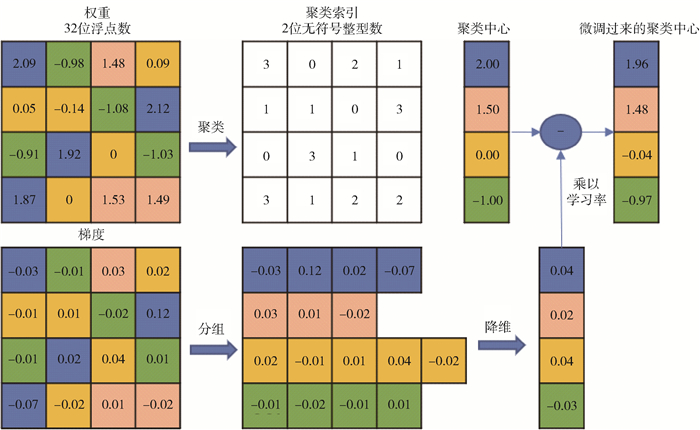
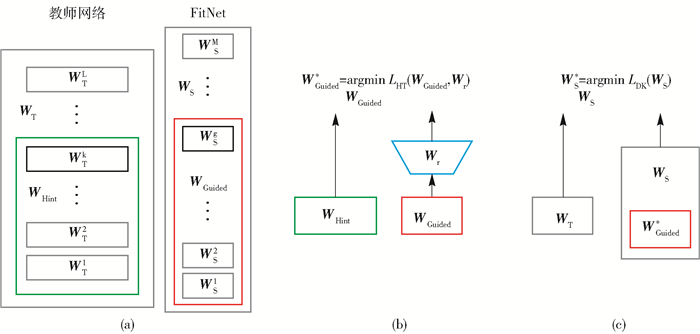
| [1] |
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436 doi: 10.1038/nature14539
|
| [2] |
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, 2012: 1097
|
| [3] |
Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2015-04-10)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556
|
| [4] |
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y Q, et al. Going deeper with convolutions//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, 2015: 1
|
| [5] |
He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington DC, 2016: 770
|
| [6] |
Huang G, Liu Z, van der Maaten L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hawaii, 2017: 4700
|
| [7] |
Le Q V, Ngiam J, Coates A, et al. On optimization methods for deep learning//Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. Omnipress, 2011: 265
|
| [8] |
Han Y F, Jiang T H, Ma Y P, et al. Compression of deep neural networks. Comput Appl Res, 2018, 35(10): 2894 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2018.10.003韓云飛, 蔣同海, 馬玉鵬, 等. 深度神經網絡的壓縮研究. 計算機應用研究, 2018, 35(10): 2894 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2018.10.003
|
| [9] |
Setiono R, Liu H. Neural-network feature selector. IEEE Trans Neural Networks, 1997, 8(3): 654 doi: 10.1109/72.572104
|
| [10] |
LeCun Y, Denker J S, Solla S A, et al. Optimal brain damage//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Denver, 1989: 598
|
| [11] |
Hassibi B, Stork D G, Wolff G J. Optimal brain surgeon and general network pruning//IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks. San Francisco, 1993: 293
|
| [12] |
Hassibi B, Stork D G. Second order derivatives for network pruning: optimal brain surgeon//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Denver, 1993: 164
|
| [13] |
Han S, Pool J, Tran J, et al. Learning both weights and connections for efficient neural network// Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, 2015: 1135
|
| [14] |
Han S, Mao H, Dally W J. Deep compression: compressing deep neural networks with pruning, trained quantization and huffman coding[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2016-02-15)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1510.00149
|
| [15] |
Srinivas S, Subramanya A, Venkatesh Babu R. Training sparse neural networks//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Hawaii, 2017: 138
|
| [16] |
Anwar S, Hwang K, Sung W. Structured pruning of deep convolutional neural networks. ACM J Emerg Technol Comput Syst, 2017, 13(3): 32 doi: 10.1145/3005348
|
| [17] |
Wen W, Wu C P, Wang Y D, et al. Learning structured sparsity in deep neural networks//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, 2016: 2074
|
| [18] |
Lin S H, Ji R R, Li Y C, et al. Toward compact ConvNets via structure-sparsity regularized filter pruning. IEEE Trans Neural Networks Learn Syst, 2019: 1. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30990448
|
| [19] |
Guo Y W, Yao A B, Chen Y R. Dynamic network surgery for efficient DNNs//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, 2016: 1379
|
| [20] |
Jia H P, Xiang X S, Fan D, et al. DropPruning for model compression[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2018-12-05)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.02035
|
| [21] |
Li H, Kadav A, Durdanovic I, et al. Pruning filters for efficient convnets[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2017-03-10)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.08710
|
| [22] |
Hu H Y, Peng R, Tai Y W, et al. Network trimming: a data-driven neuron pruning approach towards efficient deep architectures[J/OL]. arXiv preprint (2016-07-12)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.03250
|
| [23] |
Tian Q, Arbel T, Clark J J. Deep LDA-pruned nets for efficient facial gender classification//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Hawaii, 2017: 10
|
| [24] |
Luo J H, Wu J X, Lin W Y. ThiNet: a filter level pruning method for deep neural network compression//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, 2017: 5058
|
| [25] |
He Y, Kang G L, Dong X Y, et al. Soft filter pruning for accelerating deep convolutional neural networks[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2018-08-21)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.06866
|
| [26] |
He Y H, Zhang X Y, Sun J. Channel pruning for accelerating very deep neural networks[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2017-08-21)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.06168
|
| [27] |
Hu Y M, Sun S Y, Li J Q, et al. Multi-loss-aware channel pruning of deep networks[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2019-02-27)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.10364
|
| [28] |
Zhuang Z W, Tan M K, Zhuang B H, et al. Discrimination-aware channel pruning for deep neural networks[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2019-01-14)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.11809
|
| [29] |
He Y H, Han S. ADC: automated deep compression and acceleration with reinforcement learning[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2019-01-16)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.03494v1
|
| [30] |
Appuswamy R, Nayak T, Arthur J, et al. Structured convolution matrices for energy-efficient deep learning[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2016-06-08)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.02407
|
| [31] |
Sindhwani V, Sainath T N, Kumar S. Structured transforms for small-footprint deep learning[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2015-10-06)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1510.01722
|
| [32] |
Cheng Y, Yu F X, Feris R S, et al. An exploration of parameter redundancy in deep networks with circulant projections[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2015-10-27)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03436
|
| [33] |
Chen W L, Wilson J T, Tyree S, et al. Compressing neural networks with the hashing trick//Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille, 2015: 2285
|
| [34] |
Shi L, Feng S K, Zhu Z F. Functional hashing for compressing neural networks[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2016-05-20)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.06560
|
| [35] |
Wu J R, Wang Y, Wu Z Y, et al. Deep k-Means: Re-training and parameter sharing with harder cluster assignments for compressing deep convolutions[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2018-06-24)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.09228
|
| [36] |
Lu Z Y, Sindhwani V, Sainath T N. Learning compact recurrent neural networks[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2016-04-09)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1604.02594
|
| [37] |
Jin X J, Yang Y Z, Xu N, et al. WSNet: compact and efficient networks through weight sampling[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2018-05-22)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.10067
|
| [38] |
Yang Y Z, Jojic N, Huan J. FSNet: Compression of deep convolutional neural networks by filter summary[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2019-02-13)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.03264
|
| [39] |
Gupta S, Agrawal A, Gopalakrishnan K, et al. Deep learning with limited numerical precision[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2015-02-09)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.02551
|
| [40] |
Jacob B, Kligys S, Chen B, et al. Quantization and training of neural networks for efficient integer-arithmetic-only inference//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, 2018: 2704
|
| [41] |
Courbariaux M, Bengio Y, David J P. BinaryConnect: training deep neural networks with binary weights during propagations//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Canada, 2015: 3123
|
| [42] |
Courbariaux M, Hubara I, Soudry D, et al. Binarized neural networks: training deep neural networks with weights and activations constrained to +1 or -1[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2016-03-17)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.02830
|
| [43] |
Rastegari M, Ordonez V, Redmon J, et al. XNOR-Net: ImageNet classification using binary convolutional neural networks[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2016-08-02)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.05279
|
| [44] |
Li Z F, Ni B B, Zhang W J, et al. Performance guaranteed network acceleration via high-order residual quantization//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, 2017: 2584
|
| [45] |
Hwang K, Sung W. Fixed-point feedforward deep neural network design using weights+1, 0, and -1//2014 IEEE Workshop on Signal Processing Systems (SiPS). Belfast, 2014: 1
|
| [46] |
Hou L, Yao Q M, Kwok J T. Loss-aware binarization of deep networks[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2018-05-10)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.01600
|
| [47] |
Lee H, Battle A, Raina R, et al. Efficient sparse coding algorithms//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Canada, 2007
|
| [48] |
Gudovskiy D A, Rigazio L. ShiftCNN: generalized low-precision architecture for inference of convolutional neural networks[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2017-06-07)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02393
|
| [49] |
Meller E, Finkelstein A, Almog U, et al. Same, same but different-recovering neural network quantization error through weight factorization[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2019-02-05)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.01917
|
| [50] |
Xu Y H, Zhang S, Qi Y Y, et al. DNQ: Dynamic network quantization[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2018-12-06)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.02375
|
| [51] |
Golub G H, Reinsch C. Singular value decomposition and least squares solutions//Linear Algebra. Springer, Berlin, 1971: 134
|
| [52] |
Jaderberg M, Vedaldi A, Zisserman A. Speeding up convolutional neural networks with low rank expansions[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2014-05-15)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1405.3866
|
| [53] |
Kim Y D, Park E, Yoo S, et al. Compression of deep convolutional neural networks for fast and low power mobile applications[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2016-02-24)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.06530
|
| [54] |
Denil M, Shakibi B, Dinh L, et al. Predicting parameters in deep learning//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, 2013: 2148
|
| [55] |
Calvi G G, Moniri A, Mahfouz M, et al. Tucker tensor layer in fully connected neural networks[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2019-03-14)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.06133
|
| [56] |
Bucilu? C, Caruana R, Niculescu-Mizil A. Model compression//Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Philadelphia, 2006: 535
|
| [57] |
Ba J, Caruana R. Do deep nets really need to be deep?//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Canada, 2014: 2654
|
| [58] |
Hinton G, Vinyals O, Dean J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2015-03-09)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1503.02531
|
| [59] |
Romero A, Ballas N, Kahou S E, et al. FitNets: hints for thin deep nets[J/PL]. ArXiv Preprint (2015-03-27)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6550
|
| [60] |
Chen T Q, Goodfellow I, Shlens J. Net2Net: accelerating learning via knowledge transfer[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2016-04-23)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.05641
|
| [61] |
Li Z Z, Hoiem D. Learning without forgetting. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2018, 40(12): 2935 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2773081
|
| [62] |
Zagoruyko S, Komodakis N. Paying more attention to attention: Improving the performance of convolutional neural networks via attention transfer[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2017-02-12)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.03928
|
| [63] |
Mirzadeh S I, Farajtabar M, Li A, et al. Improved knowledge distillation via teacher assistant: bridging the gap between student and teacher[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2019-02-09)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.03393
|
| [64] |
Liu X, Wang X G, Matwin S. Improving the interpretability of deep neural networks with knowledge distillation[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2018-12-28)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.10924
|
| [65] |
Yang C L, Xie L X, Su C, et al. Snapshot distillation: Teacher-student optimization in one generation[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2018-12-01)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.00123
|
| [66] |
Wang J, Bao W D, Sun L C, et al. Private model compression via knowledge distillation[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2018-11-13)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.05072
|
| [67] |
Lee S H, Kim D H, Song B C. Self-supervised knowledge distillation using singular value decomposition[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2018-07-18)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.06819
|
| [68] |
Lan X, Zhu X T, Gong S G. Knowledge distillation by on-the-fly native ensemble[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2018-09-08)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.04606
|
| [69] |
Liu Y J, Che W X, Zhao H P, et al. Distilling knowledge for search-based structured prediction[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2018-05-29)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.11224
|
| [70] |
Li Q Q, Jin S Y, Yan J J. Mimicking very efficient network for object detection//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, 2017: 6356
|
| [71] |
Chen G B, Choi W, Yu X, et al. Learning efficient object detection models with knowledge distillation//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, 2017: 742
|
| [72] |
Wang T, Yuan L, Zhang X P, et al. Distilling object detectors with fine-grained feature imitation//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, 2019: 4933
|
| [73] |
Liu Y F, Chen K, Liu C, et al. Structured knowledge distillation for semantic segmentation//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, 2019: 2604
|
| [74] |
He T, Shen C H, Tian Z, et al. Knowledge adaptation for efficient semantic segmentation//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, 2019: 578
|
| [75] |
Iandola F N, Han S, Moskewicz M W, et al. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and < 0.5 MB model size[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2016-11-04)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.07360
|
| [76] |
Haward A G, Zhu M L, Chen B, et al. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2017-04-17)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861
|
| [77] |
Sandler M, Haward A, Zhu M L, et al. MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks// Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, 2018: 4510
|
| [78] |
Haward A, Sandler M, Chu G, et al. Searching for MobileNetV3[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2019-08-24)[2019-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.02244
|
| [79] |
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, 2018: 7132
|
| [80] |
Zhang X Y, Zhou X Y, Lin M X, et al. ShuffleNet: an extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, 2018: 6848
|
| [81] |
Ma N N, Zhang X Y, Zheng H T, et al. ShuffleNet V2: practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design// Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, 2018: 116
|
| [82] |
Chollet F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, 2017: 1251
|
| [83] |
Xie S N, Girshick R, Dollar P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, 2017: 1492
|
| [84] |
Gao H Y, Wang Z Y, Ji S W. ChannelNets: Compact and efficient convolutional neural networks via channel-wise convolutions//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Salt Lake City, 2018: 5197
|
| [85] |
Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V, et al. Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2016-08-23)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.07261
|
| [86] |
Tan M X, Chen B, Pang R M, et al. MnasNet: Platform-aware architecture search for mobile//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, 2019: 2820
|
| [87] |
Tan M X, Le Q V. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2019-06-10)[2019-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946
|
| [88] |
Liu C X, Chen L C, Schroff F, et al. Auto-DeepLab: Hierarchical neural architecture search for semantic image segmentation// Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, 2019: 82
|
| [89] |
Huang G, Chen D L, Li T H, et al. Multi-scale dense networks for resource efficient image classification[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2018-06-07)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.09844
|
| [90] |
Shelhamer E, Rakelly K, Hoffman J, et al. Clockwork convnets for video semantic segmentation[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2016-08-11)[2019-03-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.03609
|




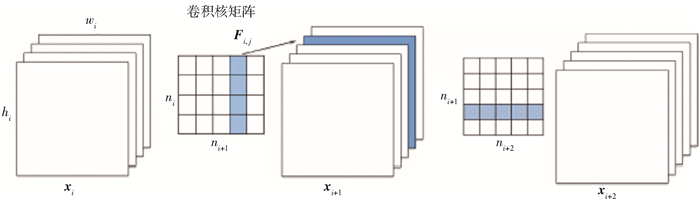
 下載:
下載: