-
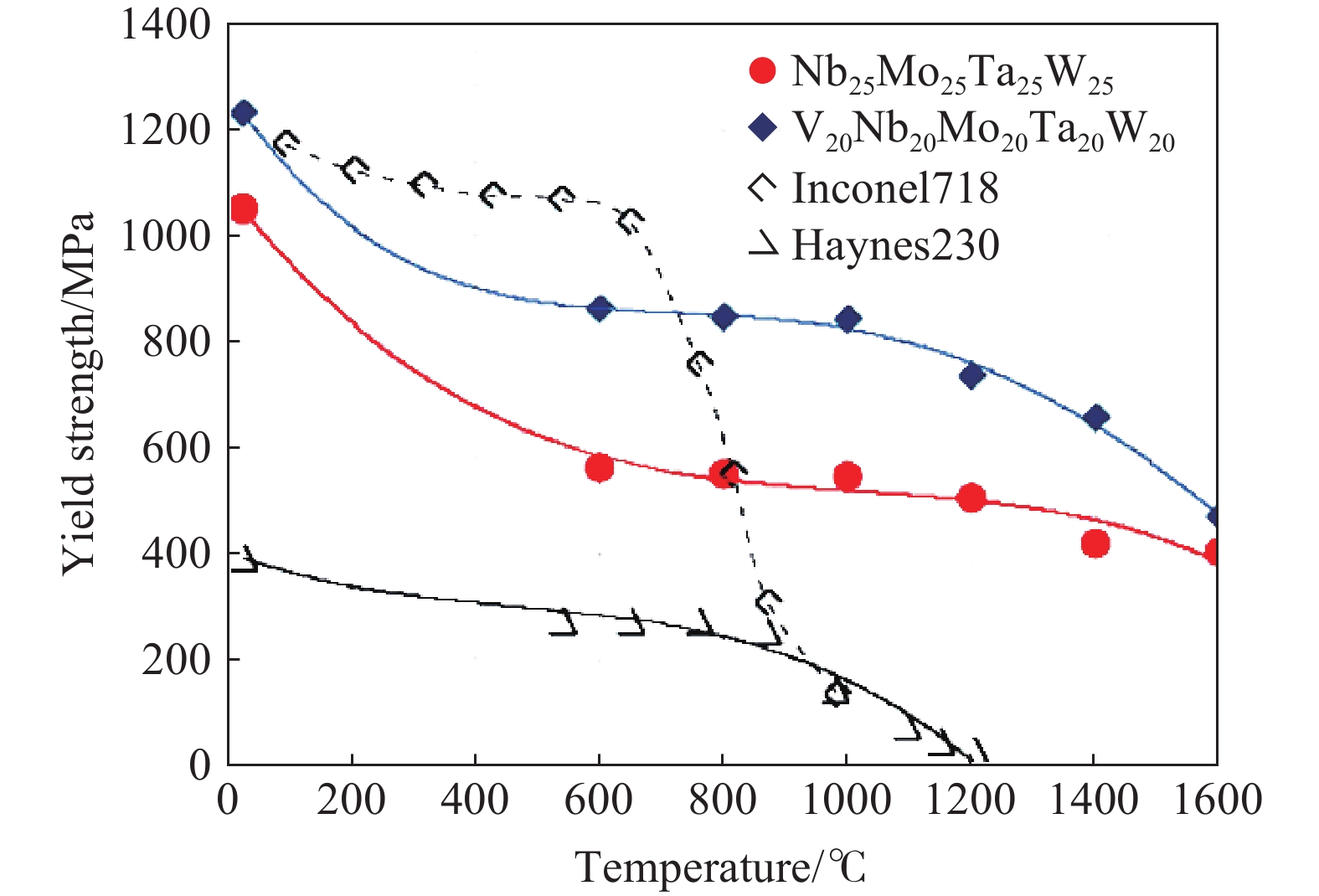
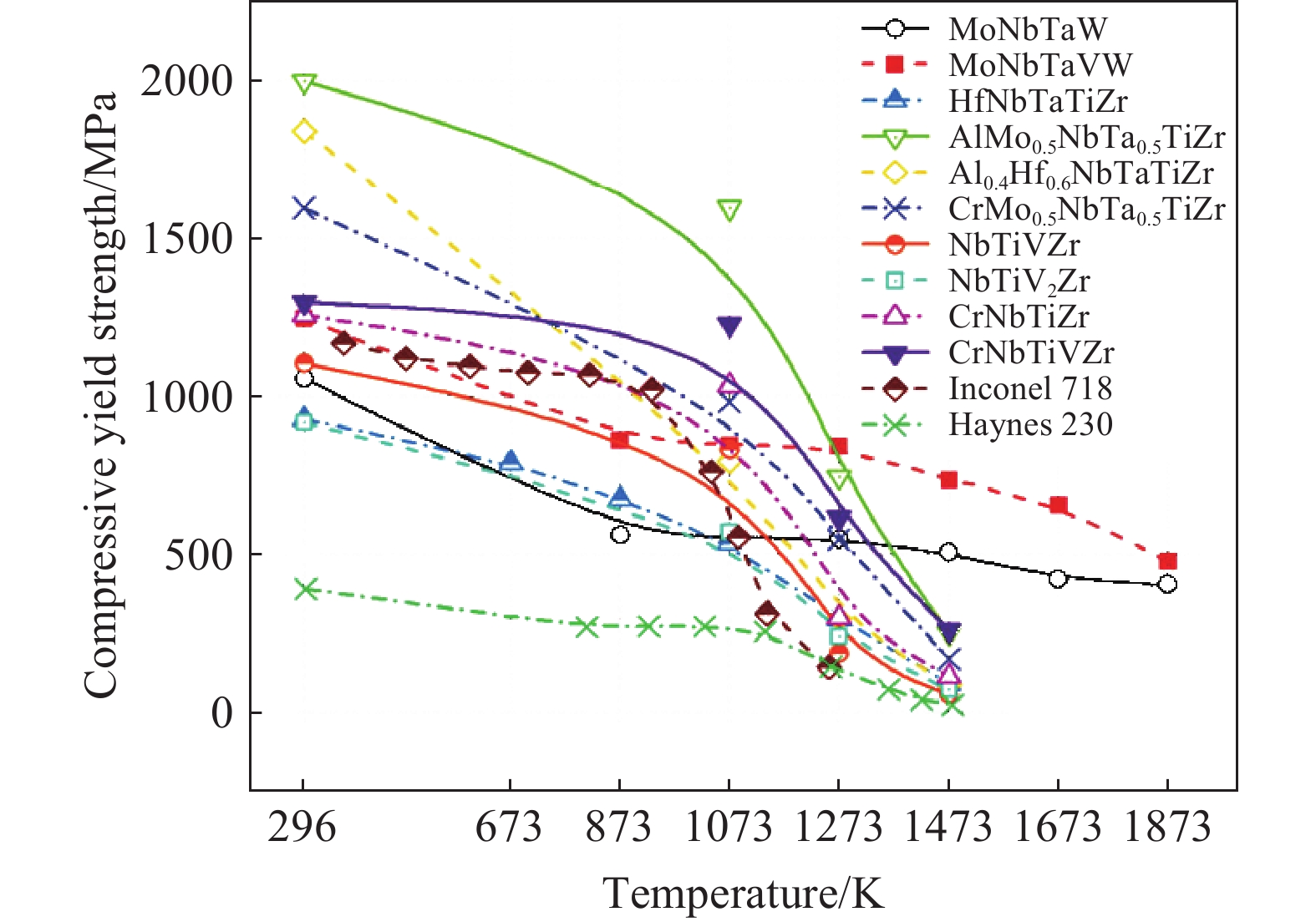
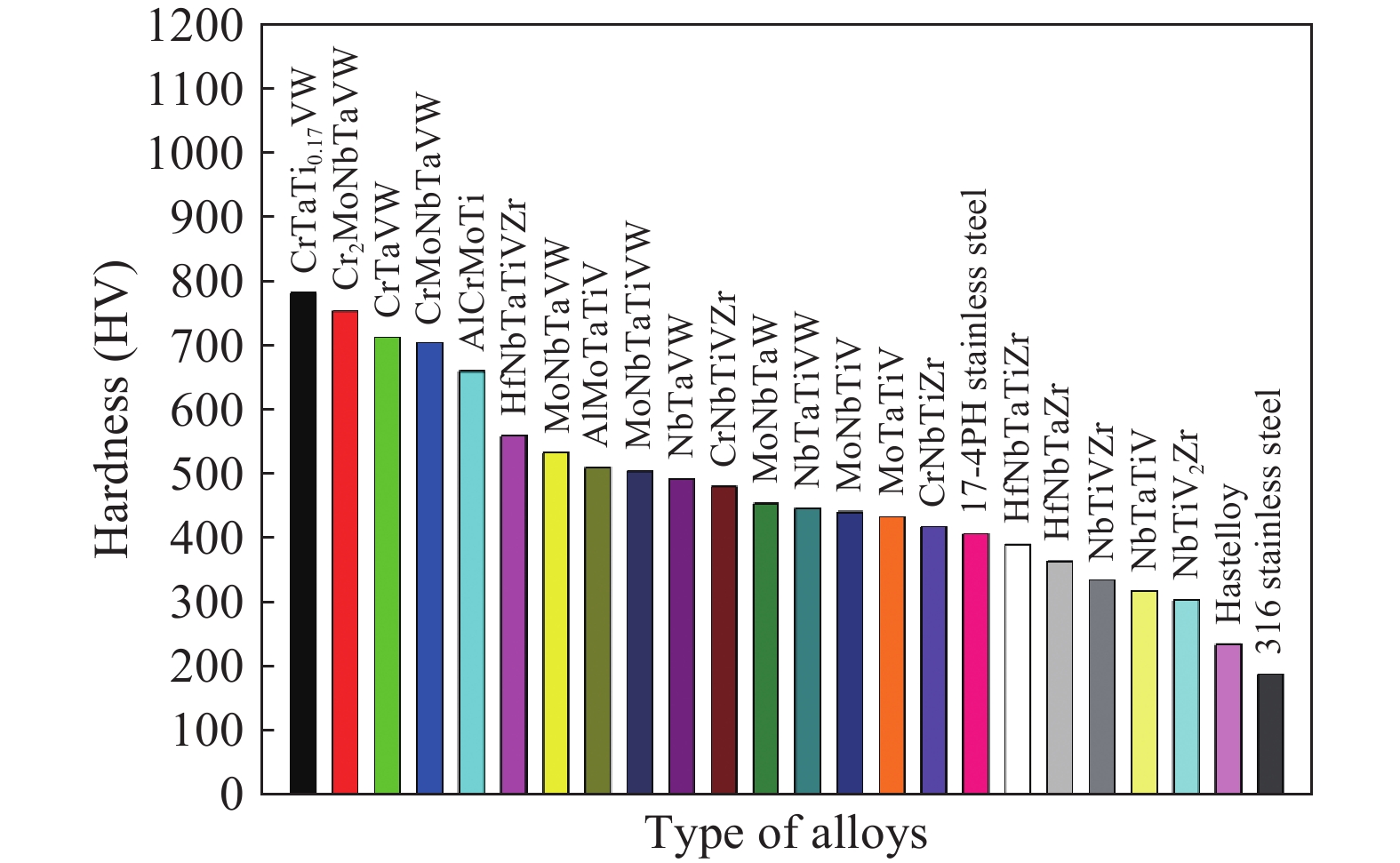
摘要: 從加工方法、微觀結構以及各類性能三方面介紹了難熔高熵合金(Refractory high-entropy alloys,RHEAs),最后對難熔高熵合金的發展和未來進行了展望。以MoNbTaVW為代表的難熔高熵合金在高溫下表現出優于傳統鎳基高溫合金的壓縮屈服強度,且屈服強度隨溫度的變化更加緩慢,高溫力學性能優異;以MoNbTaVW、MoNbTaTiZr、HfNbTiZr等為代表的難熔高熵合金,與商用高溫合金、難熔金屬、難熔合金以及工具鋼相比,展現出更優的耐磨性能。以W38Ta36Cr15V11合金為代表的難熔高熵合金在輻照后,除了析出小顆粒第二相外,不存在位錯環缺陷結構,抗輻照性能優異。提出了難熔高熵合金未來發展的兩大方向:建立高通量的實驗和計算方法繼續探索更多的難熔高熵合金組成和結構模型;探索多場耦合環境下難熔高熵合金的服役行為。Abstract: Alloying is one of the main ways to achieve desirable properties in materials. The design concept is based on one or two metal elements, supplemented with multiple trace elements to achieve altered or optimized properties. With the advancement in technology, the traditional alloy has evolved from simple to complex compositions, thus improving their properties and promoting the progress of civilization. High-entropy alloys (HEAs) are a new type of multi-master alloys that are popular in the recent two decades. Unlike conventional alloys, HEAs comprise multiple alloying elements according to the isoatomic or non-isoatomic ratios and have several unique properties, such as high strength and hardness, excellent wear and corrosion resistance, thermal stability, and irradiation resistance. Refractory high-entropy alloys (RHEAs), HEAs made of refractory metals, have attracted great attention because of their excellent high-temperature mechanical properties. This paper discusses RHEAs from three aspects: processing methods, microstructure, and properties. Finally, this work presents the development and future prospects of RHEAs. RHEAs represented by MoNbTaVW alloys show better compressive yield strengths at high temperatures and a slower change of yield strength with temperature than traditional Ni-based high-temperature alloys. Compared with commercial superalloys, refractory metals, refractory alloys, and tool steels, RHEAs, such as MoNbTaVW, MoNbTaTiZr, and HfNbTiZr, show excellent wear resistance. RHEAs represented by W38Ta36Cr15V11 have no dislocation ring defect structure and excellent anti-irradiation performance after irradiation, except for the precipitation of small particles in the second phase. In this paper, two directions of future development of RHEAs were proposed: (1) establishing high-throughput experimental and computational methods to continue exploring composition and structural models of RHEAs and (2) exploring the service behavior of RHEAs in a multi-field coupled environment.
-
Key words:
- refractory high entropy alloys /
- processing methods /
- microstructure /
- phase composition /
- properties
-
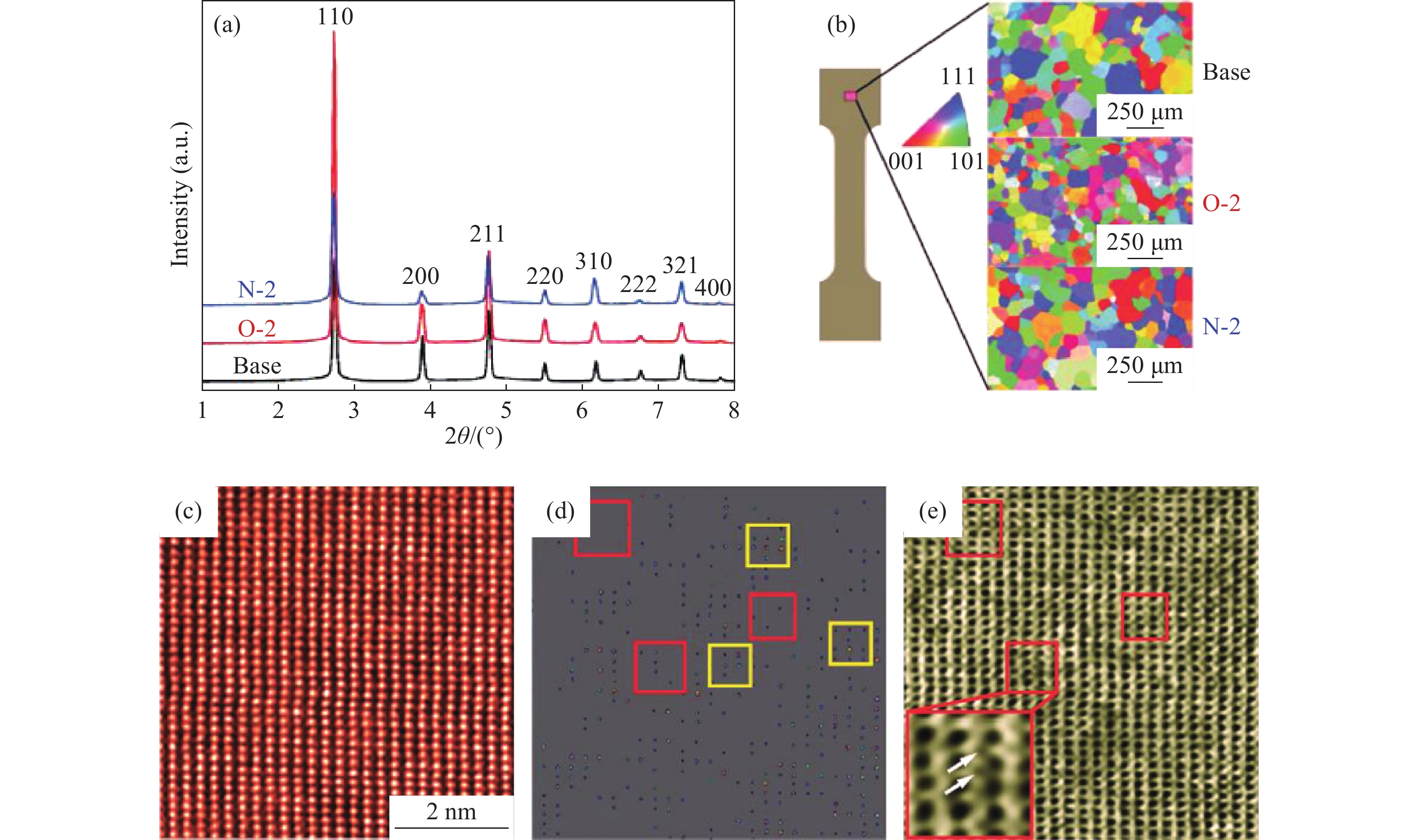
圖 9 鑄態TiZrHfNb、(TiZrHfNb)98O2和(TiZrHfNb)98N2的高能同步加速器X射線衍射圖(a)和電子背散射衍射圖(b),(TiZrHfNb)98O2沿[011]軸的球差矯正掃描電子顯微鏡高角度環形暗場圖(c)和原子序數對比度圖(d),以及相應的球差矯正掃描電子顯微鏡環形亮場圖(e),(e)中的插圖是有序間隙原子復合體的放大視圖[43]
Figure 9. Synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction (a) and the corresponding electron back-scattering diffraction patterns (b) of the as-cast TiZrHfNb, (TiZrHfNb)98O2 and (TiZrHfNb)98N2; scanning transmission electron microscope high-angle annular dark field images (c) for [011] axis, Z-contrast of the scanning transmission electron microscope high-angle annular dark field image (d) and the corresponding scanning transmission electron microscope-annular bright field image (e) that reveals the ordered oxygen complexes; the inset in (e) is an enlarged view of the ordered oxygen complexes[43]
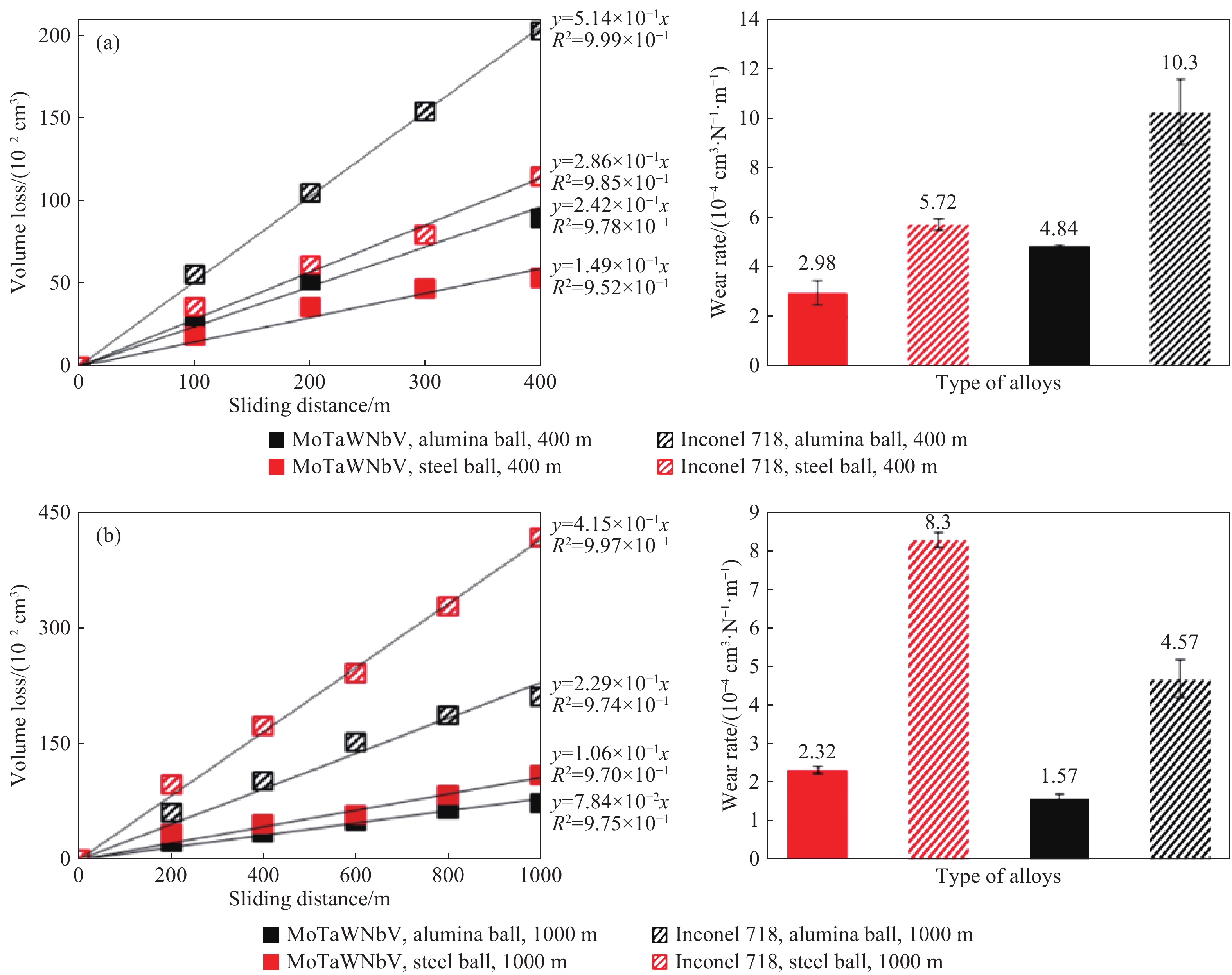
圖 12 不同條件下MoTaWNbV和Inconel 718的體積損失(左)和磨損率(右)的對比圖[55],用鋼球和氧化鋁球進行400 m (a)和1000 m (b)滑動距離測試
Figure 12. Comparative diagrams of the volume loss (left) and the wear rate (right) of MoTaWNbV versus Inconel 718 under different conditions[55],tested with both an alumina and a steel ball for sliding distances of 400 m (a), 1000 m (b)
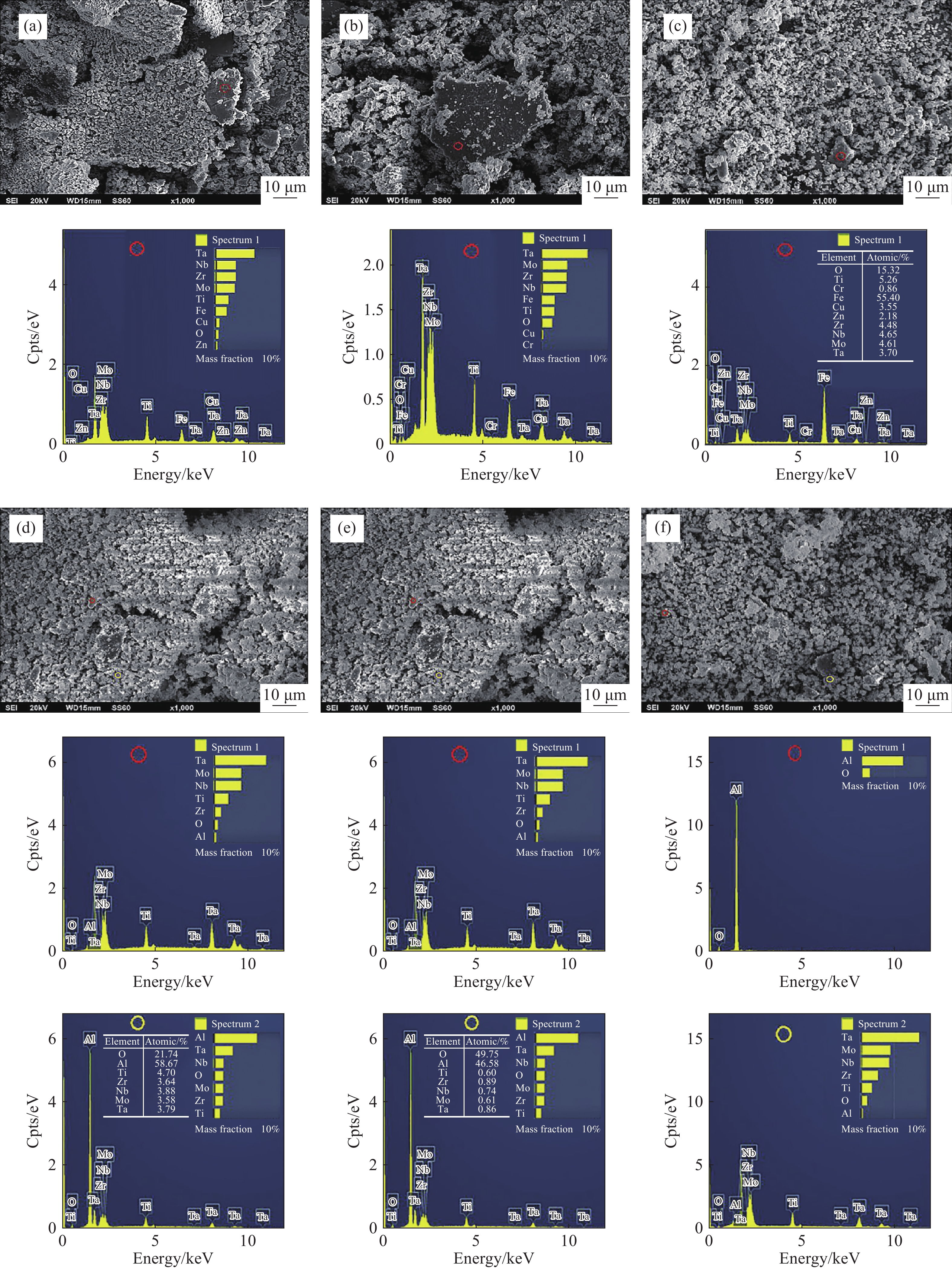
圖 13 MoTaNbZrTi合金磨損表面收集的碎片的掃描電子顯微鏡圖,用鋼球(a, b, c)和氧化鋁球(d, e, f)分別滑動(a和d)400 m;(b和e)1000 m和(c和f)2000 m[57]
Figure 13. Scanning electron microscope images of the debris collected from the worn surface of MoTaNbZrTi tested with a steel ball (a, b, c) and an alumina ball (d, e, f) for the sliding distances of (a and d) 400 m; (b and e) 1000 m; and (c and f) 2000 m[57]
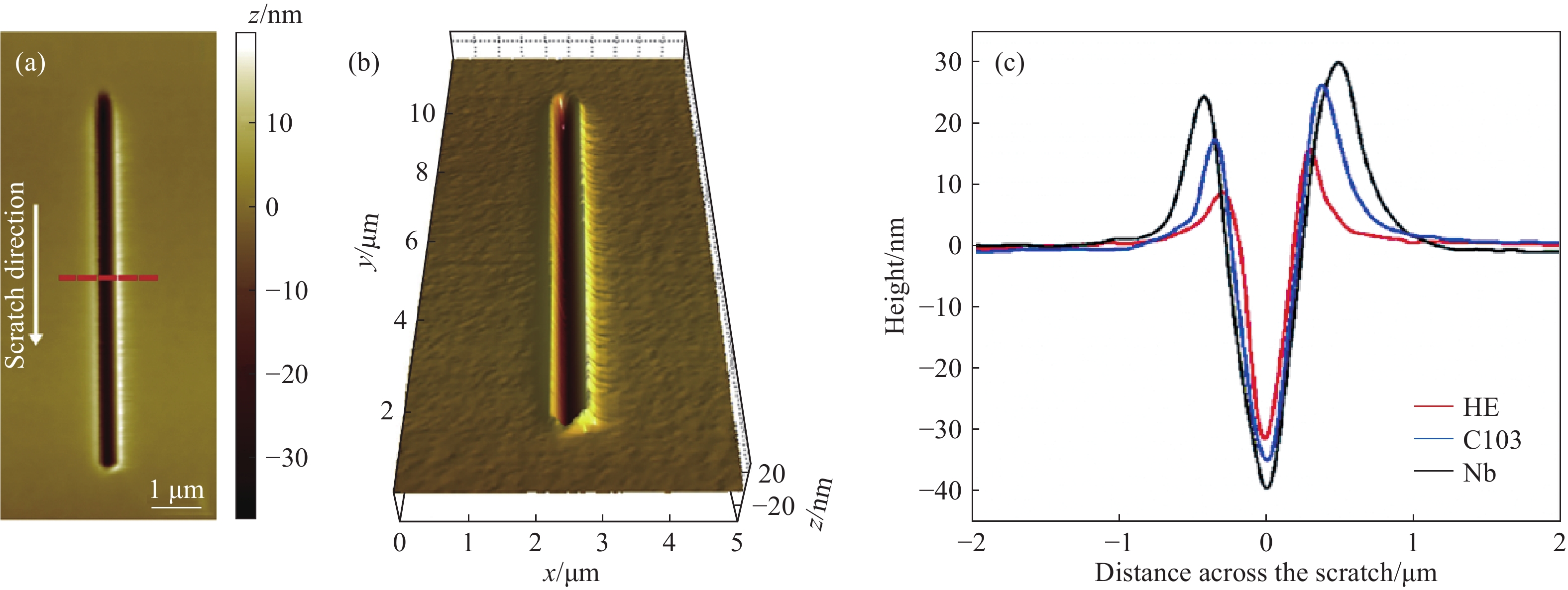
圖 14 HfNbTiZr合金在500 mN恒定載荷下劃痕形貌的掃描探針顯微鏡圖(a)和對應的3D圖(b),純Nb和C103以及(a)中所示的橫截面輪廓(c)[58]
Figure 14. Scanning probe microscopy image showing the topography of the scratch track of the HfNbTiZr alloy under a constant load testing at 500 mN (a), the corresponding 3D view (b), and cross-section profiles (c) as indicated in the pure Nb and C103 alloy as well as (a)[58]
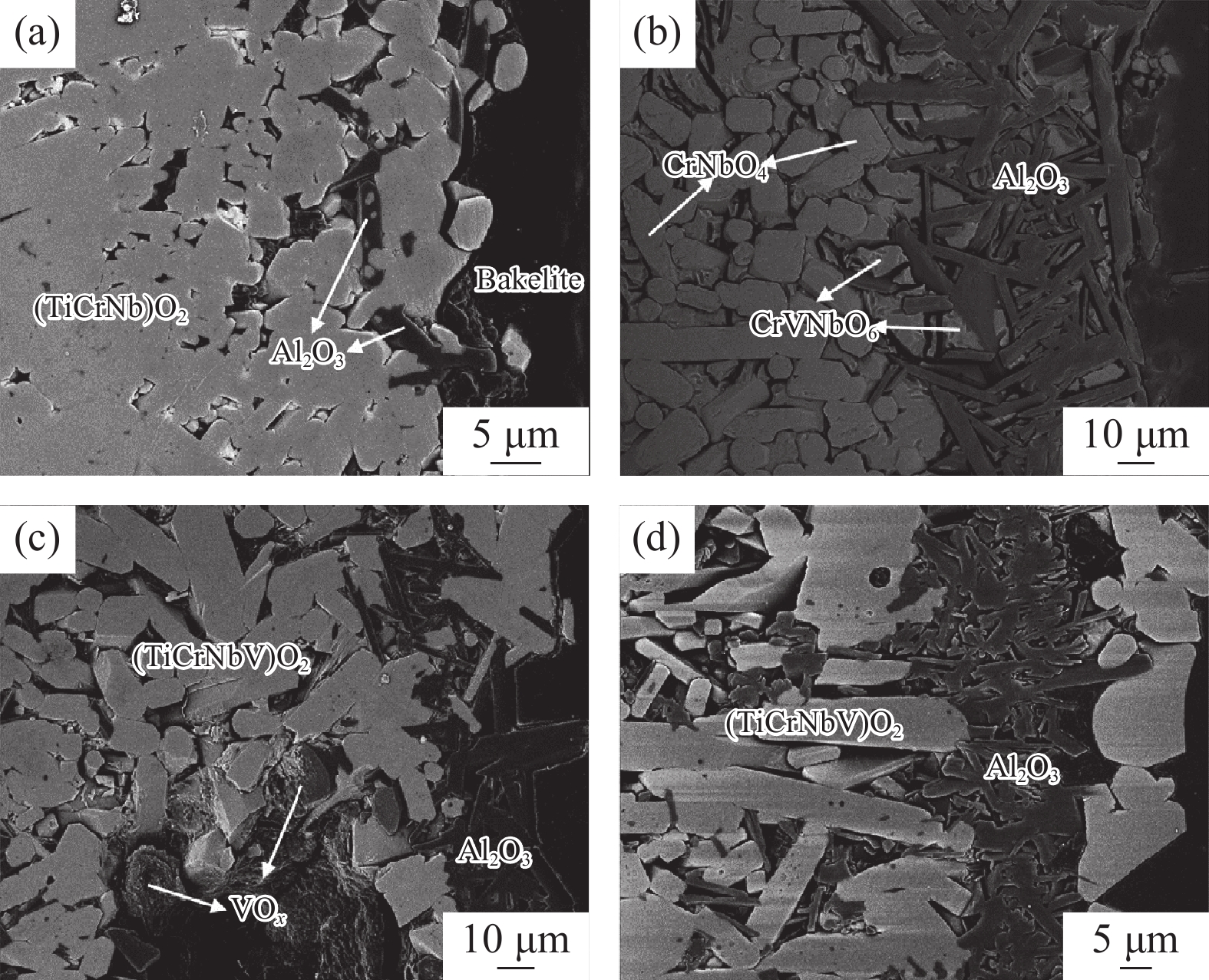
圖 15 在1300℃下氧化10 h的RHEAs外部氧化膜橫截面的背散射電子圖像[21]。(a)NbCrMoTiAl0.5;(b)NbCrMoVAl0.5;(c)NbCrMoTiVAl0.5;(d)NbCrMoTiVAl0.5Si0.3
Figure 15. Backscattered electron microscopy images showing the cross sections of the outer oxide scales of the RHEAs oxidized at 1300 ℃ for 10 h[21]: (a) NbCrMoTiAl0.5; (b) NbCrMoVAl0.5; (c) NbCrMoTiVAl0.5; (d) NbCrMoTiVAl0.5Si0.3
久色视频表 1 近幾年難熔高熵合金的結構特征及制備工藝
Table 1. Structural characteristics and preparation technology of refractory high-entropy alloys in recent years
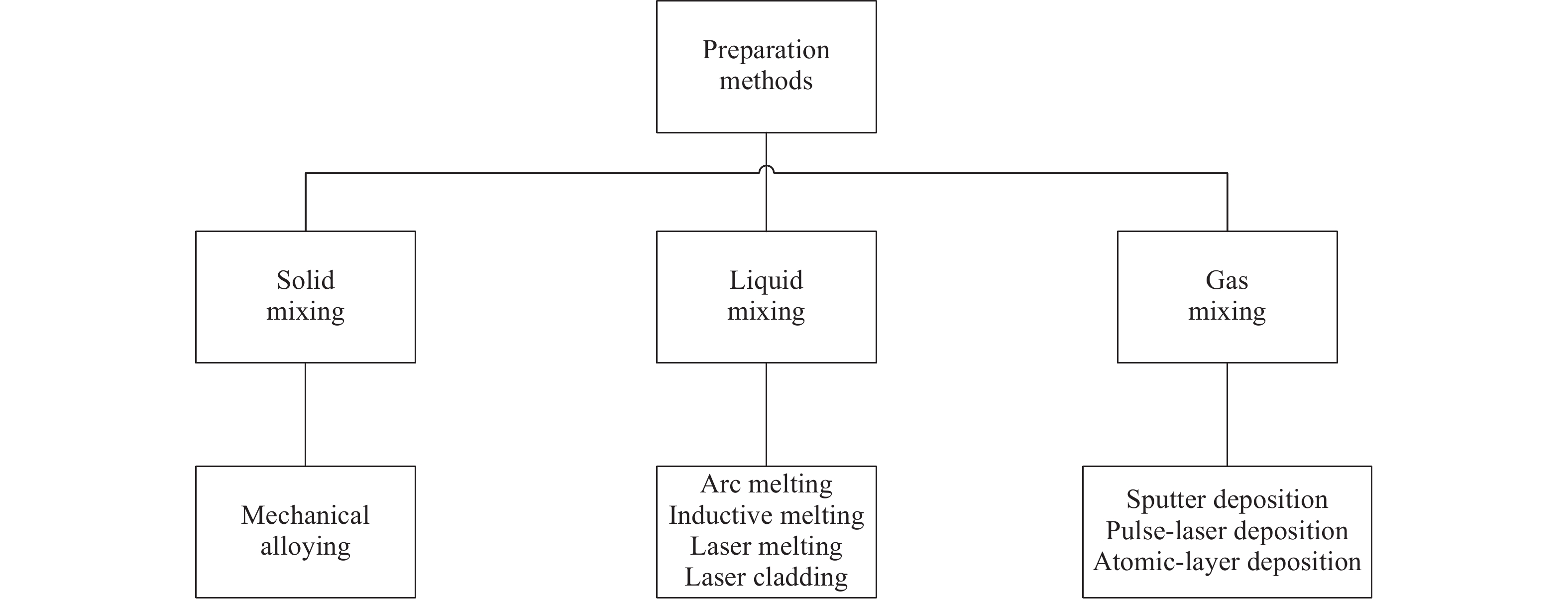
Phase structure Elemental composition Preparation technology BCC WMoNbTa[11] As-cast WMoNbTaV[11] As-cast TaNbHfZrTi[14-15] Hot isostatic pressing NbTiVTa[16] As-cast NbTiVTaAl0.25[16] As-cast NbTiVTaAl0.5[16] As-cast NbTiVTaAl[16] As-cast TiZrNbMoVx(x=0~3)[17] As-cast NbTiVZr[18-19] Hot isostatic pressing HfNbTiZr[20] Annealed NbCrMoTiAl0.5[21] As-cast NbCrMoVAl0.5[21] As-cast NbCrMoTiVAl0.5[21] As-cast AlNb1.5Ta0.5Ti1.5Zr0.5[22] Hot isostatic pressing Al0.3NbTa0.8Ti1.4V0.2Zr1.3[22] Hot isostatic pressing Al0.4Hf0.6NbTaTiZr[22-23] Hot isostatic pressing AlNbTiV[24] Annealed HfMoTaTiZr[25] As-cast HfMoNbTaTiZr[25] As-cast TaNbHfZr[26] As-cast NbMoCrTiAl[27] Mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering WMoNbTa[5] Mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering WMoNbTaV[5] Mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering MoNbTaTiV[28] As-cast MoNbTaTiW[29] As-cast HfMoTiWZr[30] As-cast AlCrMoTi[31] As-cast AlMoNbTi[31] As-cast BCC+Laves CrNbTiZr[18-19] Hot isostatic pressing CrNbTiVZr[18-19] Hot isostatic pressing TiZrHfNbV[32] Annealed TiZr0.5NbCr0.5[33] As-cast TiZr0.5NbCr0.5Mo[33] As-cast TiZr0.5NbCr0.5V[33] As-cast AlCrMoTiW[34] As-cast AlCrMoTaTi[35] As-cast BCC+B2 AlMo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr[36-37] Hot isostatic pressing Al0.5Mo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr[38] Hot isostatic pressing Al0.25NbTaTiZr[38] Hot isostatic pressing B2 AlNbTa0.25TiZr0.25[38] Hot isostatic pressing BCC+HCP HfTaTiZr[39] As-cast HfTa0.4TiZr[39] As-cast HfTa0.5TiZr[39] As-cast HfTa0.6TiZr[39] As-cast FCC+L12 W0.5Ni2Co2VMo0.5[40] As-cast W0.5Ni2Co2VCr0.5[40] As-cast W0.5Ni2Co2CrMo0.5[40] As-cast -
參考文獻
[1] Yeh J W, Chen S K, Lin S J, et al. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv Eng Mater, 2004, 6(5): 299 doi: 10.1002/adem.200300567 [2] Yeh J W, Lin S J, Chin T S, et al. Formation of simple crystal structures in Cu?Co?Ni?Cr?Al?Fe?Ti?V alloys with multiprincipal metallic elements. Metall Mater Trans A, 2004, 35(8): 2533 doi: 10.1007/s11661-006-0234-4 [3] Tsai Y L, Wang S F, Bor H Y, et al. Effects of alloy elements on microstructure and creep properties of fine-grained nickel-based superalloys at moderate temperatures. Mater Sci Eng A, 2013, 571: 155 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2013.02.002 [4] Yang X N, Deng W L, Huang X B, et al. Research on preparation methods of high-entropy alloy. Hot Work Technol, 2014, 43(22): 30楊曉寧, 鄧偉林, 黃曉波, 等. 高熵合金制備方法進展. 熱加工工藝, 2014, 43(22):30 [5] Guo W J. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of NbMoTaW(V) High-Entropy Alloy Prepared by Mechanical Alloying [Dissertation]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2016郭文晶. 機械合金化NbMoTaW(V)高熔點高熵合金的組織及其性能[學位論文]. 廣州: 華南理工大學, 2016 [6] Liu Y, Zhang Y, Zhang H, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of refractory HfMo0.5NbTiV0.5 Six high-entropy composites. J Alloys Compd, 2017, 694: 869 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.10.014 [7] He C J, Liu X J, Zhang P, et al. Applications of powder metallurgy technology in high-entropy materials. Chin J Eng, 2019, 41(12): 1501何春靜, 劉雄軍, 張盼, 等. 粉末冶金在高熵材料中的應用. 工程科學學報, 2019, 41(12):1501 [8] Sheng W J, Yang X, Wang C, et al. Nano-crystallization of high-entropy amorphous NbTiAlSiWxNy films prepared by magnetron sputtering. Entropy, 2016, 18(6): 226 doi: 10.3390/e18060226 [9] Xin W, Wang Y J, Wei S C, et al. Research progress of the preparation of high entropy alloy coatings by spraying. Chin J Eng, 2021, 43(2): 170辛蔚, 王玉江, 魏世丞, 等. 熱噴涂制備高熵合金涂層的研究現狀與展望. 工程科學學報, 2021, 43(2):170 [10] Chen Y Y, Duval T, Hung U D, et al. Microstructure and electrochemical properties of high entropy alloys—a comparison with type-304 stainless steel. Corros Sci, 2005, 47(9): 2257 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2004.11.008 [11] Senkov O N, Wilks G B, Scott J M, et al. Mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics, 2011, 19(5): 698 doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2011.01.004 [12] Han Z D, Luan H W, Liu X, et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of TixNbMoTaW refractory high-entropy alloys. Mater Sci Eng A, 2018, 712: 380 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2017.12.004 [13] Yan X H, Li J S, Zhang W R, et al. A brief review of high-entropy films. Mater Chem Phys, 2018, 210: 12 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.07.078 [14] Senkov O N, Scott J M, Senkova S V, et al. Microstructure and room temperature properties of a high-entropy TaNbHfZrTi alloy. J Alloys Compd, 2011, 509(20): 6043 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.02.171 [15] Senkov O N, Scott J M, Senkova S V, et al. Microstructure and elevated temperature properties of a refractory TaNbHfZrTi alloy. J Mater Sci, 2012, 47(9): 4062 doi: 10.1007/s10853-012-6260-2 [16] Yang X, Zhang Y, Liaw P K. Microstructure and compressive properties of NbTiVTaAlx high entropy alloys. Procedia Eng, 2012, 36: 292 doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2012.03.043 [17] Zhang Y, Yang X, Liaw P K. Alloy design and properties optimization of high-entropy alloys. JOM, 2012, 64(7): 830 doi: 10.1007/s11837-012-0366-5 [18] Senkov O N, Senkova S V, Miracle D B, et al. Mechanical properties of low-density, refractory multi-principal element alloys of the Cr?Nb?Ti?V?Zr system. Mater Sci Eng A, 2013, 565: 51 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.12.018 [19] Senkov O N, Senkova S V, Woodward C, et al. Low-density, refractory multi-principal element alloys of the Cr?Nb?Ti?V?Zr system: Microstructure and phase analysis. Acta Mater, 2013, 61(5): 1545 doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2012.11.032 [20] Wu Y D, Cai Y H, Wang T, et al. A refractory Hf25Nb25Ti25Zr25 high-entropy alloy with excellent structural stability and tensile properties. Mater Lett, 2014, 130: 277 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2014.05.134 [21] Liu C M, Wang H M, Zhang S Q, et al. Microstructure and oxidation behavior of new refractory high entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd, 2014, 583: 162 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.08.102 [22] Senkov O N, Woodward C, Miracle D B. Microstructure and properties of aluminum-containing refractory high-entropy alloys. JOM, 2014, 66(10): 2030 doi: 10.1007/s11837-014-1066-0 [23] Senkov O N, Senkova S V, Woodward C. Effect of aluminum on the microstructure and properties of two refractory high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater, 2014, 68: 214 doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2014.01.029 [24] Stepanov N D, Shaysultanov D G, Salishchev G A, et al. Structure and mechanical properties of a light-weight AlNbTiV high entropy alloy. Mater Lett, 2015, 142: 153 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2014.11.162 [25] Juan C C, Tsai M H, Tsai C W, et al. Enhanced mechanical properties of HfMoTaTiZr and HfMoNbTaTiZr refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics, 2015, 62: 76 doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2015.03.013 [26] Maiti S, Steurer W. Structural-disorder and its effect on mechanical properties in single-phase TaNbHfZr high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater, 2016, 106: 87 doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2016.01.018 [27] Yan J H, Li K L, Wang Y, et al. NbMoCrTiAl high-entropy alloy prepared by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Mater Rep, 2019, 33(10): 1671 doi: 10.11896/cldb.18020113顏建輝, 李凱玲, 汪異, 等. 機械合金化和放電等離子燒結制備NbMoCrTiAl高熵合金. 材料導報, 2019, 33(10):1671 doi: 10.11896/cldb.18020113 [28] Yao H W, Qiao J W, Hawk J A, et al. Mechanical properties of refractory high-entropy alloys: experiments and modeling. J Alloys Compd, 2017, 696: 1139 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.11.188 [29] Han Z D, Chen N, Zhao S F, et al. Effect of Ti additions on mechanical properties of NbMoTaW and VNbMoTaW refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics, 2017, 84: 153 doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2017.01.007 [30] Karantzalis A E, Poulia A, Georgatis E, et al. Phase formation criteria assessment on the microstructure of a new refractory high entropy alloy. Scr Mater, 2017, 131: 51 doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.01.004 [31] Chen H, Kauffmann A, Laube S, et al. Contribution of lattice distortion to solid solution strengthening in a series of refractory high entropy alloys. Metall Mater Trans A, 2018, 49(3): 772 doi: 10.1007/s11661-017-4386-1 [32] Fazakas é, Zadorozhnyy V, Varga L K, et al. Experimental and theoretical study of Ti20Zr20Hf20Nb20X20 (X=V or Cr) refractory high-entropy alloys. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater, 2014, 47: 131 doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2014.07.009 [33] Li J M, Yang X, Zhu R L, et al. Corrosion and serration behaviors of TiZr0.5NbCr0.5VxMoy high entropy alloys in aqueous environments. Metals, 2014, 4(4): 597 doi: 10.3390/met4040597 [34] Gorr B, Azim M, Christ H J, et al. Phase equilibria, microstructure, and high temperature oxidation resistance of novel refractory high-entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd, 2015, 624: 270 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.11.012 [35] Gorr B, Müller F, Azim M, et al. High-temperature oxidation behavior of refractory high-entropy alloys: Effect of alloy composition. Oxid Met, 2017, 88(3-4): 339 doi: 10.1007/s11085-016-9696-y [36] Senkov O N, Isheim D, Seidman D N, et al. Development of a refractory high entropy superalloy. Entropy, 2016, 18(3): 102 doi: 10.3390/e18030102 [37] Jensen J K, Welk B A, Williams R E A, et al. Characterization of the microstructure of the compositionally complex alloy Al1Mo0.5Nb1Ta0.5Ti1Zr1. Scr Mater, 2016, 121: 1 doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.04.017 [38] Senkov O N, Jensen J K, Pilchak A L, et al. Compositional variation effects on the microstructure and properties of a refractory high-entropy superalloy AlMo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr. Mater Des, 2018, 139: 498 doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2017.11.033 [39] Huang H L, Wu Y, He J Y, et al. Phase-transformation ductilization of brittle high-entropy alloys via metastability engineering. Adv Mater, 2017, 29(30): 1701678 doi: 10.1002/adma.201701678 [40] Jiang H, Jiang L, Lu Y P, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the W-Ni-Co system refractory high-entropy alloys. Mater Sci Forum, 2015, 816: 324 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.816.324 [41] Yao H W, Qiao J W, Gao M C, et al. NbTaV-(Ti, W) refractory high-entropy alloys: Experiments and modeling. Mater Sci Eng A, 2016, 674: 203 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2016.07.102 [42] Sosa J M, Jensen J K, Huber D E, et al. Three-dimensional characterisation of the microstructure of an high entropy alloy using STEM/HAADF tomography. Mater Sci Technol, 2015, 31(10): 1250 doi: 10.1179/1743284715Y.0000000049 [43] Lei Z F, Liu X J, Wu Y, et al. Enhanced strength and ductility in a high-entropy alloy via ordered oxygen complexes. Nature, 2018, 563(7732): 546 doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0685-y [44] Diao H Y, Xie X, Sun F, et al. Mechanical properties of high-entropy alloys. High-Entropy Alloys, 2016: 181 [45] Waseem O A, Lee J, Lee H M, et al. The effect of Ti on the sintering and mechanical properties of refractory high-entropy alloy TixWTaVCr fabricated via spark plasma sintering for fusion plasma-facing materials. Mater Chem Phys, 2018, 210: 87 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.06.054 [46] Zhang B, Gao M C, Zhang Y, et al. Senary refractory high-entropy alloy CrxMoNbTaVW. Calphad, 2015, 51: 193 doi: 10.1016/j.calphad.2015.09.007 [47] Zhang Y, Zuo T T, Tang Z, et al. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog Mater Sci, 2014, 61: 1 doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2013.10.001 [48] Chen S, Yang X, Dahmen K, et al. Microstructures and crackling noise of AlxNbTiMoV high entropy alloys. Entropy, 2014, 16(2): 870 doi: 10.3390/e16020870 [49] Qiao D X, Jiang H, Chang X X, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of VTaTiMoAlx refractory high entropy alloys. Mater Sci Forum, 2017, 898: 638 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.898.638 [50] Gao M C, Zhang B, Yang S, et al. Senary refractory high-entropy alloy HfNbTaTiVZr. Metall Mater Trans A, 2016, 47(7): 3333 doi: 10.1007/s11661-015-3105-z [51] Zhang B, Gao M C, Zhang Y, et al. Senary refractory high entropy alloy MoNbTaTiVW. Mater Sci Technol, 2015, 31(10): 1207 doi: 10.1179/1743284715Y.0000000031 [52] Wei S Z, Xu L J. Review on research progress of steel and iron wear-resistant materials. Acta Metall Sin, 2020, 56(4): 523 doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2019.00370魏世忠, 徐流杰. 鋼鐵耐磨材料研究進展. 金屬學報, 2020, 56(4):523 doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2019.00370 [53] Liu X T, Lei W B, Ma L J, et al. Effect of boron on the microstructure, phase assemblage and wear properties of Al05CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2016, 45(9): 2201 doi: 10.1016/S1875-5372(17)30003-6 [54] Tong C J, Chen M R, Yeh J W, et al. Mechanical performance of the AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall Mater Trans A, 2005, 36: 1263 doi: 10.1007/s11661-005-0218-9 [55] Poulia A, Georgatis E, Lekatou A, et al. Dry-sliding wear response of MoTaWNbV high entropy alloy. Adv Eng Mater, 2017, 19(2): 1600535 doi: 10.1002/adem.201600535 [56] Poulia A, Georgatis E, Lekatou A, et al. Microstructure and wear behavior of a refractory high entropy alloy. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater, 2016, 57: 50 doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2016.02.006 [57] Mathiou C, Poulia A, Georgatis E, et al. Microstructural features and dry - Sliding wear response of MoTaNbZrTi high entropy alloy. Mater Chem Phys, 2018, 210: 126 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.08.036 [58] Ye Y X, Liu C Z, Wang H, et al. Friction and wear behavior of a single-phase equiatomic TiZrHfNb high-entropy alloy studied using a nanoscratch technique. Acta Mater, 2018, 147: 78 doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2018.01.014 [59] Grigoriev S N, Sobol O V, Beresnev V M, et al. Tribological characteristics of (TiZrHfVNbTa)N coatings applied using the vacuum arc deposition method. J Frict Wear, 2014, 35(5): 359 doi: 10.3103/S1068366614050067 [60] Jayaraj J, Thinaharan C, Ningshen S, et al. Corrosion behavior and surface film characterization of TaNbHfZrTi high entropy alloy in aggressive nitric acid medium. Intermetallics, 2017, 89: 123 doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2017.06.002 [61] Wang S P, Xu J. TiZrNbTaMo high-entropy alloy designed for orthopedic implants: as-cast microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater Sci Eng C, 2017, 73: 80 doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.12.057 [62] Senkov O N, Senkova S V, Dimiduk D M, et al. Oxidation behavior of a refractory NbCrMo0.5Ta0.5TiZr alloy. J Mater Sci, 2012, 47(18): 6522 doi: 10.1007/s10853-012-6582-0 [63] Gorr B, Mueller F, Christ H J, et al. High temperature oxidation behavior of an equimolar refractory metal-based alloy 20Nb?20Mo?20Cr?20Ti?20Al with and without Si addition. J Alloys Compd, 2016, 688: 468 [64] Li T X, Lu Y P, Cao Z Q, et al. Opportunity and challenge of refractory high-entropy alloys in the field of reactor structural materials. Acta Metall Sin, 2021, 57(1): 42 doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2020.00293李天昕, 盧一平, 曹志強, 等. 難熔高熵合金在反應堆結構材料領域的機遇與挑戰. 金屬學報, 2021, 57(1):42 doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2020.00293 [65] Egami T, Guo W, Rack P D, et al. Irradiation resistance of multicomponent alloys. Metall Mater Trans A, 2014, 45(1): 180 doi: 10.1007/s11661-013-1994-2 [66] El-Atwani O, Li N, Li M, et al. Outstanding radiation resistance of tungsten-based high-entropy alloys. Sci Adv, 2019, 5(3): eaav2002 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aav2002 [67] Lu Y P, Huang H F, Gao X Z, et al. A promising new class of irradiation tolerant materials: Ti2ZrHfV0.5Mo0.2 high-entropy alloy. J Mater Sci Technol, 2019, 35(3): 369 doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2018.09.034 [68] Waseem O A, Ryu H J. Powder metallurgy processing of a WxTaTiVCr high-entropy alloy and its derivative alloys for fusion material applications. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 1926 doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02168-3 -




 下載:
下載: