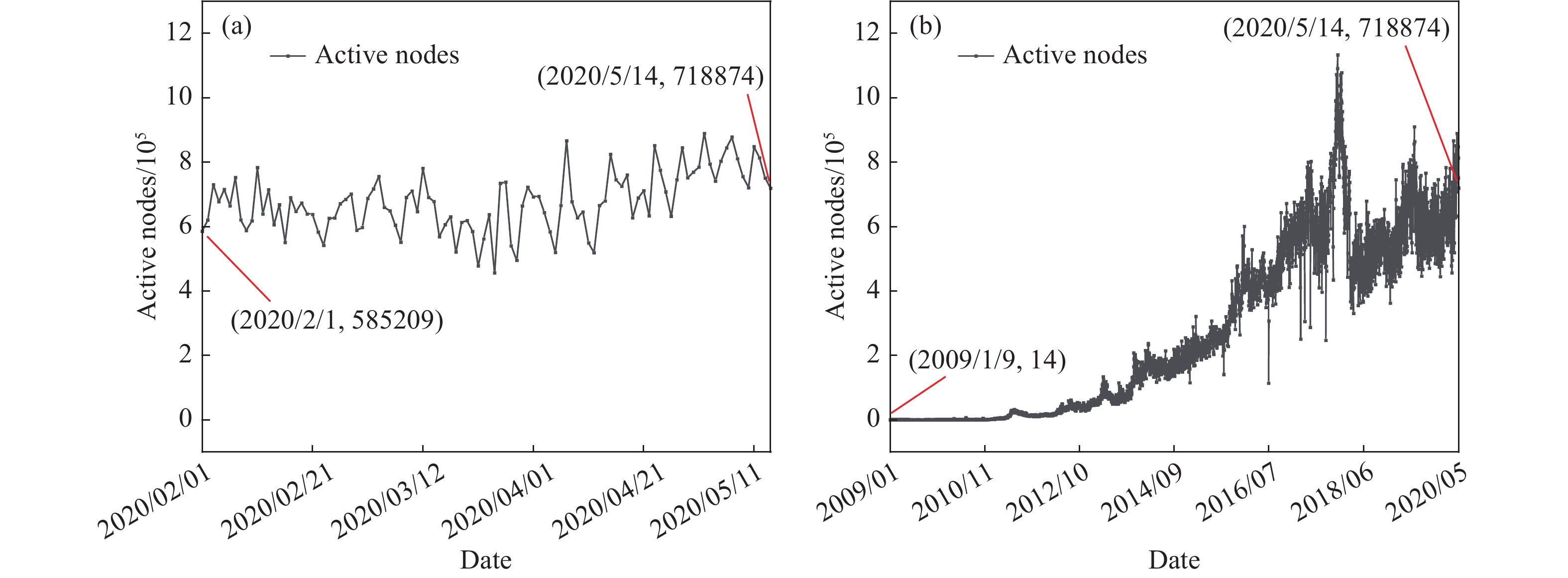
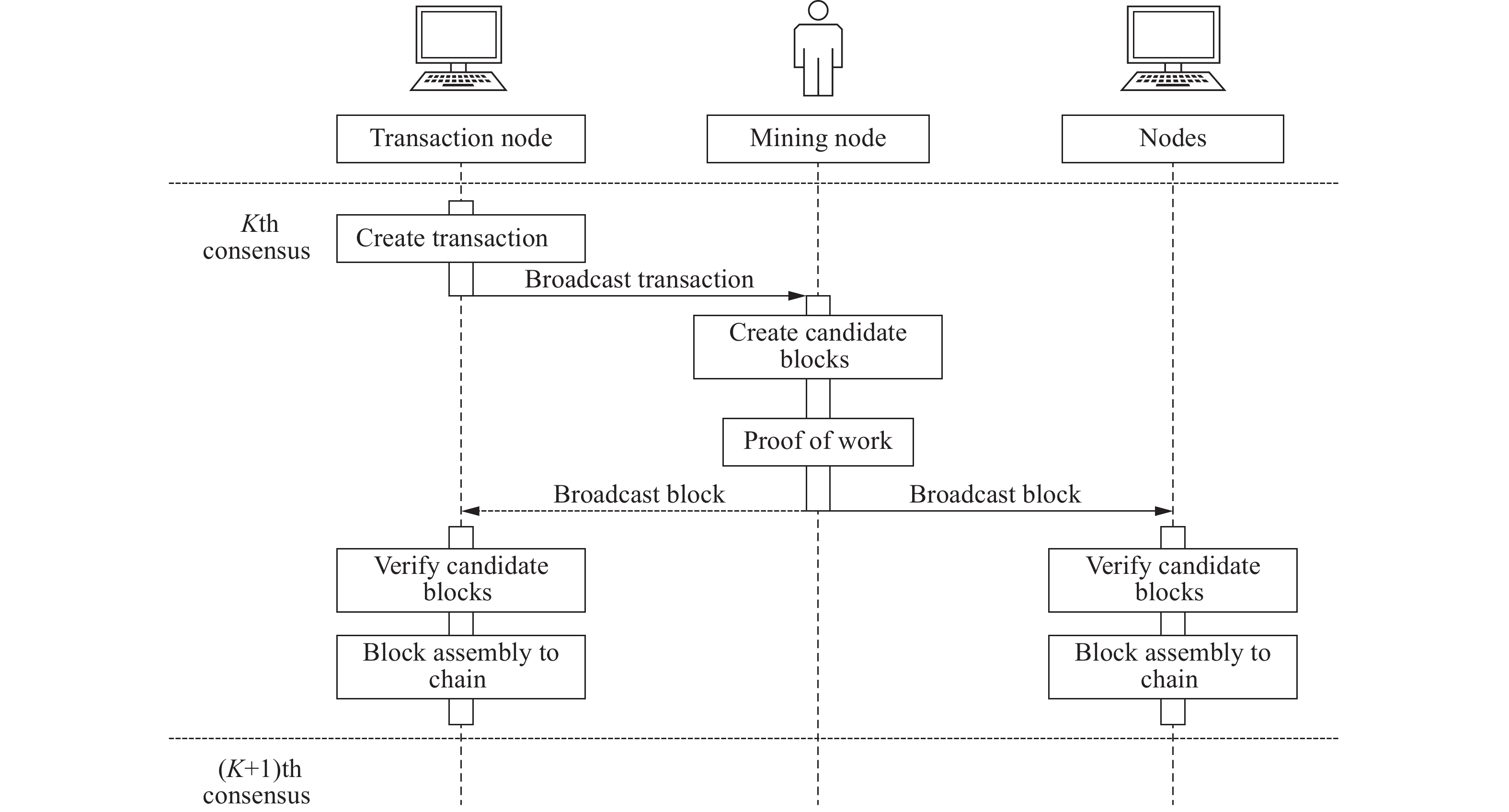
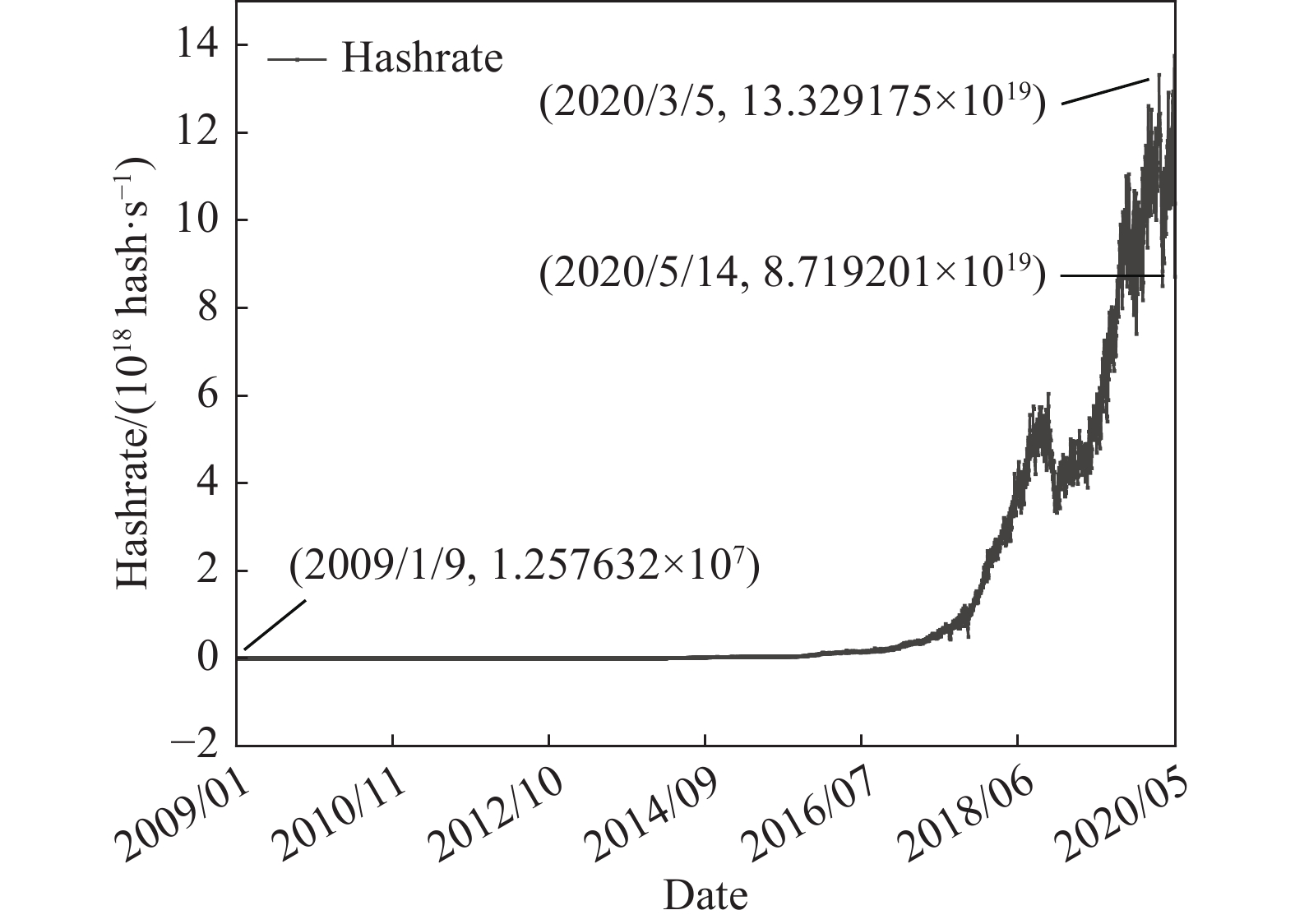
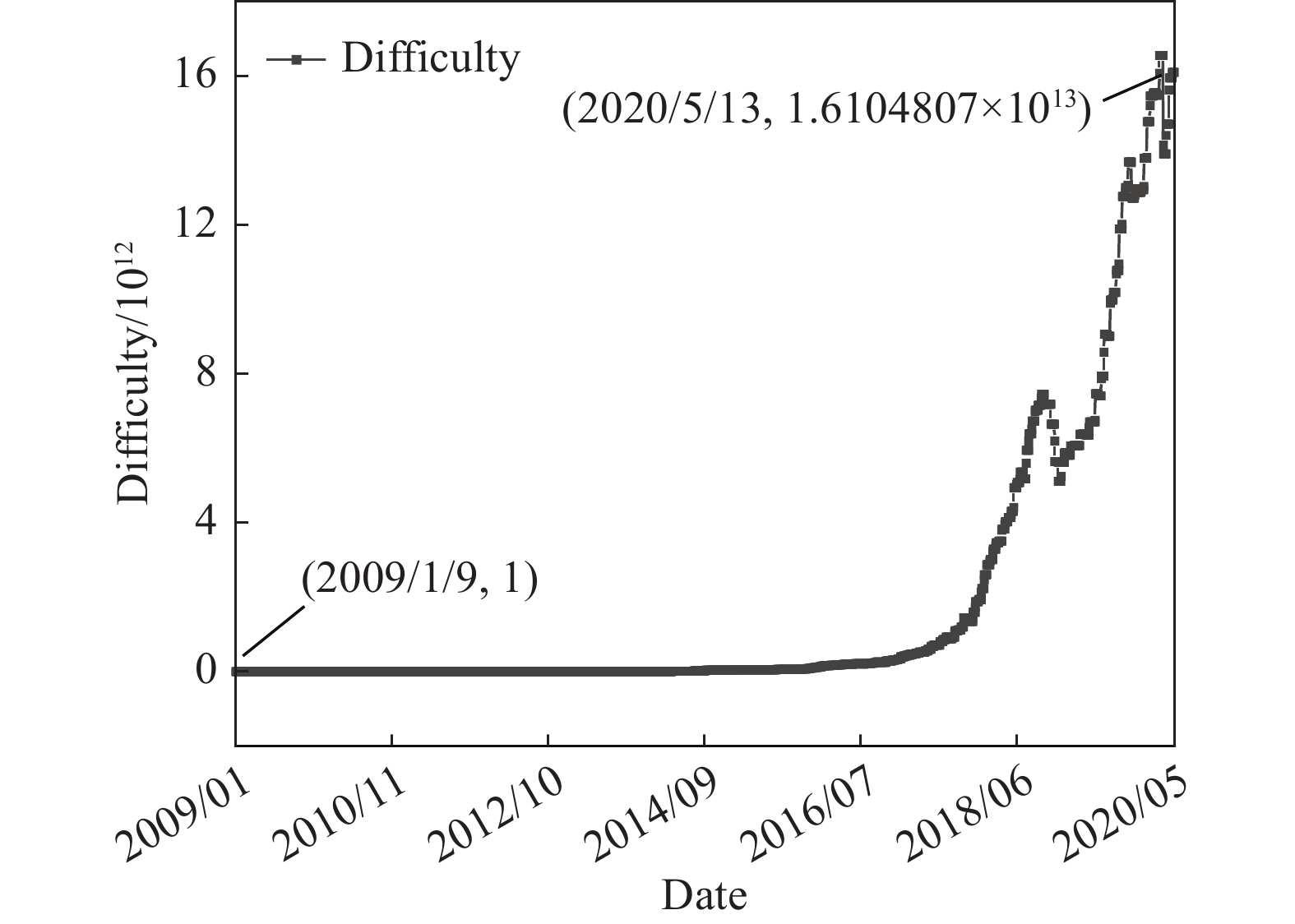
Research on blockchain evaluation methods under the classified protection of cybersecurity
-
摘要: 等級保護(簡稱等保)是我國信息安全的基本政策,隨著區塊鏈技術在各行業中的應用日趨廣泛,有必要同步推進區塊鏈系統的等級保護測評工作,這將有利于推動該技術在我國的持續健康發展。有鑒于此,依據等保第三級的應用和數據安全要求,給出了區塊鏈系統中對等網絡、分布式賬本、共識機制和智能合約等核心技術的具體測評要求及實施方案,并從等保2.0規定的控制點出發,分別對當前區塊鏈系統運行數據與基于日志流程的安全審計機制進行了歸納與分析。通過上述評估與分析可知區塊鏈系統在軟件容錯、資源控制和備份與恢復等方面滿足等保要求,而在安全審計、身份鑒別、數據完整性等方面則有待進一步改進。Abstract: A blockchain is a cryptographic distributed database and network transaction accounting system. In the current era of major technological changes, blockchain technology, with its cryptographic structure, peer-to-peer (P2P) network, consensus mechanism, smart contract and other mechanisms, is decentralized, tamper-proof, and traceable and has become a hot spot in the development of informatization. Classified protection is one of the basic policies of information security in China. The implementation of the information security level protection system can not only guide various industries in performing security management in accordance with the equivalent security standards, but also ensure that supervision and evaluation institutions follow the laws and regulations, which is of significance to network security. As the application of blockchain technology in various industries is becoming more extensive, it is necessary to simultaneously promote the national classified protection of blockchain security assessment, which contributes to the sustainable and healthy development of blockchains in China. According to the revised assessment methods of grade protection, in addition to the status of universality requirements, evaluation specifications should be formulated for specific technologies and fields (such as cloud computing, mobile Internet, Internet of Things, industrial control, and big data). In view of the particularity of blockchain technology, China has initiated the formulation of blockchain evaluation specifications, but has not applied the level protection standards to the formulation of blockchain evaluation specifications. Therefore, the assessment requirements and enforcement proposals are specified for the blockchain’s core technologies, such as P2P network, distributed ledger, consensus mechanism, and smart contracts, according to the application and data security layer requirements at Level 3. Moreover, the current running data of blockchains and their security audit mechanism based on the log workflow were summarized and analyzed respectively in compliance with the control points specified in classified protection 2.0. Our investigation indicates that blockchains can satisfy the requirements of evaluation items in three aspects, namely, software fault tolerance, resource control, and backup and recovery. However, further improvements are needed for other aspects, including security audit, access control, identification and authentication, and data integrity.
-
表 1 定級要素與安全等級的關系
Table 1. Relation between grading elements and safety level
程度
Degree公民、法人、其他組織
Citizens, corporations and other organizations社會秩序、社會公共利益
Social order, public interest國家安全
National security損害
General damage第一級
Level 1第二級
Level 2第三級
Level 3嚴重損害
Significant damage第二級
Level 2第三級
Level 3第四級
Level 4特別嚴重損害
Especially significant damage第三級
*Level 3第四級
Level 4第五級
Level 5* Classified protection 1.0 is level 2. 表 2 等級保護1.0與2.0三級應用層控制點對比
Table 2. Comparison of application layer control points in classified protection 1.0 and 2.0 at level 3
版本
Version類別
Category控制點
Control points等級保護1.0
Classified protection 1.0應用安全
Application security身份鑒別、訪問控制、安全審計、通信完整性、通信保密性、軟件容錯、資源控制
Identity authentication, access control, security audit, communication integrity, communication confidentiality, software fault tolerance, resource control數據安全及備份恢復
Data security and backup recovery數據完整性、數據保密性、備份和恢復
Data integrity, data confidentiality, backup and recovery等級保護2.0
Classified protection 2.0應用和數據安全
Application and data security身份鑒別、訪問控制、安全審計、軟件容錯、資源控制、數據完整性、數據保密性、
數據備份和恢復、剩余信息保護、個人信息保護
Identity authentication, access control, security audit, software fault tolerance, resource control, data integrity, data confidentiality, data backup and recovery, residual
information protection, personal information protection表 3 分布式對等網絡測評
Table 3. Distributed peer-to-peer network assessment
類別
Categories測評項
Items實施
Implementation預期效果
Expected Effectiveness實際測評結果說明
Description of actual evaluation results達標
Y/N身份鑒別
Identification節點接入控制
Node link control查看連入區塊鏈是否
需要認證
Check if the connection to the Blockchain requires authentication當節點連入系統時,對其進行身份認證,控制節點接入
When nodes are connected, the system authenticates themto restrict node access.節點接入時沒有對身份
進行認證
The identity is not authenticated when the node is connected.否
N軟件容錯
Software fault tolerance自我保護與自適應
Self-protection and self-adaptation網絡不穩定時查看信息傳輸情況
Inspect information transmission when the network is unstable.網絡抖動對傳輸不會造成太大影響,系統運行穩定Network jitter does not have much impact on transmission. Blockchain runs stably. 網絡抖動時,區塊鏈
系統運行穩定
Blockchain system runs stably when network jitter occurs.是
Y資源控制
Resource control并發連接限制
Concurrent connection restriction查看節點最大連接數目
View the maximum number of connections on nodes對最大并發連接進行限制,防止系統資源耗盡
Limit maximum concurrent connections to prevent system resource exhaustion節點連接不超過117個輸入連接,向其他節點發起
8個輸出連接。
Node connections do not exceed 117 input connections and 8 output connections.是
Y連接超時限制
Connection timeout limit查看相關網絡配置
View related network configurations自動結束長期無應答的會話防止系統資源占用
Automatically end long-term unanswered sessions to prevent system resource usage.某個節點超過30 min沒有新消息,則發送心跳消息,長達90 min沒有通信,則結束會話
If there is no communication for more than 30 minutes, a heartbeat message is sent. End the session if there is no communication for 90 minutes.是
Y數據完整性
Data integrity單播通信防篡改
Anti-tampering of unicast查看數據傳輸是否加密防
篡改安全
Check whether data transmission is encrypted and tamper-proof數據在點對點通信過程中不被篡改
Data is not tampered with in the process of point-to-point communication.不能保障數據在單播通信過程中的完整性
The integrity of data in unicast communication cannot be guaranteed.否
N廣播通信防篡改
Multicast communication tamper-proof能否提供通信多播,廣播功能,通信過程中數據是否防篡改
Check whether the system can provide communication multicast, broadcast function and tamper-proof data in the process of communication數據在廣播通信過程中
不被篡改
Data is not tampered with during broadcast communication.不能保障數據在廣播通信過程中的完整性
The Bitcoin system does not guarantee the integrity of data in the broadcast communication process.否
N轉發通信防篡改
Forwarding communication tamper-proof轉發功能及數據防篡改
Data tampering prevention in forwarding communication數據在某節點通過轉發時
不被篡改
Data is not tampered with when forwarded by a node.不能保障數據在轉發通信過程中的完整性
The integrity of data in the process of forwarding communication cannot be guaranteed否
N安全審計
Security audit網絡狀態獲取更新
Network status get update查看日志是否記錄
節點狀態信息
Check whether the log records
node status information.能夠為系統的穩定運行提供可信的節點數據
Ability to provide trusted node data for stable operation of the system.存在單個節點的狀態更新記錄,但更新記錄不進行全網交換,無法獲取全網狀態
There is a status update record for a single node. However, update records are not exchanged in the whole network, the whole network status cannot be obtained.否
N網絡節點動態監測
Network node dynamic monitoring是否對在線節點數量
進行統計
Statistics on the number of
online nodes具備對節點動態增加和減少的識別能力
Ability to recognize nodes dynamically increasing and decreasing.區塊鏈系統具備全網節點數量實時統計能力
The Bitcoin system does not have the real-time statistical ability of the number of nodes in the whole network.是
Y表 4 不同區塊鏈參數選擇對網絡傳輸影響[43]
Table 4. Impact of parameter selection on network transmission in different blockchains[43]
Parameter Bitcoin Litecoin Dogecoin Ethereum 區塊間隔
Block interval10 min
10 min2.5 min
2.5 min1 min
1 min10?20 s
10?20 s公共節點
Public nodes6000 800 600 4000 挖礦池
Mining pools16 12 12 13 陳腐塊率/%
Stale block rate0.41 0.273 0.619 6.8 區塊大小/KB
Block size534.8 6.11 8 1.5 表 5 共識機制測評
Table 5. Consensus mechanism assessment
類別
Categories測評項
Items實施
Implementation預期效果
Expected effectiveness實際測評結果說明
Description of actual
evaluation results達標
Y/N資源控制
Resource control共識資源控制
Consensus resource control檢測計算機中資源
使用情況。
Check the use of resources in the computer共識機制消耗計算機資源
應該最小化原則
Consensus mechanisms should minimize the consumption of computer resources.PoW共識機制計算資源耗費較大,但系統資源可控
PoW consumes a lot of computing resources, but the system resources are controllable.是
Y備份與恢復
Backup and recovery實時備份
Real-time backup查看節點是否同步了
新共識區塊
Check whether the node has synchronized the new consensus block全網節點具有相同的數據副本
All network nodes have the
same data replica.節點實時備份區塊鏈中產生的交易數據
Real-time backup of transaction data generated in Bitcoin system by nodes.是
Y系統熱冗余
System hot redundancy查看節點癱瘓后
系統可用性
View system availability after node paralysis業務連續性未被中斷
Business continuity not interrupted.節點之間互為冗余,單一或少數節點故障不影響系統穩定性和可用性
Nodes are redundant to each other and single or few node failures do not affect the stability and availability of the system.是
Y共識效果
Consensus effect共識容錯性
Consensus fault tolerance設置異常節點,查看共識情況
Set exception nodes and view consensus.存在共識閾值,使得超過閾值的節點達到共識即代表全網共識完成
There is a consensus threshold, so that the node exceeding the threshold reaches the consensus, which means that the consensus of the whole network is completed.系統可容納5%的節點共識錯誤。95%以上的節點
共識成功即可
The system can accommodate 5% node consensus errors. More than 95% of the nodes are successful.是
Y共識有效性
Consensus Effectiveness發起非法交易,查看共識是否失敗
Initiate an illegal transaction to see if the consensus failed非法交易共識失敗。通過對交易進行正確性和邏輯性驗證,使惡意造假交易的代價昂貴,避免惡意共識
Illegal transaction consensus failed. By verifying the correctness and logic of the transaction, the cost of malicious fraudulent transactions is expensive and avoids malicious consensus.非法交易不能被共識通過
Illegal transactions cannot be passed by consensus.是
Y共識結果一致性
Consensus consistency發起合法交易,查看共識結果是否滿足一致
Initiate a legal transaction and see if the consensus result is consistent忠誠參與方共識結果
具有一致性
Loyal participant consensus results are consistent.對于合法交易區塊鏈系統達成共識后寫入區塊鏈
After agreeing on the legal transaction of Bitcoin system, it is written into the blockchain.是
Y表 6 分布式賬本測評
Table 6. Distributed ledger assessment
類別
Categories測評項
Items實施
Implementation預期效果
Expected effectiveness實際測評結果說明
Description of actual evaluation results達標
Y/N軟件容錯
Software fault tolerance賬本格式規范性
Standardization of ledger查看賬本中的數據格式是否有統一標準
Check whether the data format in the ledger has a uniform standard交易、區塊等數據按照數據格式進行存儲
Data such as transactions and blocks are stored
in data format.區塊鏈系統交易、區塊等均有統一組織標準
Blockchain system transactions, blocks, etc. have unified organizational standards.是
Y訪問控制
Access control賬本訪問控制
Ledger access control查看是否存在訪問策略監管節點及訪問控制策略
Check whether there is an access policy supervision node and access control policy對賬本上的數據資源進行保護,防止非法訪問
Protect the data resources
on the ledger against
illegal access作為公有鏈系統沒有完備的訪問控制策略
Bitcoin as a public blockchain, there is no complete access control strategy否
N數據完整性
Data integrity存儲完整性
Storage integrity查看數據存儲是否存在哈希、指紋等機制保障存儲的完整性
Check if there is a hash mechanism in the data storage to ensure the integrity of the storage存儲內容被哈希處理,完整性得到保障
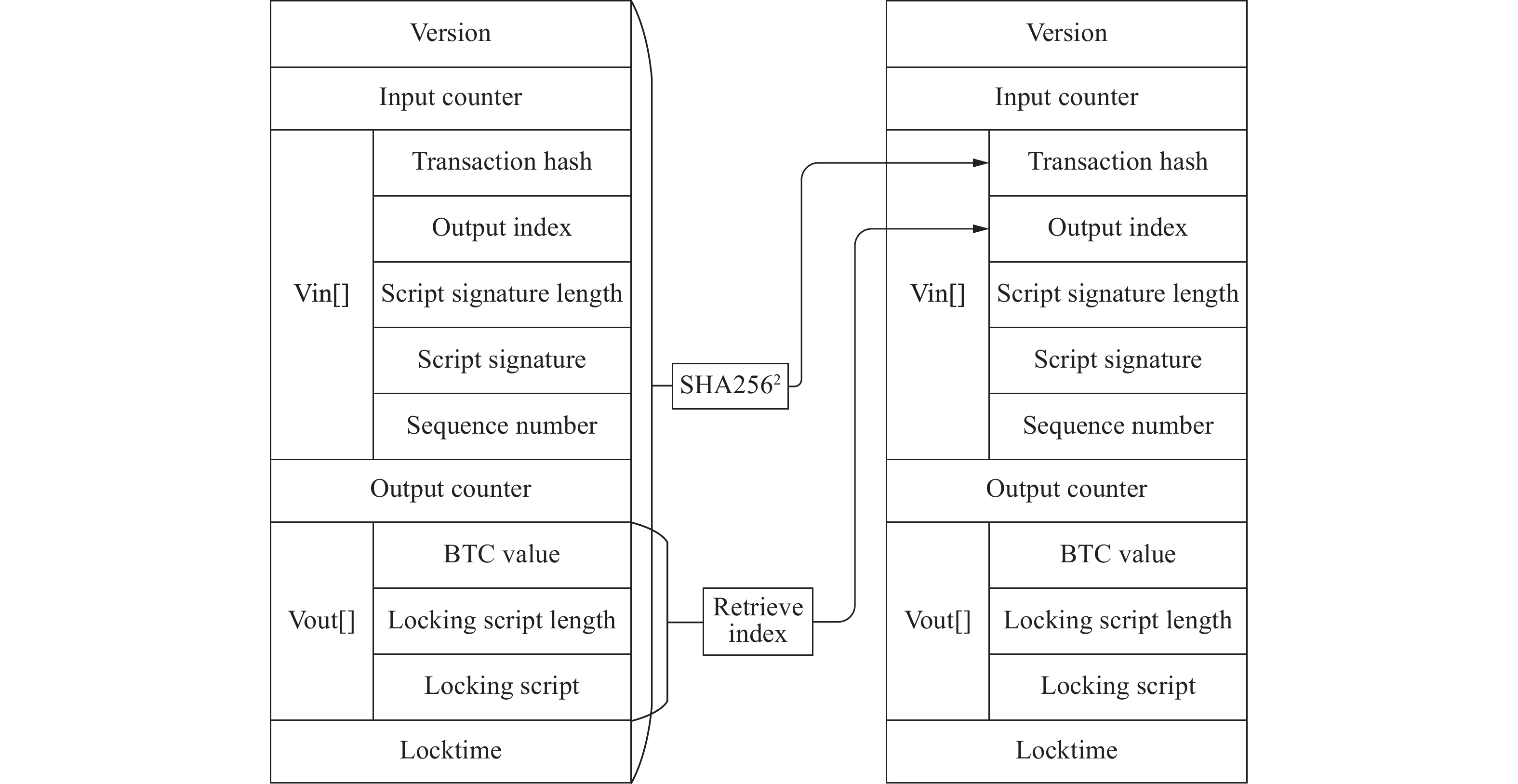
Stored data is hashed and integrity is guaranteed.將交易按照默克爾樹的形式進行哈希并存儲于區塊
Bitcoin hashes transactions in the form of Merkel trees and stores them in blocks.是
Y數據保密性
Data confidentiality存儲保密性
Storage Confidentiality查看機密數據的存儲
是否加密
Check if the storage of confidential data is encrypted數據存儲不是以明文格式
Data is not stored in plaintext format.數據存儲是以明文的16進制形式進行存儲,方便查詢和驗證
Bitcoin data storage is stored in plaintext in hexadecimal form, which is convenient for query and verification.否
N賬本功能
Ledgerfunction數據抗抵賴
Data non-repudiation查看賬本中的交易數據來源是否有效
Check if the transaction data in the ledger is signed交易被各個參與方簽名,使交易可溯源,以達到抗抵賴的作用。
The transaction is signed by each participant, so that the transaction can be traceable to achieve the role of non-repudiation.區塊鏈系統通過對交易數據進行簽名達到了數據
抗抵賴的作用
Bitcoin achieves data non-repudiation by signing transaction data.是
Y賬本數據同步
Ledger data synchronization查看是否有完全節點,
節點間存儲賬本數據
是否一致
Check if there is a full node, store all data in the ledger全節點中同步了賬本中所有的數據,可以通過全節點得到區塊鏈數據的完整副本
All the data in the ledger is synchronized in the full node. A complete copy of the blockchain data can be obtained from full nodes.區塊鏈系統中存在同步了賬本所有數據的全節點,并能對同步過程中發現的數據錯誤予以檢測及確認
There are full nodes in the Bitcoin system that synchronize all the data of the ledger.是
Y賬本數據冪等
Ledger data idempotentce查看賬本信息中檢索同樣的數據結果是否一致
Check if the results of retrieving the same data
are consistent在查詢相同記錄時具有
相同的結果,確保
數據的一致性
Ensure data consistency by querying the same records with the same results.區塊鏈系統存入賬本的數據均通過共識,賬本數據具有冪等性
The data of Bitcoin deposited in the ledger has passed the consensus, and ledger data has idempotency.是
Y表 7 區塊鏈頭信息及長度限制
Table 7. Information and length limit of Blockchain Header
數據項
Items用途
Use大小(字節)
Size(byte)區塊版本V
Version區塊版本號
Block version number4 難度D
Difficulty Target用以標注挖礦難度
To indicate the difficulty of mining4 前區塊哈希
PreH Pre-block hash基于區塊中所有交易的256位hash值
Based on the 256-bit hash value of all transactions in the block32 默克爾樹根M
Merkletree Root交易內容hash256值
The value of the transaction content 256-bit hash32 隨機數N
Nonce用以調整當前區塊頭hash值
To adjust the current block head hash value4 時間戳T
TimestampUNIX時間戳A
UNIX timestamp4 表 8 區塊鏈合約計算層測評
Table 8. Blockchain contract computing layer evaluation
類別
Categories測評項
Items實施
Implementation預期效果
Expected effectiveness實際測評結果說明
Description of actual evaluation results達標
Y/N身份鑒別
Identification執行身份驗證
Performingentity authentication查看合約是否許可查看或限定執行者身份
Check if the contract can be viewed or qualify executor’s identity應對登錄的用戶進行身份標識和鑒別,身份標識具有唯一性,身份鑒別信息具有復雜度
The identification and authentication should be carried out for the logged-in user. The identification is required to be unique and complicated.在發布交易時,區塊鏈會對執行者身份進行驗證,因此可以控制執行合約的身份
When publishing a transaction, the blockchain verifies the executor’s identity, thus constraining the execution of contract.是
Y安全審計
Security audit行為事件審計
Behavioral event audit能否驗證智能
合約的執行
Check if to verify the execution of smart contract應啟用安全審計功能,審計覆蓋到每個用戶,對重要的用戶行為和重要
安全事件進行審計
The security audit function should be enabled to cover every user over significant user actions and
security events.所有參與挖礦節點會
驗證智能合約執行的
正確性
All nodes involved in mining can verify the correctness of smart contract execution.是
Y審計記錄
Audit records是否記錄了審計的
相關信息
Check if audit information is recorded審計記錄應包括事件的日期和時間、用戶、事件類型、事件是否成功等。應對審計記錄進行保護,定期備份,避免受到未預期的刪除、修改或覆蓋等
The audit record should include the date and time of event, the executor, the type
of event, the state if the event was successful, etc. Audit records should
be protected and backed up regularly to avoid unexpected deletions, modifications or overwrites.區塊中的交易記錄了智能合約的執行時間、執行用戶、執行的輸入與輸出
The transactions in the block record the execution time, the executors, the input and output of the smart contract.否
N惡意代碼防范
Malicious code protection免受惡意代碼攻擊
Protection from
malicious code是否有免受惡意代碼攻擊的機制
Check if there is a mechanism to protect against malicious code應采用免受惡意代碼攻擊的技術措施或主動免疫可信驗證機制及時識別入侵和病毒行為,并將其有效阻斷。
It is necessary to adopt the technical measures to avoid the attack of malicious code or the trusted verification mechanism with active immunity to identify the intrusion and virus behavior in time and block it effectively.通過限定的尋址方式、
限定的指令集以及Docker等運行環境或其他機制使得本地計算機及區塊鏈系統不會
受到影響
Local computers and blockchain systems do not be affected byrestricted addressing methods, limited instruction sets, operating platforms such as Docker, or other mechanisms.是
Y數據完整性
Data integrity傳輸完整性
Transmission integrity查看是否通過校驗技術或密碼技術保證
數據完整性
Check if data integrity is guaranteed by CRC or cryptography應采用校驗技術或密碼技術保證重要數據在傳輸過程中的完整性。
Verification technology or cryptography should be adopted to ensure the integrity of important data during transmission.存在單個節點的狀態
更新記錄
There are status updating records for individual nodes.是
Y數據保密性
Data confidentiality傳輸保密性
Transmission confidentiality查看是否通過密碼技術保證數據保密性
Check if data onidenticality is guaranteed by cryptography.應采用密碼技術保證重要數據
在傳輸過程中的保密性。
Cryptography should be adopted to ensure the confidentiality of important data during transmission.區塊鏈系統不具備全網節點數量實時統計能力
The blockchain system does not have the real-time statistical ability on the number of nodes in the whole network.否
N表 9 區塊鏈系統error審計分類
Table 9. Blockchain error audit classification
功能
Function接口函數
Interface function輸出錯誤
Output error初始化錯誤
Initialization errorAppInit2_Cold() Winsock庫、初始化完整性檢測、錢包文件損壞等
Winsock Library, Initial Integrity Detection, Wallet File Damage, etc.交易錯誤
Transaction errorCheckTransaction() 檢查交易時出錯,如輸入輸出為空等交易格式錯誤
Errors in checking transactions, such as empty input and output, etc.AcceptToMemoryPool() 驗證交易合理性并存入交易池時發生錯誤,如輸入已經被花費等
Errors occur when validating the reasonableness of transactions
and storing them in the trading pool, such as input being spent, etc.CScriptCheck() 腳本簽名錯誤
Script signature errorCheckInputs() 交易輸入錯誤,如:交易總輸入<總輸出
Transaction input errors, such as: total transaction input <total outputCheckSignature() 檢查簽名時出錯
Error in checking signature區塊錯誤
Block errorWriteBlockToDisk() 將區塊寫入磁盤出錯,如文件打開失敗
Errors in writing blocks to disk, such as file opening failureReadBlockFromDisk() 從磁盤讀出區塊出錯,如打開區塊文件失敗
Error reading block from disk, such as failure to open block fileDisconnectBlock() 斷開區塊鏈接時出錯
Error while disconnecting block linksConnectBlock() 連接區塊時出錯,如資產提交時出錯
Error connecting blocks, such as asset submissionCheckBlock() 檢查區塊時出錯,如默克爾樹根不匹配
Error checking blocks, such as Merkle root mismatchContextualCheckBlockHeader 檢查區塊頭部信息是否出錯,如塊的時間戳太早
Check if block header information is wrong, such as block timestamp too earlyLoadBlockIndex() 加載區塊索引出錯,如將創世塊寫入磁盤失敗
Error loading block index, such as failure to write Genesis block to disk共識錯誤
Consensus errorCheckBlockHeader() 工作量證明失敗 Proof-of-work error AcceptBlock() 未找到工作量證明
Accepting blocks makes errors, such as failing to find proof-of-work網絡錯誤
Network errorRecvLine() socket錯誤Socket error Read() 連接節點數據文件peer.dat讀錯誤
Error in peer.dat reading of connection node data fileWrite() 連接節點數據文件peer.dat寫錯誤
Error in peer.dat writing of connection node data fileConnect() 連接錯誤 Connection error ProcessMessage() 偵聽并處理網絡中的不同的消息時出錯
Errors in listening for and processing different messages in the network遠程過程調用
Remote procedure callJSONRPCError 遠程過程調用請求、解析、參數等錯誤
Errors in remote procedure call requests, parsing, parameters, etc.久色视频表 10 區塊鏈系統測評結果總結
Table 10. Summary of evaluation results of blockchain system
類別
Categories測評項
Items達標 √/× 比特幣
Bitcoin以太坊
Ethereum超級賬本
Hyperledger分布式對等網絡測評
Distributed P2P network assessment軟件容錯
Software fault tolerance自我保護與自適應
Self-protection and self-adaptation√ √ √ 資源控制
Resource control并發連接限制
Concurrent connection restriction√ √ √ 連接超時限制
Connection timeout limit√ √ √ 身份鑒別
Identification節點接入控制
Node link control× × √ 分布式對等網絡測評
Distributed P2P network assessment數據完整性
Data integrity單播通信防篡改
Anti-tampering of unicast× × × 廣播通信防篡改
Multicast communication tamper-proof× × × 轉發通信防篡改
Forwarding communication tamper-proof× × × 安全審計
Security audit網絡狀態獲取更新
Network status get update× × √ 網絡節點動態監測
Network node dynamic monitoring√ √ √ 分布式賬本測評
Distributed ledgers assessment軟件容錯
Software fault tolerance賬本格式規范性
Standardization of ledger√ √ √ 訪問控制
Access control賬本訪問控制
Ledger access control× × √ 數據完整性
Data integrity存儲完整性
Storage integrity√ √ √ 數據保密性
Data confidentiality存儲保密性
Storage confidentiality× × × 賬本功能
Ledger function數據抗抵賴
Data non-repudiation√ √ √ 賬本數據同步
Ledger data synchronization√ √ √ 賬本數據冪等
Ledger data idempotence√ √ √ 共識機制測評
Consensus mechanism assessment資源控制
Resource control共識資源測評
Consensus Resource Control√ √ √ 備份與恢復
Backup and recovery實時備份
Real-time backup√ √ √ 系統熱冗余
System hot redundancy√ √ √ 共識效果
Consensus effect共識容錯性
Consensus fault tolerance√ √ √ 共識有效性
Consensus effectiveness√ √ √ 共識結果一致性
Consensus Consistency√ √ √ 合約計算層測評
Contract computing layer assessment身份鑒別
Identification執行身份驗證
Performing entity authentication√ √ √ 安全審計
Security audit行為事件審計
Behavioral event audit√ √ √ 審計記錄
Audit records× × × 惡意代碼防范
Malicious code protection免受惡意代碼攻擊
Protection from malicious code√ √ √ 數據完整性
Data integrity傳輸完整性
Transmission integrity√ √ √ 數據保密性
Data confidentiality傳輸保密性
Transmission confidentiality× × × 統計
Statistics達標個數
Number of qualified items19
Nineteen19
Nineteen22
Twenty-two -
參考文獻
[1] Nakamoto S, Bitcoin: a peer-to-peer electronic cash system[J/OL]. Bitcoin Online (2008-10-31)[2019-12-17] https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf [2] Mettler M. Blockchain technology in healthcare: the revolution starts here // 2016 IEEE 18th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom). Munich, 2016: 1 [3] An R, He D B, Zhang Y R, et al. The design of an anti-counterfeiting system based on blockchain. J Cryptol Res, 2017, 4(2): 199安瑞, 何德彪, 張韻茹, 等. 基于區塊鏈技術的防偽系統的設計與實現. 密碼學報, 2017, 4(2):199 [4] Tian H B, He J J, Fu L Q. A privacy preserving fair contract signing protocol based on block chains. J Cryptologic Res, 2017, 4(2): 187田海博, 何杰杰, 付利青. 基于公開區塊鏈的隱私保護公平合同簽署協議. 密碼學報, 2017, 4(2):187 [5] Wijaya D A. Extending asset management system functionality in bitcoin platform // 2016 International Conference on Computer, Control, Informatics and its Applications (IC3INA). Tangerang, 2016: 97 [6] Tian Z H, Wang B L, Ye Z W, et al. The survey of information system security classified protection // Electrical Engineering and Control. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2011: 975 [7] Xia B. Cybersecurity Law and Classified Protection of Cybersecurity 2.0. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2017夏冰. 網絡安全法和網絡安全等級保護2.0. 北京: 電子工業出版社, 2017 [8] Guo Q Q. Book of Cybersecurity Law and Classified Protection of Cybersecurity. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2018郭啟全. 網絡安全法與網絡安全等級保護制度培訓教程(2018版). 北京: 電子工業出版社, 2018 [9] Deng R Y, Yu M L, Ding Y, et al. Safeguarding cyberspace security by law and building a cyber power— —Interpretation of cybersecurity law of the People’s Republic of China and National cyberspace security strategy. E-Government, 2017(02): 2鄧若伊, 余夢瓏, 丁藝, 等. 以法制保障網絡空間安全構筑網絡強國——《網絡安全法》和《國家網絡空間安全戰略》解讀. 電子政務, 2017(02):2 [10] Zhu J F, Zhao Y J, Yang H, et al. The evolution of classified protection idea. Inform Security Commun Privacy, 2011(4): 70 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8054.2011.04.029朱繼鋒, 趙英杰, 楊賀, 等. 等級保護思想的演化. 信息安全與通信保密, 2011(4):70 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8054.2011.04.029 [11] Ma L, Zhu G B, Lu L. Baseline for classified protection of cybersecurity (GB/T 22239—2019) standard interpretation. Netinfo Security, 2019, 19(2): 77 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2019.02.010馬力, 祝國邦, 陸磊. 《網絡安全等級保護基本要求》(GB/T 22239—2019)標準解讀. 信息網絡安全, 2019, 19(2):77 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2019.02.010 [12] Gao Y, Huang X K, Li X W. Cloud computing security requirements and measurement practices in the classified protection 2.0Era. J Inform Security Res, 2018, 4(11): 987 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1057.2018.11.004高員, 黃曉昆, 李秀偉. 等保2.0時代云計算安全要求及測評實踐. 信息安全研究, 2018, 4(11):987 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1057.2018.11.004 [13] Huang Z, Chen X, Wen S H, et al. Security testing frame and technology of big data. Commun Technol, 2017, 50(8): 1810 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0802.2017.08.038黃鐘, 陳肖, 文書豪, 等. 大數據安全測評框架和技術研究. 通信技術, 2017, 50(8):1810 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0802.2017.08.038 [14] Wang N, Liu Z J. The internet of things security protection level of the research. Netinfo Security, 2011(6): 5王寧, 劉志軍. 物聯網安全中的等級保護研究. 信息網絡安全, 2011(6):5 [15] Wood G. Ethereum: a secure decentralised generalised transaction ledger. Ethereum Project Yellow Paper, 2014, 151: 1 [16] Androulaki E, Barger A, Bortnikov V, et al. Hyperledger fabric: A distributed operating system for permissioned Blockchains // Proceedings of the Thirteenth EuroSys Conference (EuroSys 2018). Porto, 2018: 1 [17] Kosba A, Miller A, Shi E, et al. Hawk: The blockchain model of cryptography and privacy-preserving smart contracts // 2016 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). San Jose, 2016: 839 [18] Zhu Y, Gan G H, Deng D, et al. Security architecture and key technologies of blockchain. J Inform Security Res, 2016, 2(12): 1090朱巖, 甘國華, 鄧迪, 等. 區塊鏈關鍵技術中的安全性研究. 信息安全研究, 2016, 2(12):1090 [19] Antonopoulos A M. Mastering Bitcoin: Unlocking Digital Cryptocurrencies. California: O'Reilly Media, Inc, 2014 [20] Ben Mariem S, Casas P, Donnet B. Vivisecting blockchain P2P networks: Unveiling the bitcoin IP network // ACM CoNEXT Student Workshop. Crete, 2018 [21] Gencer A E, Basu S, Eyal I, et al. Decentralization in bitcoin and ethereum networks // International Conference on Financial Cryptography and Data Security. Berlin, 2018: 439 [22] Donet J A D, Pérez-Sola C, Herrera-Joancomartí J. The bitcoin P2P network // Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Bitcoin Research (in Assocation with Financial Crypto 14). Berlin, 2014: 87 [23] Du M X, Ma X F, Zhang Z, et al. A review on consensus algorithm of blockchain // 2017 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC). Banff, 2017: 2567 [24] Gramoli V. From blockchain consensus back to byzantine consensus. Future Generation Comput Syst, 2020, 107: 760 doi: 10.1016/j.future.2017.09.023 [25] Nguyen G T, Kim K. A survey about consensus algorithms used in blockchain. J Inform Process Syst, 2018, 14(1): 101 [26] Fullmer D, Morse A S. Analysis of difficulty control in bitcoin and proof-of-work blockchains // 2018 IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC). Miami Beach, 2018: 5988 [27] Taylor D. An Analysis of Bitcoin and the Proof of Work Protocols Energy Consumption, Growth, Impact and Sustainability[Dissertation]. Glasgow: University of Strathclyde, 2018 [28] Castro M, Liskov B. Practical Byzantine fault tolerance // Proceedings of the Third USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI). New Orleans, 1999: 173 [29] Borran F, Schiper A. A leader-free byzantine consensus algorithm // International Conference on Distributed Computing and Networking. Berlin, 2010: 67 [30] Saleh, F. Blockchain without waste: proof-of-stake. Economics Networks eJ. http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3183935 [31] Bach L M, Mihaljevic B, Zagar M. Comparative analysis of blockchain consensus algorithms // 2018 41st International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO). Opatija, 2018: 1545. [32] Kiayias A, Koutsoupias E, Kyropoulou M, et al. Blockchain mining games // Proceedings of the 2016 ACM Conference on Economics and Computation. ACM, 2016: 365 [33] Levine M. Scientific method and the adversary model: Some preliminary thoughts. Am Psychologist, 1974, 29(9): 661 doi: 10.1037/h0037627 [34] Dey S. A proof of work: Securing majority-attack in blockchain using machine learning and algorithmic game theory. Int J Wireless Microwave Technol, 2018, 8(5): 1 doi: 10.5815/ijwmt.2018.05.01 [35] Heusser J. SAT solving-An alternative to brute force bitcoin mining[J/OL]. Technical Report(2013-02-03)[2019-12-17]. https://jheusser.github.io/2013/02/03/satcoin.html [36] Eyal I, Sirer E G. Majority is not enough: Bitcoin mining is vulnerable. Commun ACM, 2018, 61(7): 95 doi: 10.1145/3212998 [37] Heilman E, Kendler A, Zohar A, et al. Eclipse attacks on bitcoin’s peer-to-peer network// Proceedings of the 24th USENIX Conference on Security Symposium (SEC'15). Washington D.C., 2015: 129 [38] Douceur J R. The sybil attack // International Workshop on Peer-to-Peer Systems. Berlin, 2002: 251 [39] Chohan, Usman W. The double spending problem and cryptocurrencies. Inf Syst Economics eJ, http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3090174 [40] Decker C, Wattenhofer R. Information propagation in the bitcoin network // IEEE P2P 2013 Proceedings. Trento, 2013: 1 [41] Decker C, Wattenhofer R. Bitcoin transaction malleability and MtGox // 19th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security. Wroclaw, 2014: 313 [42] Zhu Y, Guo R Q, Gan G H, et al. Interactive incontestable signature for transactions confirmation in bitcoin blockchain // 2016 IEEE 40th Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC). Atlanta, 2016: 443 [43] Gervais A, Karame G O, Wüst K, et al. On the security and performance of proof of work blockchains // Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Cnference on Computer and Communications Security. New York, 2016: 3 [44] Sekiguchi K, Chiba M, Kashima M. The Securities Settlement System and Distributed Ledger Technology. Bank of Japan Research Laboratory Series, 2018 [45] Bowden R, Keeler H P, Krzesinski A E, et al. Block arrivals in the Bitcoin blockchain[J/OL]. arXiv preprint(2018-01-23)[2019-12-17]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1801.07447.pdf [46] Son K T, Thang N T, Dong T M, et al. Blockchain technology for data entirety. Sci Research, 2019, 6(6): 68 [47] Merkle R C. Protocols for public key cryptosystems // 1980 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. Oakland, 1980: 122 [48] Szydlo M. Merkle tree traversal in log space and time // International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Interlaken, 2004: 541 [49] Jakobsson M, Leighton T, Micali S, et al. Fractal Merkle tree representation and traversal // Cryptographers’ Track at the RSA Conference. San Francisco, 2003: 314 [50] Delgado-Segura S, Pérez-Solà C, Herrera-Joancomartí J, et al. Bitcoin private key locked transactions. Inform Process Lett, 2018, 140: 37 doi: 10.1016/j.ipl.2018.08.004 [51] Stanciu N. Importance of event log management to ensure information system security. Metalurgia Int, 2013, 18(2): 144 [52] Kreps J, Narkhede N, Rao J. Kafka: a distributed messaging system for log processing // Proceedings of the NetDB. Athens, 2011 [53] Aniello L, Baldoni R, Gaetani E, et al. A prototype evaluation of a tamper-resistant high performance blockchain-based transaction log for a distributed database // 2017 13th European Dependable Computing Conference (EDCC). Geneva, 2017: 151 -




 下載:
下載: