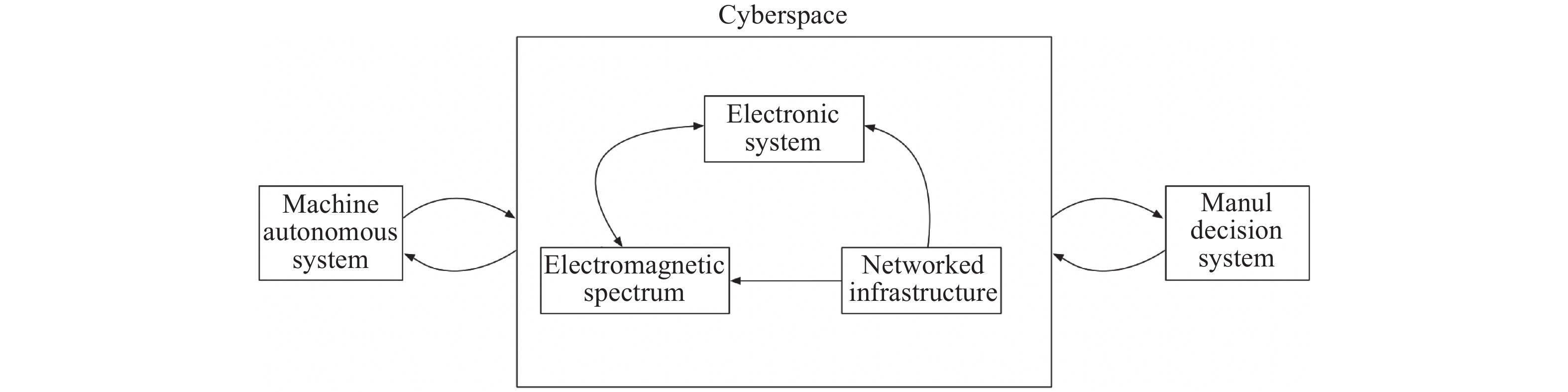
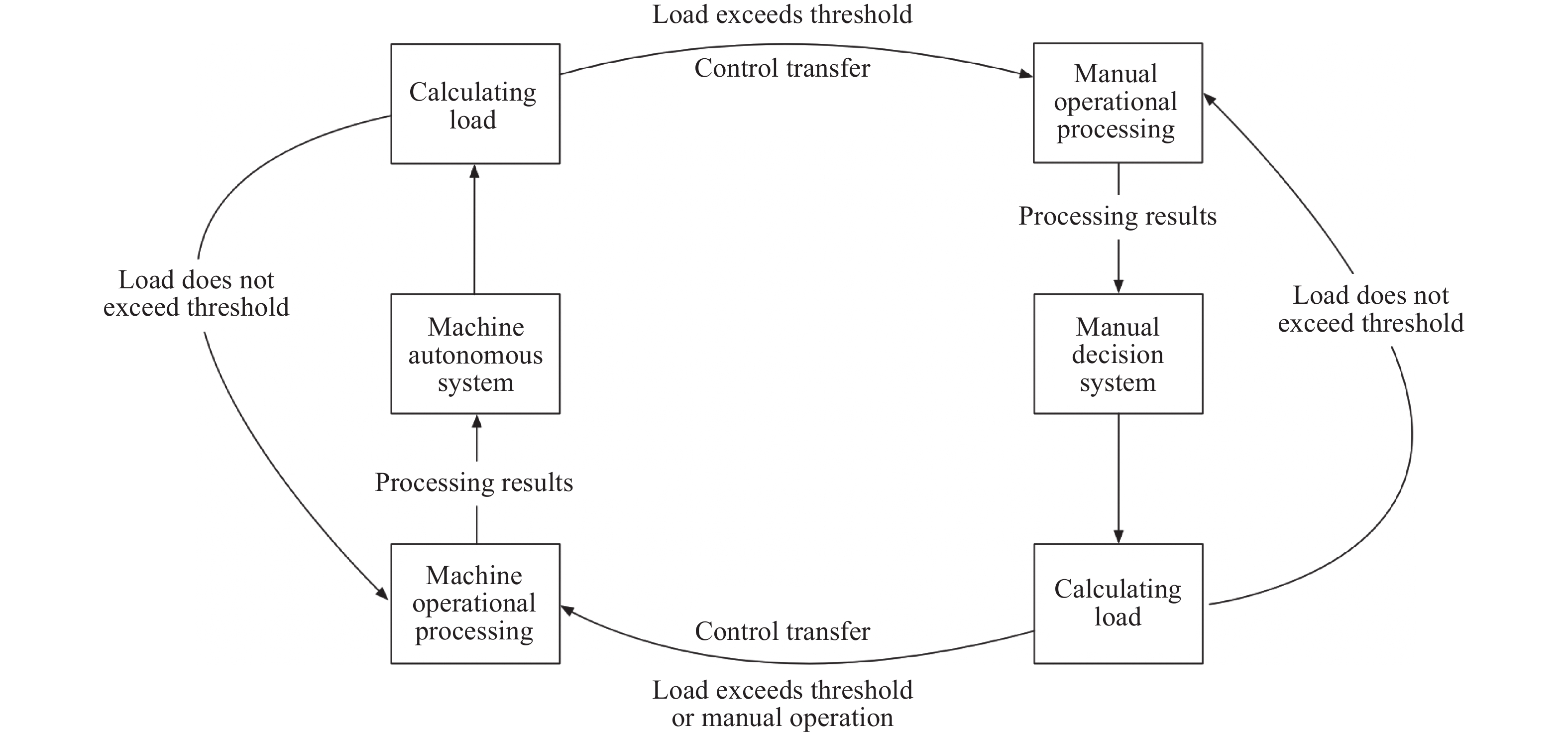
-
摘要: 人工智能特別是近幾年深度學習的飛速發展,深刻的影響著軍事領域,并賦予現代戰爭智能性、交叉性和破壞性的新特點。要想在軍事對抗中取勝,不僅需要機器智能,同樣需要人類智慧,能在軍事作戰中達到人機高度協同,是實現人與機器取長補短的重要途徑,也是在愈發復雜的戰爭形勢中取得勝利的關鍵。本文將軍事對抗中人工智能的應用作為切入點,羅列了代表性國家在軍事領域對人工智能的重視程度,從對抗策略和物聯網三層架構兩大角度對發展現狀進行總結,同時指出在目前軍事領域使用人工智能存在的不足,對人機融合智能在軍事對抗中的發展趨勢進行分析,并給出可能實現的技術方案,對未來的研究方向作出展望。如何實現高度的人機融合,從而獲得“1+1>2”的良好效果,是人工智能在軍事對抗中的下一步研究工作。Abstract: Artificial intelligence (AI), especially the rapid development of deep learning, has a profound impact on various industries and has continuously changed the traditional production methods and lifestyles. From passive learning with computing power to autonomous learning and enhanced learning, the development of machine intelligence is largely due to the innovation of the AI theory and practice. AI has also had a far-reaching impact on the military field, as it has provided modern warfare with new features such as intelligence, interconnectedness, and destructiveness. Winning in a military confrontation requires not only machine intelligence but also human wisdom. Therefore, human-machine collaboration would combine the strengths and complement the weaknesses of human and machine, which is the key to victory in the increasingly complex war environment. How to achieve a high degree of hybrid human–artificial intelligence to obtain a good result of “1+1>2” is also a problem that needs to be further explored in military confrontation. This paper reviewed the application of AI in military confrontation as the starting point and highlighted the important measures and achievements of representative countries in the use of AI technology in the military development process. Moreover, we analyzed the development status from the two perspectives of confrontation strategy and the three-tier architecture of the Internet of Things, revealed the shortcomings of using AI in the current military field, and analyzed the development trend of hybrid human–artificial intelligence in military confrontation. We also presented three possible technical schemes and detailed explanations and finally proposed future research directions. We believe that the future development trend of intelligent military may be based on the hybrid human–artificial intelligence, which will further improve the adaptability of machines to the combat environment and reveal the merits of the integration of human wisdom and machine intelligence; this integration may be the next step of AI research in military confrontation.
-
表 1 智能防御方面典型方法總結
Table 1. Summary of typical methods in intelligent defense
Research angle of intelligent defense Method/structure Main technology Citation number Data anti-interference PixelDP DNN Adding noise layer to the original DNN;
introducing cryptography differential privacy[5] Defense distillation model Redesign of the DNN; new architecture based on defensive distillation;
flexible setting of distillation temperature[6] ADV-BNN Modeling randomness in Bayesian neural network;
constructing minimax problem[7] Intelligent cooperative formation Leader-follower strategy formation Leader-follower strategy [9] Arbitrary switching of multi-agent formation Multi-agent formation control chart [10-11] Multi-robot formation and formation switching Omnidirectional vision [12] Immune multi-agent network Combining biological immune system mechanisms with multi-agent approaches [13] Switching formation and topology in cooperative multi-agent source seeking Gradient estimation [14] Distributed cooperative control for UAV Distributed cooperative control protocol and implementation of error system [15] Intelligent avoidance The definition and framework of UAV perception and avoidance Layered perception and avoidance process [16] Vision-based UAV perception and avoidance system Target detection combining image threshold method and frame difference method and based on the artificial potential field method to avoid target [17] UAV perception and avoidance based on multi-source information fusion Multi-sensor information fusion technology; multi-modal image technology [18] 表 2 智能檢測方面典型方法總結
Table 2. Summary of typical methods in intelligent detection
Research angle of
intelligent detectionMethod/structure Main technology Citation number Risk assessment Threat assessment based on the preferred
value of threat degreeFuzzy optimization theory [19] Information security risk assessment model Knowledge and fuzzy logic [20] Risk assessment model of information transmission security Combination of genetic algorithm and
neural network technology[21] Environmental perception Environment-sensing radar Interdisciplinary fusion of microwave remote sensing technology and AI technology [22] Integration of AI and radar technology Cognitive recognition [23] 表 3 智能攻擊方面典型方法總結
Table 3. Summary of typical methods in intelligent attack
Research angle of intelligent attack Method/structure Main technology Citation number Attack behavior modeling Cooperative combat system action planning method based on multi-agent system Agent abstraction; using the MAS theory in decision process and planning strategy of master-slave overlapping structure [24] Application of multi-agent system
in combat simulationFusion of multi-agent system and complex adaptive system [25] Fast data transfer and on-demand shared distribution Intelligent database system Integration of database technology and AI [27] Construction of military information center based on data processing Data mining, data fusion, and other AI technologies [28] Multi-sensor information fusion Data-level fusion, feature-level fusion, and decision-level fusion [29] Situational awareness Situation awareness based on radar
network in cyberspaceDesign of radar network based on situation awareness
framework in cyberspace war[30] Attention mechanism of battlefield
situation awarenessIntroduced attention mechanism into situation
awareness decision and action[31] 表 4 感知層安全典型技術總結
Table 4. Summary of typical technologies of perceptual layer security
Research angle of perceptual level Method/structure Main technology Citation number Sensor security Internet of Things authentication
and key managementSymmetric encryption mechanism based on Hash [33] Public key authentication scheme
for sensor networksOne-way Hash function used in public key authentication,
and Merkle tree established with public key[34] Sensor network security DiDrip protocol Distributed design and using different security
parameters to improve security[35] Cross-layer intrusion detection in wireless sensor network using mobile agent Fusing cross-layer features such as the MAC layer and network layer [36] Access control of wireless sensor network
based on information coverageDesign of a THC algorithm; introducing the Merkle
Hash tree and one-way chain[37] Access control of wireless sensor networks
with strong anonymityIntegrating Hash function, message verification
code and other technologies[38] Data and key privacy protection in data aggregation of wireless sensor networks Organizing nodes in sensor network into tree structure and
encryption in homomorphism[40] Application of chaotic sequence cipher in wireless sensor network Improved chaotic sequence cipher [41] Multi-sensor data fusion Multi-sensor information fusion predictor Based on ARMA information model and augmented state space
model combined with two kinds of variance formulas[42] Fuzzy method of multi-sensor data fusion Feature extraction and fusion based on fuzzy method
and membership function[44] Super dimensional data fusion
in hyperspectral sensorFeature and decision fusion by maximum rule, neural
network and other technologies[45] 表 5 網絡漏洞評估與安全態勢感知典型技術總結
Table 5. Summary of typical technologies of network vulnerability assessment and security situation awareness
Network vulnerability assessment and security situation awareness Method/structure Citation number Multi-agent network security model Using a two-tier multi-agent framework to integrate AI to monitor resources and attacks [47] Prediction of network security situation based on RBF neural network Based on an RBFNN neural network and the integration of the cuckoo search algorithm, simulated annealing algorithm, and dynamic discovery probability mechanism in the neural network [48] Time series prediction of network situation awareness Prediction method with support vector regression [49] 久色视频表 6 人工智能缺點及衍生在軍事對抗中的問題
Table 6. Shortcomings of AI and the associated problems in military confrontation
Defects of AI Possible problems in military confrontation Unable to implement complex reasoning In the face of a complex battlefield environment, reasoning is likely to go beyond the scope of
AI understanding, resulting in “thinking” stagnation.Support from a large number of samples In the battlefield environment, data collection and processing speed may not meet the needs of AI,
and the good self-learning ability of AI cannot be reflected.Essentially a software program There may be defects in program design; errors may occur in high-intensity use,
or the program may be attacked and interfered by enemies.High requirements for computing power In the battlefield environment, the batteries of equipment are limited and the power supply is tight, but AI usually requires large power consumption for modeling and training. No social history [51] Machines cannot think on their own. They can only be used to replace part of human thinking activities. They have no purpose or feelings. In the battlefield environment, they will not accurately judge a new situation. -
參考文獻
[1] Hinton G E, Osindero S, Teh Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput, 2006, 18(7): 1527 doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527 [2] Silver D, Schrittwieser J, Simonyan K, et al. Mastering the game of Go without human knowledge. Nature, 2017, 550(7676): 354 doi: 10.1038/nature24270 [3] Xiao Z Z, Liu Y M. Intelligent Weapons and Unmanned War. Beijing: Military Friendship Press, 2001肖占中, 劉昱旻. 智能武器與無人戰爭. 北京: 軍事誼文出版社, 2001 [4] Wang X C. Artificial intelligence algorithm: the invisible hand of rewriting war. Military Digest, 2017(21): 19王雪誠. 人工智能算法: 改寫戰爭的無形之手. 軍事文摘, 2017(21):19 [5] Lecuyer M, Atlidakis V, Geambasu R, et al. Certified robustness to adversarial examples with differential privacy // 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). San Francisco, 2019 [6] Papernot N, McDaniel P, Wu X, et al. Distillation as a defense to adversarial perturbations against deep neural networks//2016 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). San Jose, 2016 [7] Liu X Q, Li Y, Wu C R, et al. Adv-BNN: improved adversarial defense through robust bayesian neural network // International Conference on Learning Representations. New Orleans, 2019 [8] Shi Z Z. Intelligent Agent and Its Application. Beijing: Science Press, 2002史忠植. 智能主體及其應用. 北京: 科學出版社, 2002 [9] Desai J P, Ostrowski J, Kumar V. Controlling formations of multiple mobile robots//1998 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Belgium, 1998: 2864 [10] Desai J P, Ostrowski J P, Kumar V. Modeling and control of formations of nonholonomic mobile robots. IEEE Trans Robot Autom, 2001, 17(6): 905 doi: 10.1109/70.976023 [11] Desai J P. A graph theoretic approach for modeling mobile robot team formations. J Robot Syst, 2002, 19(11): 511 doi: 10.1002/rob.10057 [12] Das A K, Fierro R, Kumar V, et al. A vision-based formation control framework. IEEE Trans Robot Autom, 2002, 18(5): 813 doi: 10.1109/TRA.2002.803463 [13] Wang J, Zhao X Z, Zhang Y H, et al. Cooperative air-defense system of system model for surface warship formation based on immune multi-agent. J Syst Simul, 2012, 24(2): 263王軍, 趙曉哲, 張瑛涵, 等. 基于免疫多智能體的艦艇編隊協同防空體系模型. 系統仿真學報, 2012, 24(2):263 [14] Sahal M, Agustinah T, Jazidie A. Switching formation and topology in cooperative multi-agent source seeking using gradient estimation // 2019 International Conference of Artificial Intelligence and Information Technology (ICAIIT). Yogyakarta, 2019: 151 [15] Liu L, Liang X L, Zhu C C, et al. Distributed cooperative control for UAV swarm formation reconfiguration based on consensus theory // 2017 2nd International Conference on Robotics and Automation Engineering (ICRAE). Shanghai, 2017: 264 [16] Lü Y, Kang T N, Pan Q, et al. UAV sense and avoidance: concepts, technologies and systems. Sci Sin Inform, 2019, 49(5): 520 doi: 10.1360/N112018-00318呂洋, 康童娜, 潘泉, 等. 無人機感知與規避: 概念、技術與系統. 中國科學: 信息科學, 2019, 49(5):520 doi: 10.1360/N112018-00318 [17] Han J Y, Wang H L, Liu C, et al. Vision-based system design for UAV target detection and avoidance. Tactical Missile Technol, 2014(5): 11韓靜雅, 王宏倫, 劉暢, 等. 基于視覺的無人機感知與規避系統設計. 戰術導彈技術, 2014(5):11 [18] Li Y J, Pan Q, Yang F, et al. Research on UAV perception and avoidance based on multi-source information fusion // Proceedings of the 29th China Control Conference. Beijing, 2010: 2861李耀軍, 潘泉, 楊峰, 等. 基于多源信息融合的無人機感知與規避研究 // 第二十九屆中國控制會議論文集. 北京, 2010: 2861 [19] Huang J P. Study on Threat Assessment of Surface to Air Missile Forces in Anti-Air Attack Operations[Dissertation]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2009黃劍平. 地空導彈部隊在反空襲作戰中的威脅評估研究[學位論文]. 廈門: 廈門大學, 2009 [20] Azan Basallo Y, Estrada Senti V, Martinez Sanchez N. Artificial intelligence techniques for information security risk assessment. IEEE Latin America Trans, 2018, 16(3): 897 doi: 10.1109/TLA.2018.8358671 [21] Du G, Han Z Q, Li N X, et al. Risk assessment model of information transmission security based on neural network and genetic algorithm. J Intell, 2010, 29(Suppl 1): 207杜戈, 韓增奇, 李寧霞, 等. 基于神經網絡和遺傳算法的信息傳輸安全風險度評估模型. 情報雜志, 2010, 29(增刊1): 207 [22] Sun X Z, Liu L. Development of unmanned ground combat system and environmental sensing radar. Sci Technol Vision, 2017(8): 1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2457.2017.08.001孫曉舟, 劉露. 地面無人作戰系統及環境感知雷達發展概述. 科技視界, 2017(8):1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2457.2017.08.001 [23] Li B, Ren H M, Xiao Z H. Limitation and development prospect of artificial intelligence in radar application. Military Digest, 2019(3): 42李波, 任紅梅, 肖志河. 人工智能在雷達應用中的限制和發展前景. 軍事文摘, 2019(3):42 [24] Yang F, Wang Q, Wu Z D. Cooperative combat system action planning method based on multi-agent system // 2010 Second International Workshop on Education Technology and Computer Science. Wuhan, 2010: 490 [25] Liu Y F, Zhang A. Multi-agent system and its application in combat simulation // 2008 International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design. Wuhan, 2008: 448 [26] Brodie M L, Cui J. Future intelligent information system: the combination of AI and DB technology. Comput Sci, 1989(3): 23Brodie M L, 崔靖. 未來的智能信息系統: AI與DB技術的結合. 計算機科學, 1989(3):23 [27] Nihalani N, Silakari S, Motwani M. Integration of artificial intelligence and database management system: An inventive approach for intelligent databases // 2009 First International Conference on Computational Intelligence, Communication Systems and Networks. Indore, 2009: 35 [28] Shao J, Wu H, Chen L. Construction of military information center based on correlation techniques of data processing. Microcomput Inform, 2006, 22(3): 89 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0570.2006.03.032邵軍, 吳華, 陳蕾. 基于數據處理相關技術的軍事信息中心構建. 微計算機信息, 2006, 22(3):89 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0570.2006.03.032 [29] Niu Z Y. Research on multi-sensor information fusion technology in modern war. Comput Inform Technol, 2006(3): 71牛志一. 現代化戰爭中的多傳感器信息融合技術研究. 計算機與信息技術, 2006(3):71 [30] Yang X, Shan W, Jia L. Technology of situation awareness based on radar network in cyberspace //Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Green Computing and Communications and IEEE Internet of Things and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing. Beijing, 2013: 1505 [31] Kong Y S, Hu X F, Zhu F, et al. Attention mechanism in battlefield situation awareness. J Syst Simul, 2017, 29(10): 2233孔亦思, 胡曉峰, 朱豐, 等. 戰場態勢感知中的注意力機制探析. 系統仿真學報, 2017, 29(10):2233 [32] www.cecb2b.com. Experts call for a higher level of sensor safety. Comput Telecommun, 2014, 11(11): 21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6609.2014.11.015元器件交易網. 專家呼吁提升傳感器安全層級. 電腦與電信, 2014, 11(11):21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6609.2014.11.015 [33] Chen L. Research on Authentication Technology and Key Management in Internet of Things[Dissertation]. Changsha: Central South University, 2013陳雷. 物聯網中認證技術與密鑰管理的研究[學位論文]. 長沙: 中南大學, 2013 [34] Du W L, Wang R H, Ning P. An efficient scheme for authenticating public keys in sensor networks // Proceedings of the 6th ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking & Computing. Urbana-Champaign IL, 2005: 58 [35] Ghormare S, Sahare V. Implementation of data confidentiality for providing high security in Wireless Sensor Network // 2015 International Conference on Innovations in Information, Embedded and Communication Systems (ICIIECS). Coimbatore, 2015: 1 [36] Gandhimathi L, Murugaboopathi G. Cross layer intrusion detection and prevention of multiple attacks in Wireless Sensor Network using Mobile agent // 2016 International Conference on Information Communication and Embedded Systems (ICICES). Chennai, 2016: 1 [37] Du Z Q, Shen Y L, Ma J F, et al. Two-hop cover-based access control scheme for wireless sensor networks. J Commun, 2010, 31(2): 113 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436X.2010.02.017杜志強, 沈玉龍, 馬建峰, 等. 基于信息覆蓋的無線傳感器網絡訪問控制機制. 通信學報, 2010, 31(2):113 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436X.2010.02.017 [38] Chen T, Lu J Z, Jiang J H. An access control scheme with strong anonymity in wireless sensor network. Comput Eng, 2015, 41(1): 126 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2015.01.023陳婷, 盧建朱, 江俊暉. 一種具有強匿名性的無線傳感器網絡訪問控制方案. 計算機工程, 2015, 41(1):126 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2015.01.023 [39] Jin N, Zhang D Y, Gao J Q, et al. A study on the application of symmetric ciphers and asymmetric ciphers in wireless sensor networks. Chin J Sens Actuators, 2011, 24(6): 874 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2011.06.019金寧, 張道遠, 高建橋, 等. 對稱密碼和非對稱密碼算法在無線傳感器網絡中應用研究. 傳感技術學報, 2011, 24(6):874 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2011.06.019 [40] Akila V, Sheela T. Preserving data and key privacy in data aggregation for wireless sensor networks // 2017 2nd International Conference on Computing and Communications Technologies (ICCCT). Chennai, 2017: 282 [41] Zhao C. Research on the Application of Chaotic Sequence Cipher in Wireless Sensor Network[Dissertation]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2014趙晨. 混沌序列密碼在無線傳感器網絡中的應用研究[學位論文]. 北京: 北京化工大學, 2014 [42] Mao L, Deng Z L. Multisensor information fusion wiener deconvolution predictor //2007 26th Chinese Control Conference. Zhangjiajie, 2007: 1013毛琳, 鄧自立. 多傳感器信息融合Wiener反卷積預報器 // 第二十六屆中國控制會議論文集. 張家界, 2007: 1013 [43] Li N G, Zhao H. The requirements on the data fusion of multiple-sensor of UAV. Natl Defense Sci Technol, 2015, 36(5): 52李念國, 趙慧. 無人機多傳感器數據融合的設計要求. 國防科技, 2015, 36(5):52 [44] Ruzzo F, Ramponi G. Fuzzy methods for multisensor data fusion // 1993 IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference. Irvine, 1993: 676 [45] Jimenez L O, Morales-Morell A, Creus A. Classification of hyperdimensional data based on feature and decision fusion approaches using projection pursuit, majority voting, and neural networks. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens, 1999, 37(3): 1360 doi: 10.1109/36.763300 [46] Bass T, Gruber D. A glimpse into the future of id[J/OL]. USENIX (2001-2-1)[2019-11-19]. http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/7ac9/8c4f3b72210775b08aa5849d5501de9c7048.pdf [47] Tsochev G, Trifonov R, Yoshinov R, et al. Some security model based on multi agent systems //2018 International Conference on Control, Artificial Intelligence, Robotics & Optimization (ICCAIRO). Prague, 2018: 32 [48] Ren W, Jiang X H, Sun T F. RBFNN-based prediction of networks security situation. Comput Eng Appl, 2006, 42(31): 136 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2006.31.041任偉, 蔣興浩, 孫錟鋒. 基于RBF神經網絡的網絡安全態勢預測方法. 計算機工程與應用, 2006, 42(31):136 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2006.31.041 [49] Zhang X, Hu C Z, Liu S H, et al. Research on network attack situation forecast technique based on support vector machine. Comput Eng, 2007, 33(11): 10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2007.11.004張翔, 胡昌振, 劉勝航, 等. 基于支持向量機的網絡攻擊態勢預測技術研究. 計算機工程, 2007, 33(11):10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2007.11.004 [50] Ren C G. Research on Cloud Computing and Its Key Technologies for Massive Data Processing[Dissertation]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Technology, 2013任崇廣. 面向海量數據處理領域的云計算及其關鍵技術研究[學位論文]. 南京: 南京理工大學, 2013 [51] Chu Q W. On Artificial Intelligence from the Perspective of Philosophy[Dissertation]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2014褚秋雯. 從哲學的角度看人工智能[學位論文]. 武漢: 武漢理工大學, 2014 -




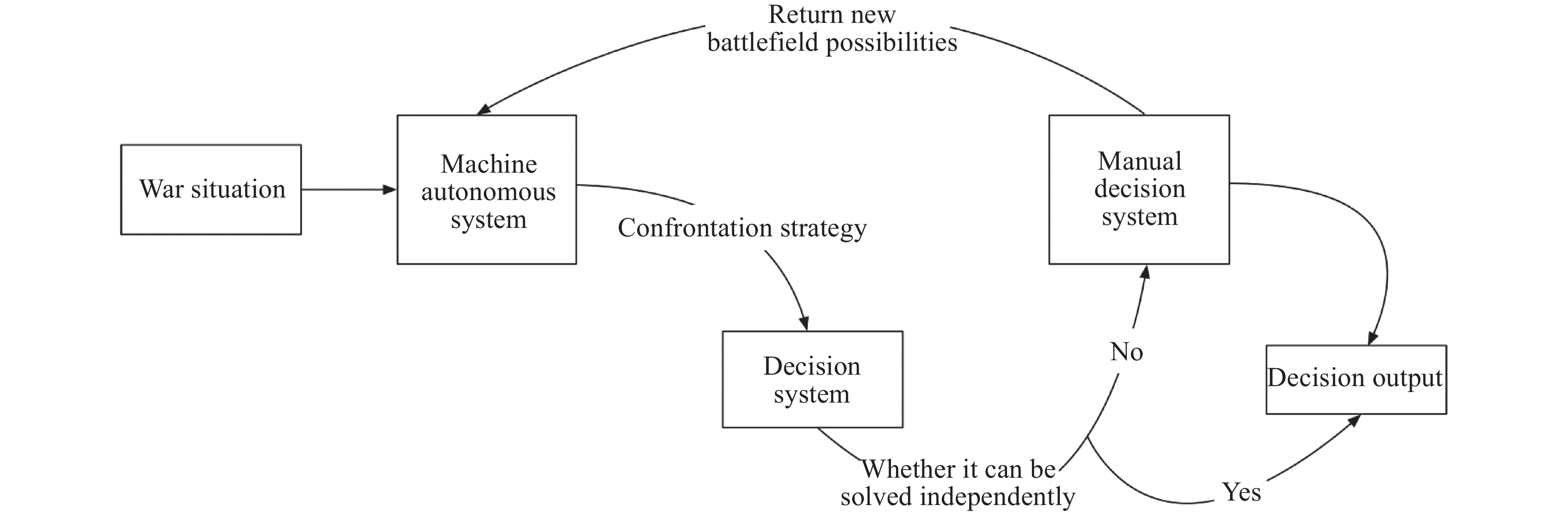
 下載:
下載: