度和轉化率等關鍵參數在煅燒窯中的分布情況,并分析了進氣溫度、進氣流量和料塊半徑三個工況參數對煅燒過程的影響。Abstract: Lime is an important industrial raw material widely used in iron- and steel-making, flue gas desulfurization, construction, and papermaking industries. Lime is generally obtained via calcining limestone in a kiln, i.e., limestone is heated and decomposed to generate lime and carbon dioxide (CO2). In the conventional lime calcination, the CO2 released by the limestone decomposition is mixed with the flue gas because the fuel is burned in the shaft kiln, requiring gas separation for CO2 capture. The new lime calcination process using CO2 as a circulating carrier gas to heat limestone particles can avoid the above mixing problem, thereby directly capturing the CO2 generated by limestone decomposition, which is expected to reduce carbon emissions from lime production by approximately 70%. However, the new calcination process based on CO2 heating is quite different from the conventional calcination process. To understand the new calcination process and accurately design and optimize it, a mathematical model of the lime calcination process based on CO2 heating was established. Based on the model, a shaft kiln with a capacity of 200 t·d?1 was simulated and calculated. In addition, profiles of key parameters such as the gas-solid temperature difference, gas flow rate, gas temperature, particle surface temperature, reacting interface temperature, and conversion ratio in the shaft kiln were obtained. Besides, the three operating parameters (feed gas temperature, feed gas flow rate, and radius of the feeding limestone particle) on the calcination were analyzed. The following observations were made: (1) the lower the feed gas temperature, the lower are the final conversion ratio, pinch temperature difference, and tail gas temperature of the kiln. In addition, the changing trend of the final conversion ratio and pinch temperature difference conforms to a quadratic polynomial law, and the changing trend of the tail gas temperature conforms to a linear law. (2) The lower the feed gas flow rate, the lower are the final conversion ratio, pinch temperature difference, and tail gas temperature of the kiln. Moreover, the changing trend of each parameter conforms to a quadratic polynomial law. (3) Finally, the larger the radius of the feeding limestone particle, the lower is the final conversion ratio of the kiln, the higher is the tail gas temperature, and the greater is the pinch temperature difference. The changing trends of various parameters conform to cubic polynomial laws. Compared with the feed gas temperature and the feed gas flow rate, the radius of the feeding limestone particle has a greater impact on the pinch temperature difference and the tail gas temperature when the final conversion ratio changes in the same range.
-
Key words:
- lime /
- carbon dioxide /
- calcination /
- kiln /
- numerical simulation
-
表 1 模型計算所需的參數
Table 1. Parameters for model calculations
Parameter Value Parameter Value A/m2 4.91 $ {\sigma _0}/\left( {{\text{kW}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{ - 2}} \cdot {{\text{K}}^{ - 4}}} \right) $ 5.67×10?11 H/m 7 $ {\varepsilon _{\text{s}}} $ 0.8 $ {m_{\text{L}}} $/(kg?s?1) 3.991 ${{\Delta } }{h_{\text{R} } }/\left( { {\text{kJ} } \cdot {\text{mo} }{ {\text{l} }^{ - 1} } } \right)$ 165 $ {r_{\text{s}}} $/m 0.032 $ {D_{\text{e}}}/\left( {{{\text{m}}^2} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}} \right) $ 2.16×10?6 $ {P_g} $/Pa 101325 $ {\rho _{\text{L}}}/\left( {{\text{kg}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}} \right) $ 2700 $ \varepsilon $ 0.4 $ {\rho _Q}/\left( {{\text{kg}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}} \right) $ 1512 $ R/\left( {{\text{J}} \cdot {\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}} \cdot {{\text{K}}^{ - 1}}} \right) $ 8.314 表 2 模型的邊界條件
Table 2. Boundary conditions of the model
Parameter Specification Unit Value $ {m_g}[H] $ $ z = H $, the feed gas flow rate $ {\text{kg}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}} $ 11.50 $ {T_g}[H] $ $ z = H $, the feed gas temperature $ {\text{K}} $ 1623 $ {P_{\text{c}}}[0] $ $ z = 0 $, the initial reaction pressure $ {\text{Pa}} $ 101325 $ {r_{\text{c}}}[0] $ $ z = 0 $, the initial reaction radius m 0.032 $ {T_{\text{c}}}[0] $ $ z = 0 $, the initial reaction temperature $ {\text{K}} $ 300 $ {T_{\text{s}}}[0] $ $ z = 0 $, the surface temperature of the particle $ {\text{K}} $ 300 久色视频表 3 模型的主要計算結果
Table 3. Major results of model calculations
Parameter Specification Unit Value $ {m_g}[0] $ $ z = 0 $, the tail gas flow rate $ {\text{kg}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}} $ 13.20 $ {T_g}[0] $ $ z = 0 $, the tail gas temperature $ {\text{K}} $ 940.5 $ {X_{\text{c}}}[H] $ $ z = H $, the final conversion ratio % 98.50 $ \Delta {T_{\text{p}}} $ $ z = {1.35_{}}{\text{m}} $, the pinch temperature difference ℃ 3.71 -
參考文獻
[1] Guo H J. Theory and Technology of Active Lime Production. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2014郭漢杰. 活性石灰生產理論與工藝. 北京: 化學工業出版社, 2014 [2] Rong W J, Li B K, Qi F S, et al. Energy and exergy analysis of an annular shaft kiln with opposite burners. Appl Therm Eng, 2017, 119: 629 doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.03.090 [3] Hallak B, Herz F, Specht E, et al. Simulation of limestone calcination in normal shaft kilns-mathematical model. ZKG Int, 2015, 68(9): 66 [4] An R, Yu B, Li R, et al. Potential of energy savings and CO2 emission reduction in China’s iron and steel industry. Appl Energy, 2018, 226: 862 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.06.044 [5] Jiang J J, Dong K, Zhu R, et al. Carbon dioxide green and clean steelmaking technology and its application. Chin J Eng, https://doi.org/10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2021.09.23.002姜娟娟, 董凱, 朱榮, 等. 二氧化碳綠色潔凈煉鋼技術及應用. 工程科學學報.https://doi.org/10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2021.09.23.002 [6] Shan Y L, Liu Z, Guan D B. CO2 emissions from China’s lime industry. Appl Energy, 2016, 166: 245 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.04.091 [7] National Bureau of Statistic. China Statistical Year Book. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2019國家統計局. 中國統計年鑒. 中國統計出版社, 2019 [8] Gutiérrez A S, Martínez J B C, Vandecasteele C. Energy and exergy assessments of a lime shaft kiln. Appl Therm Eng, 2013, 51(1-2): 273 doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2012.07.013 [9] Wang Y Y, Zhong X J. CO2 emissions and influencing factors in China’s lime industry. J Subtrop Resour Environ, 2018, 13(2): 7 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7105.2018.02.003王瑩瑩, 鐘小劍. 中國2004—2015年間石灰工業的CO2排放. 亞熱帶資源與環境學報, 2018, 13(2):7 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7105.2018.02.003 [10] Chu J M, Gao S L. Manual of Metallurgical Lime Production Technology. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2009初建民, 高士林. 冶金石灰生產技術手冊. 北京: 冶金工業出版社, 2009 [11] Hallak B, Herz F, Specht E, et al. Simulation of limestone calcination in normal shaft kilns–Part 2: Influence of process parameters. ZKG Int, 2015, 68(10): 46 [12] Hallak B, Specht E, Herz F, et al. Influence of particle size distribution on the limestone decomposition in single shaft kilns. Energy Procedia, 2017, 120: 604 doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.07.192 [13] Senega?nik A, Oman J, ?irok B. Annular shaft kiln for lime burning with kiln gas recirculation. Appl Therm Eng, 2008, 28(7): 785 doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2007.04.015 [14] Zhou N J, Yi Z M, Zhou P, et al. Numerical simulation of the processes in lime furnace. J Central South Univ Nat Sci, 2000, 31(5): 422周乃君, 易正明, 周萍, 等. 石灰爐爐內過程數值仿真. 中南工業大學學報(自然科學版), 2000, 31(5):422 [15] Shagapov V S, Burkin M V, Voronin A V, et al. Calculation of limestone burning in a coke-fired kiln. Theor Found Chem Eng, 2004, 38(4): 440 doi: 10.1023/B:TFCE.0000036974.32157.89 [16] Bes A. Dynamic Process Simulation of Limestone Calcination in Normal Shaft Kilns [Dissertation]. Magdeburg: Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg, 2006 [17] Marias F, Bruyères B. Modelling of a biomass fired furnace for production of lime. Chem Eng Sci, 2009, 64(15): 3417 doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2009.04.022 [18] Do D H, Specht E. Numerical simulation of heat and mass transfer of limestone decomposition in normal shaft kiln // Proceedings of ASME/JSME 2011 8th Thermal Engineering Joint Conference. Honolulu, 2011: T10060 [19] Gutiérrez A S, Vandecasteele C. Exergy-based indicators to evaluate the possibilities to reduce fuel consumption in lime production. Energy, 2011, 36(5): 2820 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2011.02.023 [20] Cui C, Chen Y F, Wang Y B. Numerical simulation of temperature field in gas burning shaft lime kiln. J Univ Sci Technol Liaoning, 2014, 37(3): 247 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1048.2014.03.006崔春, 陳永范, 王云波. 氣燒石灰豎窯內溫度場的數值模擬. 遼寧科技大學學報, 2014, 37(3):247 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1048.2014.03.006 [21] Do D H. Simulation of Lime Calcination in Normal Shaft a Parallel Flow Regenerative Kilns [Dissertation]. Magdeburg: Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg, 2012 [22] El-Fakharany M K M. Process Simulation of Lime Calcination in Mixed Feed Shaft Kilns[Dissertation]. Magdeburg: Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg, 2012 [23] Senega?nik A, Oman J, ?irok B. Analysis of calcination parameters and the temperature profile in an annular shaft kiln. Part 1: Theoretical survey. Appl Therm Eng, 2007, 27(8-9): 1467 doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2006.10.001 [24] Liu G H, Cui G M, Xie B, et al. Numerical simulation study on the calcination process of a dual-chamber lime kiln with parallel heat storage. J Eng Therm Energy Power, 2019, 34(6): 100劉國輝, 崔國民, 謝斌, 等. 并流蓄熱式雙膛石灰窯煅燒過程數值模擬研究. 熱能動力工程, 2019, 34(6):100 [25] Bluhm-Drenhaus T, Simsek E, Wirtz S, et al. A coupled fluid dynamic-discrete element simulation of heat and mass transfer in a lime shaft kiln. Chem Eng Sci, 2010, 65(9): 2821 doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2010.01.015 [26] Krause B, Liedmann B, Wiese J, et al. Coupled three dimensional DEM–CFD simulation of a lime shaft kiln—Calcination, particle movement and gas phase flow field. Chem Eng Sci, 2015, 134: 834 doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2015.06.002 [27] Krause B, Liedmann B, Wiese J, et al. 3D-DEM-CFD simulation of heat and mass transfer, gas combustion and calcination in an intermittent operating lime shaft kiln. Int J Therm Sci, 2017, 117: 121 doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2017.03.017 [28] Iliuta I, Dam-Johansen K, Jensen L S. Mathematical modeling of an in-line low-NOx calciner. Chem Eng Sci, 2002, 57(5): 805 doi: 10.1016/S0009-2509(01)00420-1 [29] Chuan C, Specht E, Kehse G. Influences of the origin and material properties of limestone on its decomposition behaviour in shaft kilns. ZKG Int, 2007, 60(1): 51 [30] Zhou J Q. Heat Trasfer. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1999周筠清. 傳熱學. 北京: 冶金工業出版社, 1999 -




 下載:
下載: